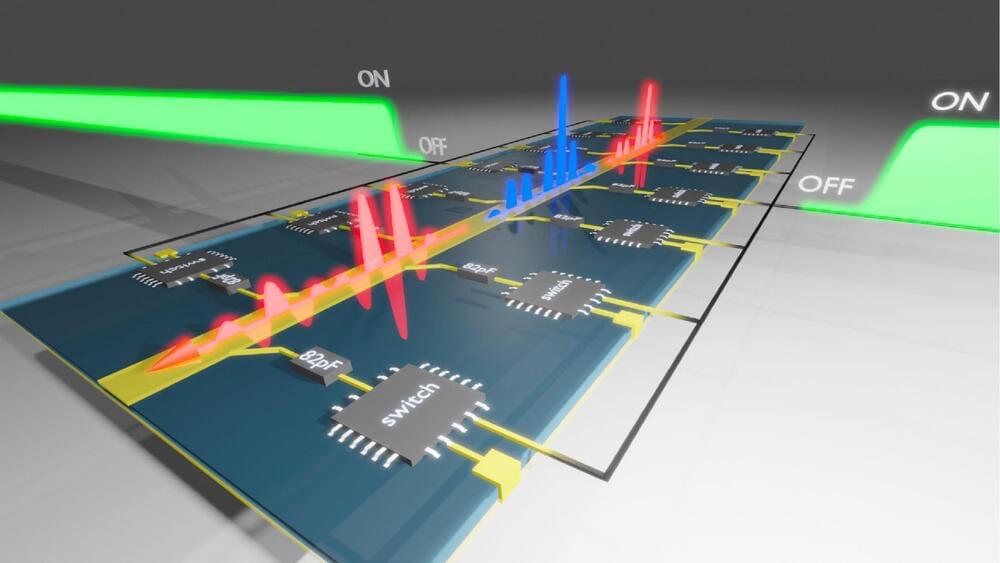
The breakthrough experiment could lead to low-energy, wave-based computers and new applications for wireless communications.
Researchers at the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) performed a breakthrough experiment in which they observed time reflections of electromagnetic signals in a tailored metamaterial.
Time reflection versus spatial reflection.
Andrea Alu.
The scientists, who published their findings in a paper in Nature Physics, were able to successfully cause time reversal as well as frequency conversion of broadband electromagnetic waves in their experiments.