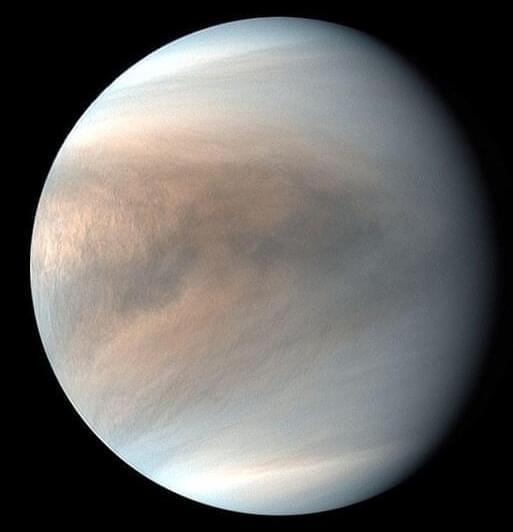
Data from BepiColombo and Solar Orbiter during Venus gravity assists reveal how a magnetic field protects the Venusian atmosphere.


Scientists at Tennessee’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are attempting to establish a doorway to a parallel reality. The goal of the project is to depict a world that is nearly comparable to ours and where life is mirrored. The experiment’s leader, Leah Broussard, told NBC that the strategy is a little crazy, but it will completely transform the game. If the studies are successful, particles will be able to morph into images of themselves, allowing them to burrow through a solid wall. This might demonstrate that the cosmos we observe is merely half of what exists. Broussard revealed that he believes the test will yield a result of zero.
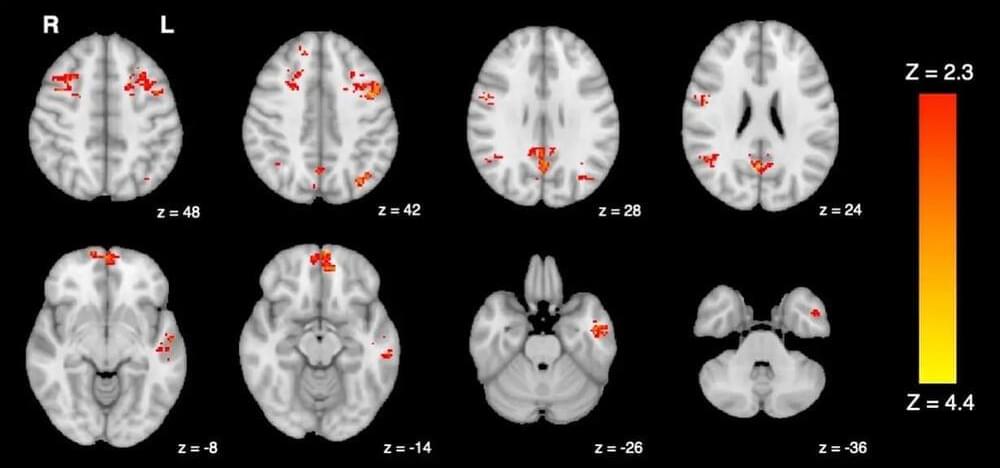
The study conducted by researchers at the University of British Columbia and the University of Victoria reveals that exposure to common levels of traffic pollution can impair brain function within hours.
The peer-reviewed study published in Environmental Health found that only two hours of exposure to diesel exhaust leads to a decrease in brain functional connectivity, which is a measure of how different areas of the brain interact and communicate with each other. This study is the first controlled experiment to provide evidence of air pollution altering brain connectivity in humans.
“For many decades, scientists thought the brain may be protected from the harmful effects of air pollution,” said senior study author Dr. Chris Carlsten, professor and head of respiratory medicine and the Canada Research Chair in occupational and environmental lung disease at UBC. “This study, which is the first of its kind in the world, provides fresh evidence supporting a connection between air pollution and cognition.”


Astronomers picked up extraterrestrial signals which they previously missed in an area they thought was devoid of potential ET activity. It could be the first hint that humans are not alone in the universe.
Mysterious Signals Detected
Experts led by University of Toronto student Peter Ma used an algorithm with artificial intelligence (AI) to examine 820 stars in an area they didn’t suspect would have any potential activity. They were surprised with their finding, especially since they missed the tentative signals earlier due to a lot of interference, Daily Mail reported.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links:
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
Use Code: ConquerAging At Checkout.
Green Tea: https://www.ochaandco.com/?ref=conqueraging.
Oral Microbiome: https://www.bmq30trk.com/4FL3LK/GTSC3/
Use Code: ConquerAging15
Epigenetic Testing: https://bit.ly/3Rken0n.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING!
At-Home Blood Testing: https://getquantify.io/mlustgarten.
The WHO said there are currently nine deaths and 16 suspected cases with symptoms including fever, fatigue, diarrhea and vomiting. The agency said it was sending medical experts to help officials in Equatorial Guinea stop the outbreak and was also sending protective equipment for hundreds of workers.
What is the Marburg virus?
Like Ebola, the Marburg virus originates in bats and spreads between people via close contact with the bodily fluids of infected people, or surfaces, like contaminated bedsheets.

BERLIN, Feb 19 (Reuters) — Clinical trials for BioNTech’s (22UAy. DE) cancer vaccines should start this year in Britain, marking an important step towards their possible sale on the open market, the German company’s top executive Ugur Sahin told magazine Der Spiegel.
BioNTech, known for its COVID vaccine with U.S. partner Pfizer (PFE.N), is currently deciding which types of cancer it wants to test its personalized cancer immunotherapies on and the locations where it will conduct the trials, Sahin said.
The company wants these therapies, which are based on messenger RNA (mRNA) technology similar to the one that underpins its COVID-19 vaccine, to soon become a regular treatment for cancer patients.