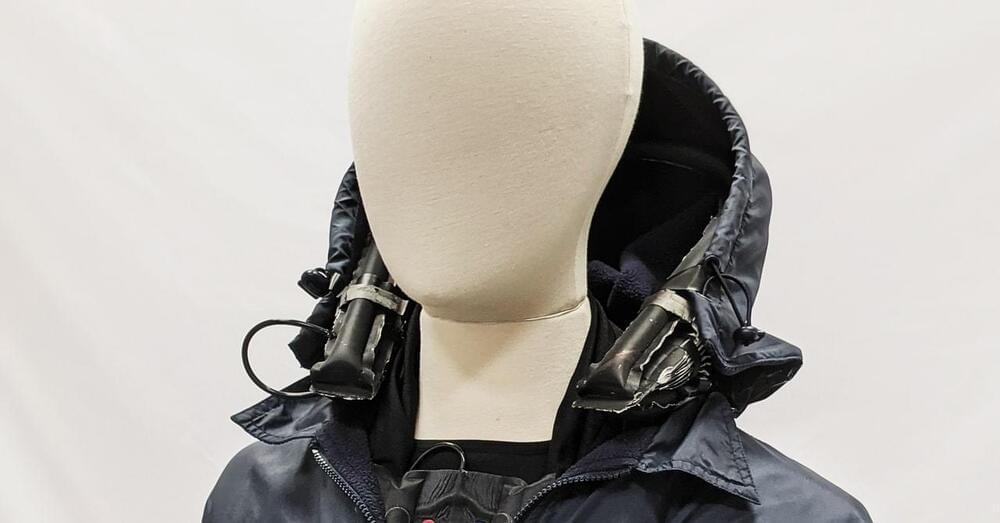
The existing jacket can perform one logical operation per second, compared to the more than a billion operations per second typical of a home computer, says Preston. In practice, this means the jacket can only execute short command sequences. Due to the speed of the logic, along with some other engineering challenges, Zhang says he thinks it’ll take five to 10 years for these textile-based robots to reach commercial maturity.
In the future, Preston’s team plans to do away with the carbon dioxide canister, which is impractical. (You have to refill it like you would a SodaStream.) Instead, his team wants to just use ambient air to pump up the jacket. As a separate project, the team has already developed a foam insole for a shoe that pumps the surrounding air into a bladder worn around the waist when the wearer takes a step. They plan to integrate a similar design into the jacket.
Preston also envisions clothing that senses and responds to the wearer’s needs. For example, a sensor on a future garment could detect when the wearer is beginning to lift their arm and inflate without any button-pressing. “Based on some stimulus from the environment and the current state, the logic system can allow the wearable robot to choose what to do,” he says. We’ll be waiting for this fashion trend to blow up.