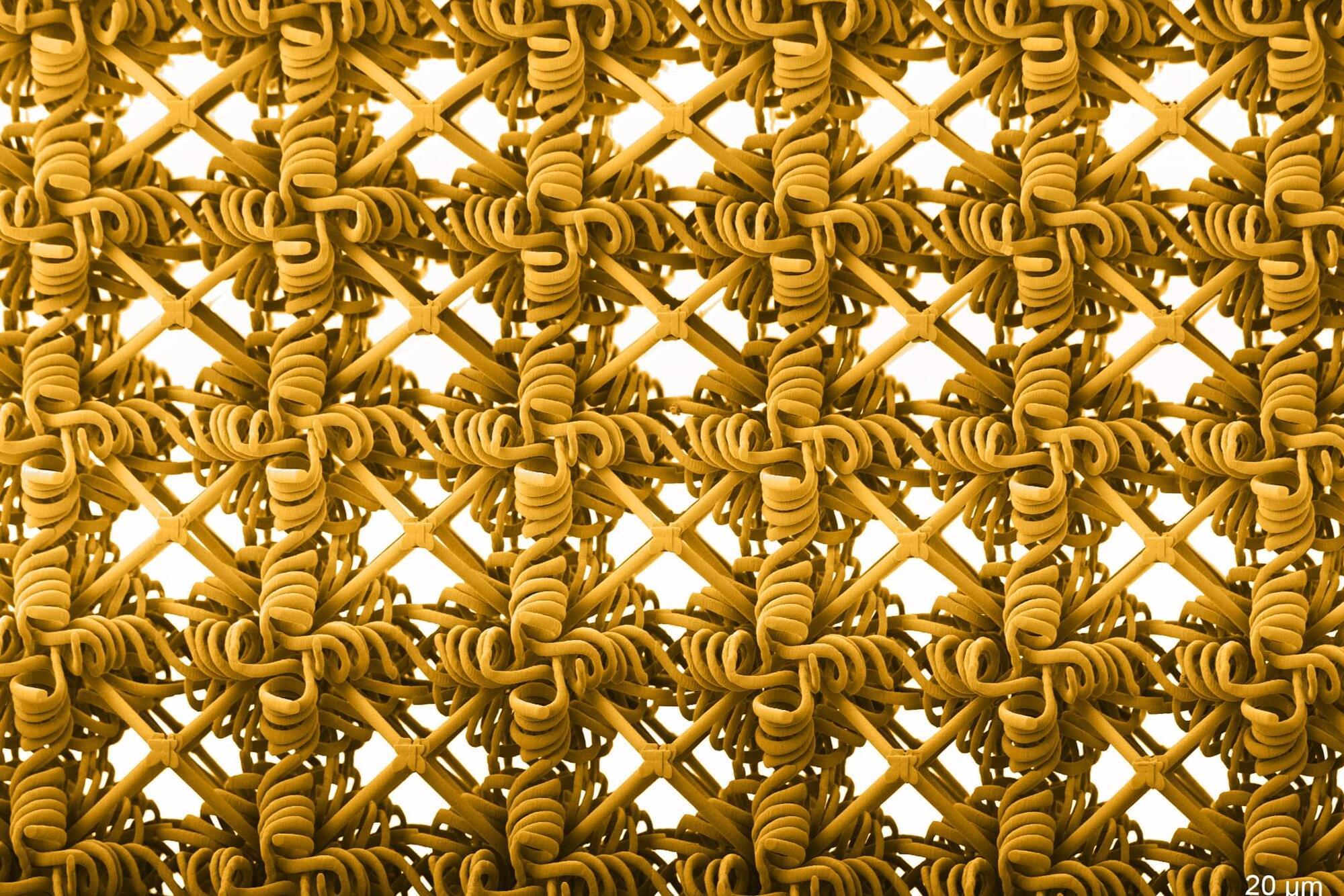
MIT engineers have fabricated a metamaterial that is not only strong but also stretchy. Their new method could enable stretchable ceramics, glass, and metals, for tear-proof textiles or stretchy semiconductors.


Hyperbaric oxygen treatment provides long-term relief for patients suffering from late radiation-induced injuries after treatment of cancer in the lower abdominal area. Five years after hyperbaric oxygen therapy, the positive effects remain. This has been shown in a study conducted at the University of Gothenburg.
Radiation therapy is a component of many cancer treatments in organs such as the prostate, colon, ovaries and cervix. While tumor cells are destroyed, 5%–10% of patients experience severe side effects due to healthy tissue being affected by the radiation therapy.
Symptoms may include urinary incontinence, bleeding and severe pain in the lower abdomen that becomes both physically and socially disabling. These problems can occur several years after radiation therapy and cause chronic and increasing discomfort.


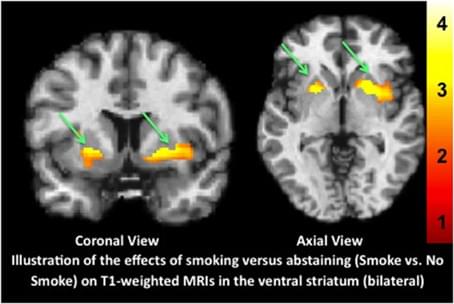
The magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo (MP-RAGE) T1-weighted high resolution structural MRI is a mainstay tool used to identify morphometric biomarkers of disease conditions, progression and treatment effects despite a critical limitation: the relaxation signal on which inferences are based is nearly indistinguishable for gray matter vs. blood flow (Lu et al., 2004; Wright et al., 2008). Thus, apparent reported morphometric findings might be at least partially related to transient changes in blood flow or other physiological signals.
Consistent with this technical limitation, using a standard analysis technique, voxel based morphometry (VBM), we recently reported that a single dose of a medication had “apparent” effects on T1-weighted MRIs (Franklin et al., 2013). Specifically, we observed medication-induced decreases in gray matter volume in the anterior cingulate and other regions that overlapped with changes in brain blood flow (perfusion). Similarly, others have shown effects of medication on T1-weighted scans that are likely transient. For example, acute levodopa administration altered gray matter indices on T1-weighted images in the midbrain (Salgado-Pineda et al., 2006). Further, in a well-controlled longitudinal VBM study of patients with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), Hoekzema et al.
Objectives: Proximal median nerve (PMN) neuropathies are caused by lesions proximal to the carpal tunnel, which include the forearm, elbow, upper arm, and brachial plexus. Differentiating between carpal tunnel syndrome and PMN neuropathies is important to guide management and is based on clinical, electrodiagnostic (EDX), and ultrasound (US) findings. This study describes the clinical, EDX, and US features in 62 patients with PMNs.
Methods: All patients underwent EDX studies, and 52 (83.9%) had a US study. The patients were assigned to one of the following four localization zones of PMN neuropathies based on clinical and EDX criteria: Zone 1: extends from the fascicles in the brachial plexus contributing to the median nerve to the innervation of the pronator teres (PT); Zone 2: distal to the branch to the PT and proximal to the origin of the anterior interosseous nerve (AIN); Zone 3: involves the origin of the AIN; and Zone 4: distal to the origin of the AIN and proximal to the carpal tunnel. The localization was based on the pattern of muscle weakness, topography of EMG abnormalities, and US study findings.
Results: The anatomical locations of the PMN neuropathies based on clinical, EDX, and US findings were as follows: Zone 1 in 38 patients (61.3%), Zone 2 in 6 patients (9.7%), Zone 3 in 7 patients (11.3%), and Zone 4 in 11 patients (17.7%). The most common etiology among all 62 patients was iatrogenic injury (30 [48.4%]), followed by non-iatrogenic trauma (20 [32.2%]). The following EDX findings were noted: prolonged distal motor latency (29 [46.8%]), decreased motor nerve conduction velocity in the forearm (22 [35.5%]), low amplitude or absent compound muscle action potentials (50 [80.6%]), and abnormal or absent sensory nerve action potentials (50 [80.6%]). Of the 52 (83.9%) patients who underwent US studies, a total of 22 (42.3%) patients showed an increased cross-sectional area of the median nerve.
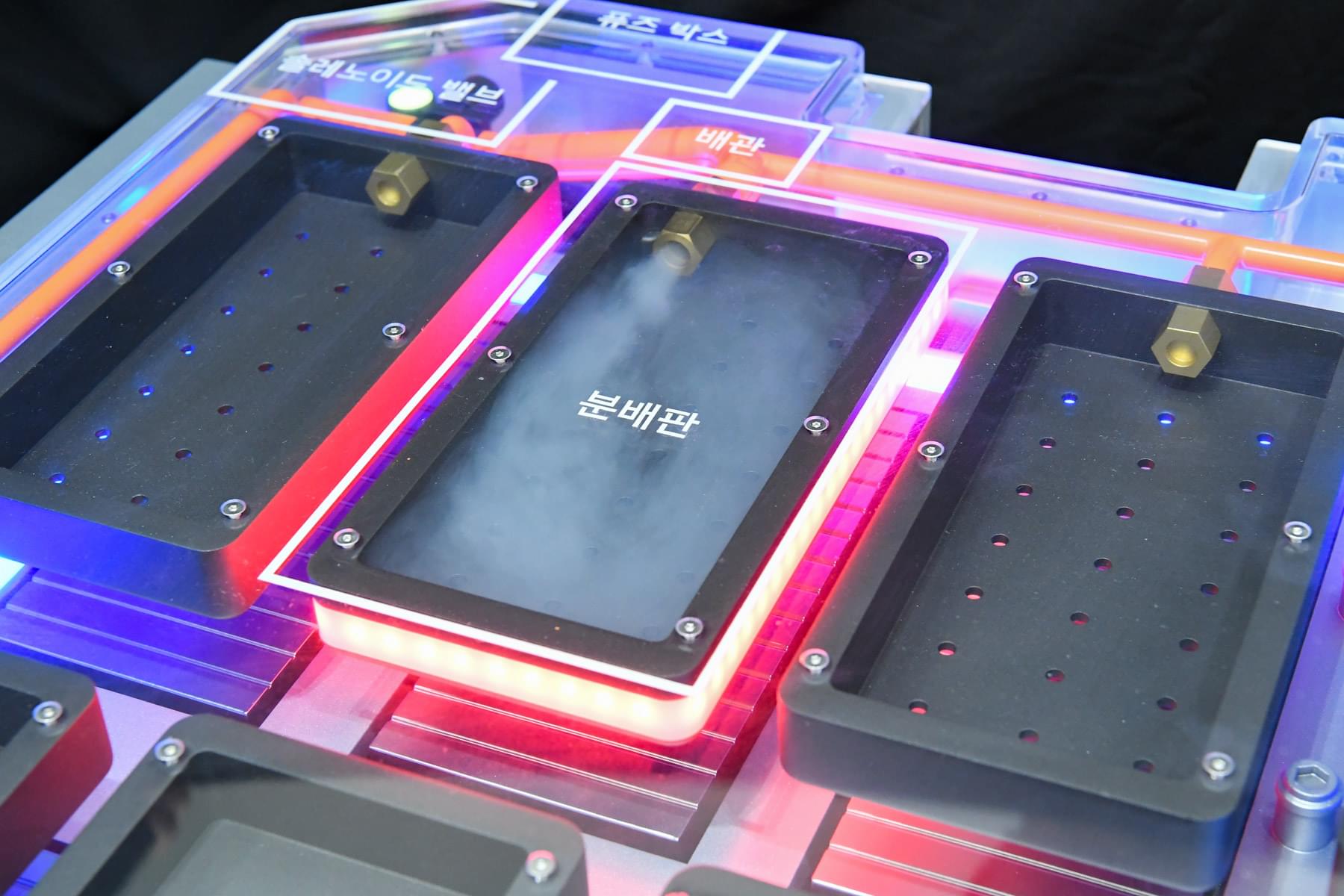

According to the South Korean supplier, the system can extinguish fires at an early stage by releasing a suppressant within five minutes of initial ignition. This five-minute window is critical: current regulations in Europe, China, and India require that thermal runaway across the battery be delayed for at least five minutes after the first cell ignites, giving vehicle occupants enough time to safely exit the vehicle after a crash.
However, Hyundai Mobis says its new Battery System Assembly (BSA) was not merely designed to meet existing requirements, but rather in anticipation of stricter safety rules aimed at preventing any heat transfer between cells in the first place. The company believes such technologies will take centre stage in the next generation of battery systems on the global market.
Hyundai Mobis has unveiled a new battery system featuring an integrated fire extinguishing unit. It is designed to prevent heat from spreading to adjacent cells in the event of a malfunction, reducing the risk of larger thermal incidents.
By Carla Westerheide.
BiOptimizers Magnesium Breakthrough 10% with code Modern10 https://bioptimizers.com/modern. This video brought to you by BiOptimizers. Here Dr Michael Lustgar…