Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Lactate mediates training of our innate defenses, research shows
The BCG vaccine protects against tuberculosis, but by inducing trained immunity it also protects against many more respiratory infections. International research led by Radboud University Medical Center shows how this process works. Lactate, a product of scaled-up energy production, appears to play a leading role.
The immune system protects people in two ways. Innate immunity protects us from birth against many bacteria and viruses, while adaptive immunity builds protection against individual pathogens after a prior infection. The adaptive immune system is aided by vaccines that protect us against new pathogens without having to go through an infection. In this way, vaccines contribute greatly to our health.
Once-a-Day Pill Slows Loss of Lung Function in Bronchiectasis Patients
Results of a large, global clinical trial spanning five continents with over 1,700 patients with bronchiectasis, published this April in the New England Journal of Medicine, demonstrated benefits of an investigational, once-a-day pill called brensocatib as a therapy for the chronic lung condition.
The clinical trial findings are important, as there are currently no FDA-approved medications for bronchiectasis, a chronic condition with persistent lung airway inflammation and infection. Bronchiectasis can often stem from various injuries to the airways causing the ‘bronchial’ tubes leading to the lungs to become permanently enlarged, and more prone to infection and chronic inflammation.

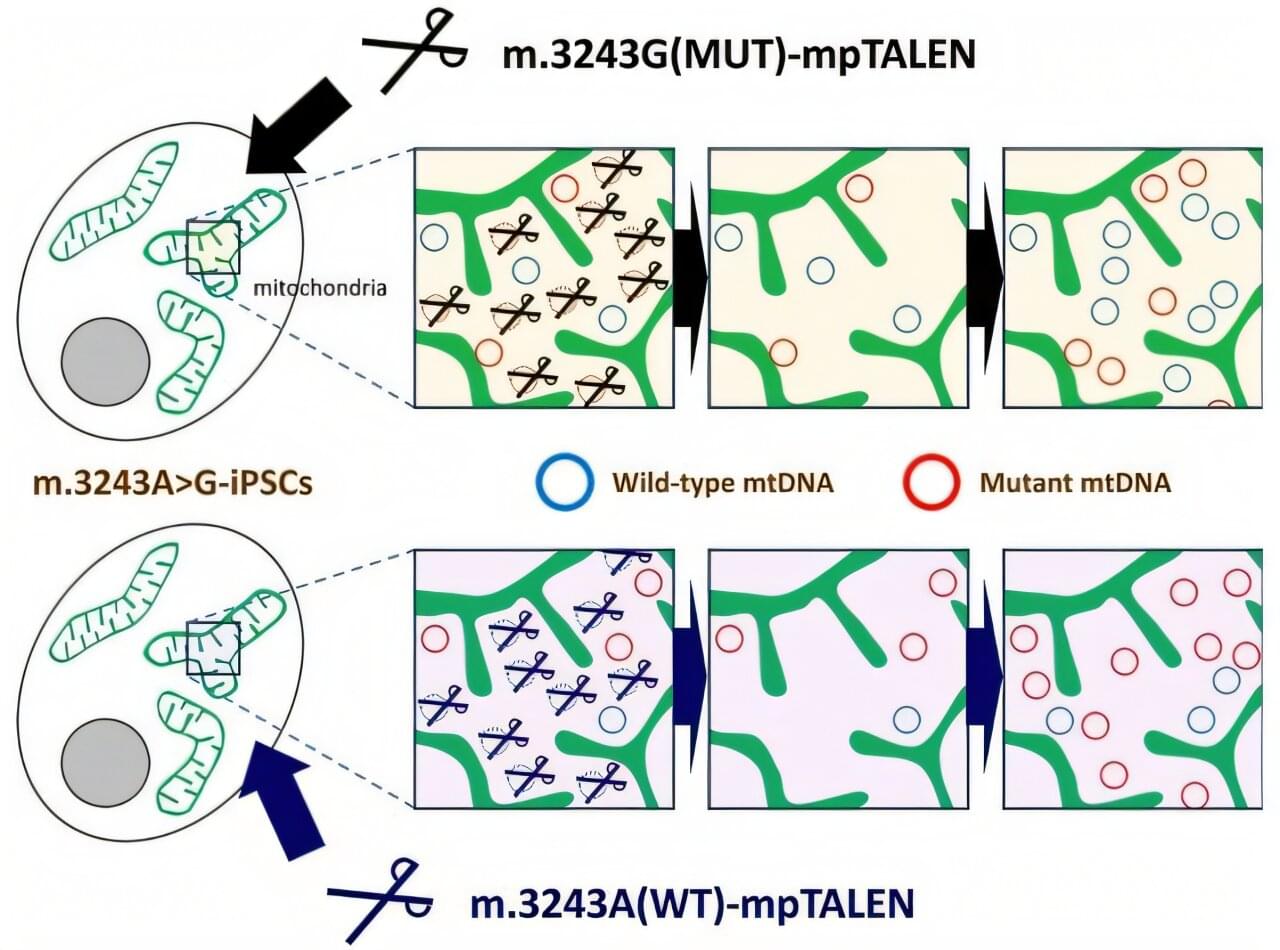
Engineered enzymes enable precise control of mitochondrial DNA mutation levels in cells
Mitochondrial diseases affect approximately 1 in 5,000 people worldwide, causing debilitating symptoms ranging from muscle weakness to stroke-like episodes. Some of these conditions result from mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), the genetic material housed in these organelles. For patients with the common m.3243A>G mutation, which can cause MELAS syndrome (mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes) and diabetes mellitus, treatments remain limited.
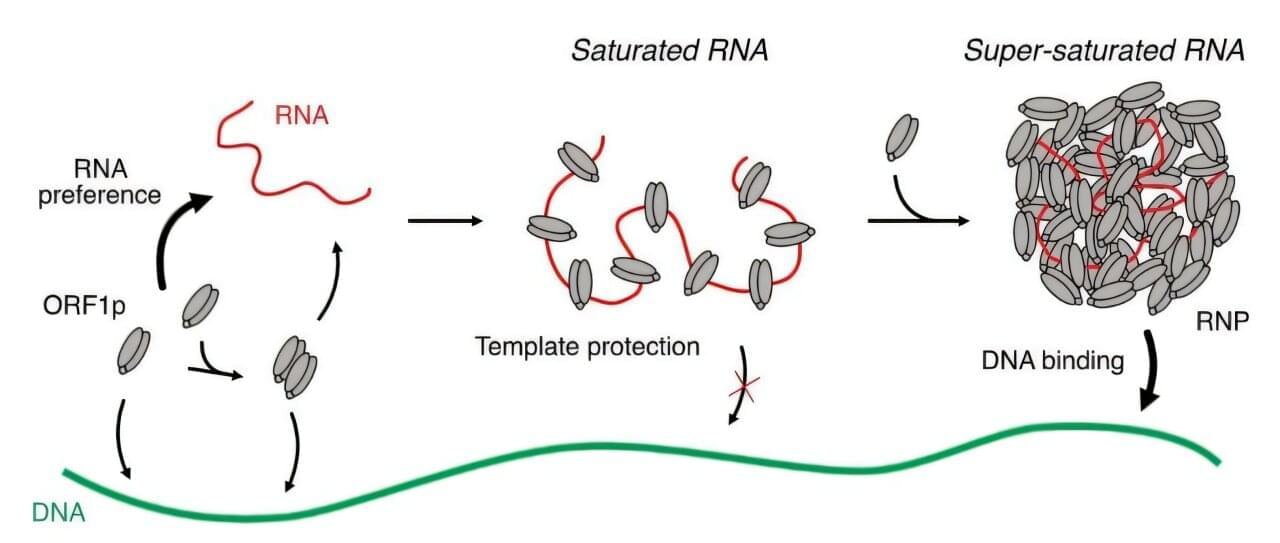
How ‘jumping genes’ infiltrate DNA during cell division
Viruses are known to use the genetic machinery of the human cells they invade to make copies of themselves. As part of the process, viruses leave behind remnants throughout the genetic material (genomes) of humans. The virus-like insertions, called “transposable elements,” are snippets of genetic material even simpler than viruses that also use host cell machinery to replicate.
Nearly all these inserted elements have been silenced by our cells’ defense mechanisms over time, but a few, nicknamed “jumping genes,” can still move around the human genome like viruses. Just one, called long interspersed nuclear element 1 (LINE-1), can still move by itself.
As an element type that behaves like the retrovirus HIV, the LINE-1 “retrotransposon” is first copied into a molecule of RNA, the genetic material that partners with DNA, and then the RNA LINE-1 copy is converted back into DNA in a new place in the genome.