Researchers claimed to have found a way to build a spacecraft that can travel at one-fifth of the speed of light, making traveling to another solar system a reality. Read the article to learn how this could be possible.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
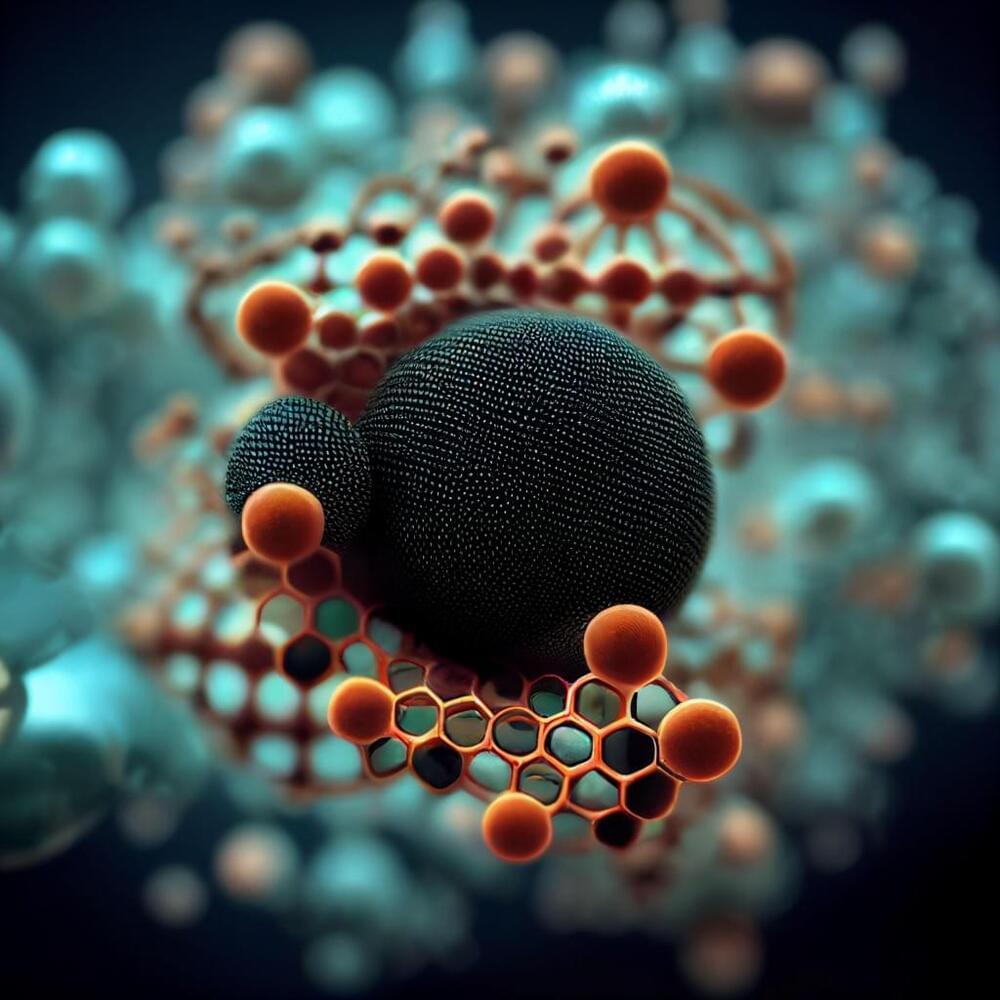
Beyond COVID vaccines: what’s next for lipid nanoparticles?
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) transport small molecules into the body. The most well-known LNP cargo is mRNA, the key constituent of some of the early vaccines against COVID-19. But that is just one application: LNPs can carry many different types of payload, and have applications beyond vaccines.
Barbara Mui has been working on LNPs (and their predecessors, liposomes) since she was a PhD student in Pieter Cullis’s group in the 1990s. “In those days, LNPs encapsulated anti-cancer drugs,” says Mui, who is currently a senior scientist at Acuitas, the company that developed the LNPs used in the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. She says it soon became clear that LNPs worked even better as carriers of polynucleotides. “The first one that worked really well was encapsulating small RNAs,” Mui recalls.
But it was mRNA where LNPs proved most effective, primarily because LNPs are comprised of positively charged lipid nanoparticles that encapsulate negatively charged mRNA. Once in the body, LNPs enter cells via endocytosis into endosomes and are released into the cytoplasm. “Without the specially designed chemistry, the LNP and mRNA would be degraded in the endosome,” says Kathryn Whitehead, professor in the departments of chemical engineering and biomedical engineering at Carnegie Mellon University.

What Can Digital Art Teach Us About Identity in a Hyper-Technologized World? A New Group Show at the Whitney Weighs In
Featuring works by six artists, “Refigured” is on view through July 3.
Richard Whiddington, March 7, 2023.

Mind-Boggling Neuromorphic Brain Chips (Part 1)
I can’t help myself. I keep thinking about the 1961 musical Stop the World—I Want to Get Off. After opening in Manchester, England, the show transferred to the West End, London, where it ran for 485 performances.
It’s not that the plot of this extravaganza has anything to do with what we are talking about here. It’s just that the sentiment embodied by the show’s title reflects the way I’m currently feeling about artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML).
On the one hand, the current state of play with AI and ML is tremendously exciting. On the other hand, I’m starting to think that I’ve enjoyed all the excitement I can stand.
Augmented Reality with X-Ray Vision
X-AR uses wireless signals and computer vision to enable users to perceive things that are invisible to the human eye (i.e., to deliver non-line-of-sight perception). It combines new antenna designs, wireless signal processing algorithms, and AI-based fusion of different sensors.
This design introduces three main innovations:
1) AR-conformal wide-band antenna that tightly matches the shape of the AR headset visor and provides the headset with Radio Frequency (RF) sensing capabilities. The antenna is flexible, lightweight, and fits on existing headsets without obstructing any of their cameras or the user’s field of view.

AGI Soon? 1 AI Using 2 Modalities Solves Visual IQ Test w/ 1,600,000,000 Parameters | Kosmos-1
Premium Robots: https://taimine.com/
Deep Learning AI Specialization: https://imp.i384100.net/GET-STARTED
A new multimodal artificial intelligence model from Microsoft called Kosmos-1 is able to process both text and visual data to the point of passing a visual IQ test with 26 percent accuracy, and researchers say this is a step towards AGI. Stable Diffusion AI can now read brain waves to reconstruct images that people are thinking about. Stanford has created a world record brain computer interface device with the help of AI to allow patients to type 62 words per minute with their thoughts.
AI News Timestamps:
0:00 Microsoft Kosmos-1 AI & AGI
3:34 AI Neuroscience Tech Reads Brain Waves.
5:43 AI & BCI Breaks Record.
#technology #tech #ai

Lithium-ion batteries made with recycled materials are better than new
Recycling spent lithium-ion batteries plays a significant role in alleviating the shorting of raw materials and environmental problems. However, recycled materials are deemed inferior to commercial materials, preventing the industry from adopting recycled materials in new batteries.
Now, researchers at Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) in Massachusetts have demonstrated that the recycled materials from used lithium-ion batteries can outperform new commercial materials, making the recycled materials a potentially green and profitable resource for battery producers. Led by Yan Wang, professor in the Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, the team of researchers used physical tests, imaging, and computer simulations to compare new cathode materials recovered from old electric vehicle batteries through a recycling process, which is being commercialized by Battery Resourcers Inc. of Worcester.
The technology involved shredding batteries and removing the steel cases, aluminum and copper wires, plastics, and pouch materials for recycling. Researchers then dissolved the metals from those battery bits in an acidic solution. They by tweaking the solution’s pH, the team removed impurities such as iron and copper and recovered over 90% of three key metals – nickel, manganese, and cobalt. The recovered metals formed the basis for the team’s cathode material.
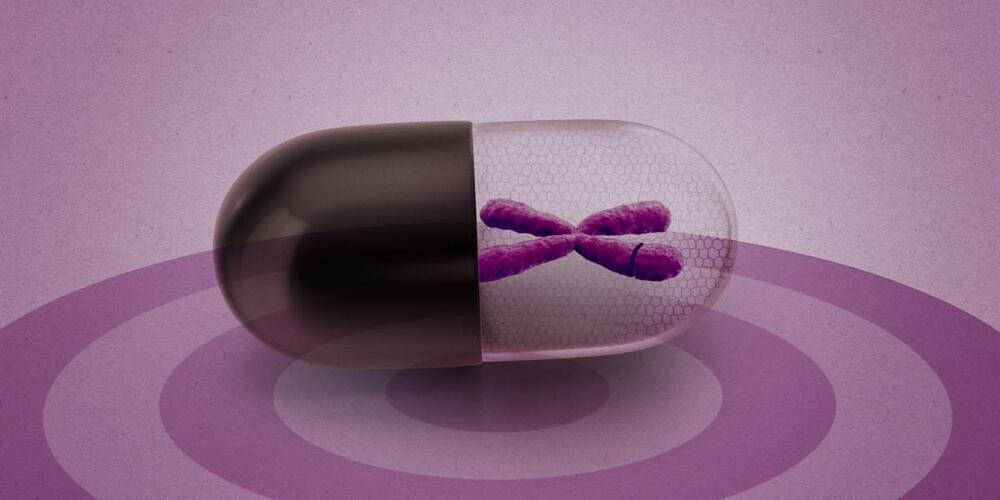
Forget designer babies. Here’s how CRISPR is really changing lives
Forget about He Jiankui, the Chinese scientist who created gene-edited babies. Instead, when you think about gene editing you should think of Victoria Gray, the African-American woman who says she’s been cured of her sickle-cell disease symptoms.
This week in London, scientists are gathering for the Third International Summit on Human Genome Editing. It’s gene editing’s big event, where researchers get to awe the audience with their new ability to modify DNA—and ethicists get to worry about what it all means.