Dec 14, 2020
An LED that can be integrated directly into computer chips
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: computing, mobile phones
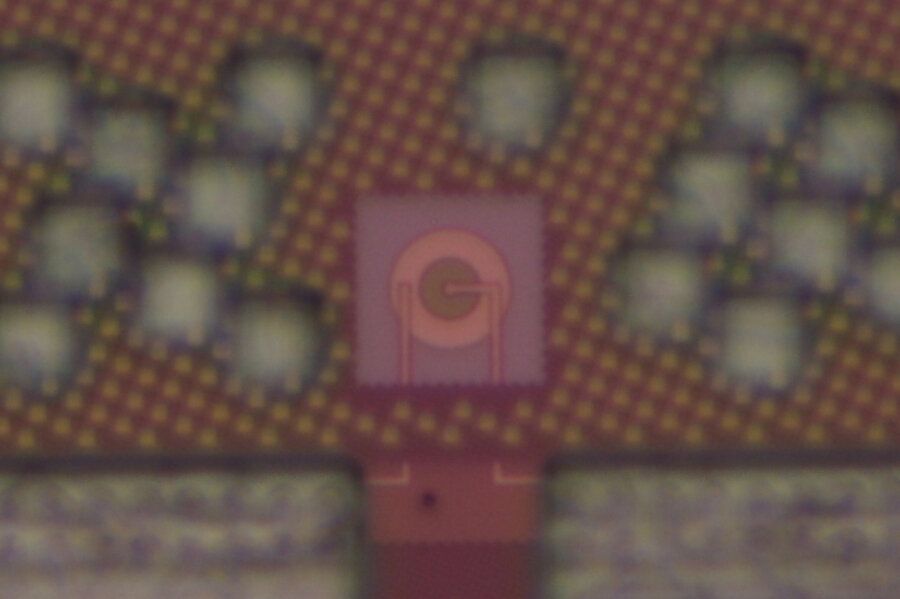
Light-emitting diodes—LEDs—can do way more than illuminate your living room. These light sources are useful microelectronics too.
Smartphones, for example, can use an LED proximity sensor to determine if you’re holding the phone next to your face (in which case the screen turns off). The LED sends a pulse of light toward your face, and a timer in the phone measures how long it takes that light to reflect back to the phone, a proxy for how close the phone is to your face. LEDs are also handy for distance measurement in autofocus cameras and gesture recognition.
One problem with LEDs: It’s tough to make them from silicon. That means LED sensors must be manufactured separately from their device’s silicon-based processing chip, often at a hefty price. But that could one day change, thanks to new research from MIT’s Research Laboratory of Electronics (RLE).