Generative AI represents a big breakthrough towards models that can make sense of the world by dreaming up visual, textual and conceptual representations, and are becoming increasingly generalist. While these AI systems are currently based on scaling up deep learning algorithms with massive amounts of data and compute, biological systems seem to be able to make sense of the world using far less resources. This phenomenon of efficient intelligent self-organization still eludes AI research, creating an exciting new frontier for the next wave of developments in the field. Our panelists will explore the potential of incorporating principles of intelligent self-organization from biology and cybernetics into technical systems as a way to move closer to general intelligence. Join in on this exciting discussion about the future of AI and how we can move beyond traditional approaches like deep learning!
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Deepmind Ada brings foundation models to reinforcement learning
Deepmind’s AdA shows that foundation models also enable generalist systems in reinforcement learning that learn new tasks quickly.
In AI research, the term foundation model is used by some scientists to refer to large pre-trained AI models, usually based on transformer architectures. One example is OpenAI’s large language model GPT-3, which is trained to predict text tokens and can then perform various tasks through prompt engineering in a few-shot setting.
In short, a foundation model is a large AI model that, because of its generalist training with large datasets, can later perform many tasks for which it was not explicitly trained.


Researcher uses AI to make texts that are thousands of years old readable
How should we live when we know we must die? This question is posed by the first work of world literature, the Gilgamesh epic. More than 4,000 years ago, Gilgamesh set out on a quest for immortality. Like all Babylonian literature, the saga has survived only in fragments. Nevertheless, scholars have managed to bring two-thirds of the text into readable condition since it was rediscovered in the 19th century.
The Babylonians wrote in cuneiform characters on clay tablets, which have survived in the form of countless fragments. Over centuries, scholars transferred the characters imprinted on the pieces of clay onto paper. Then they would painstakingly compare their transcripts and—in the best case—recognize which fragments belong together and fill in the gaps. The texts were written in the languages Sumerian and Akkadian, which have complicated writing systems. This was a Sisyphean task, one that the experts in the Electronic Babylonian Literature project can scarcely imagine today.
Enrique Jiménez, Professor of Ancient Near Eastern Literatures at LMU’s Institute of Assyriology, and his team have been working on the digitization of all surviving cuneiform tablets since 2018. In that time, the project has processed as many as 22,000 text fragments.

Scientists solve long-standing mystery about mRNAs
Messenger RNAs (mRNAs) contain chemical marks that are critical for antiviral defense in cells, according to a new study from researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine. The finding solves a 50-year mystery concerning the purpose of these chemical modifications, and suggests that faulty mRNA modification may underlie some autoimmune and inflammatory disorders.

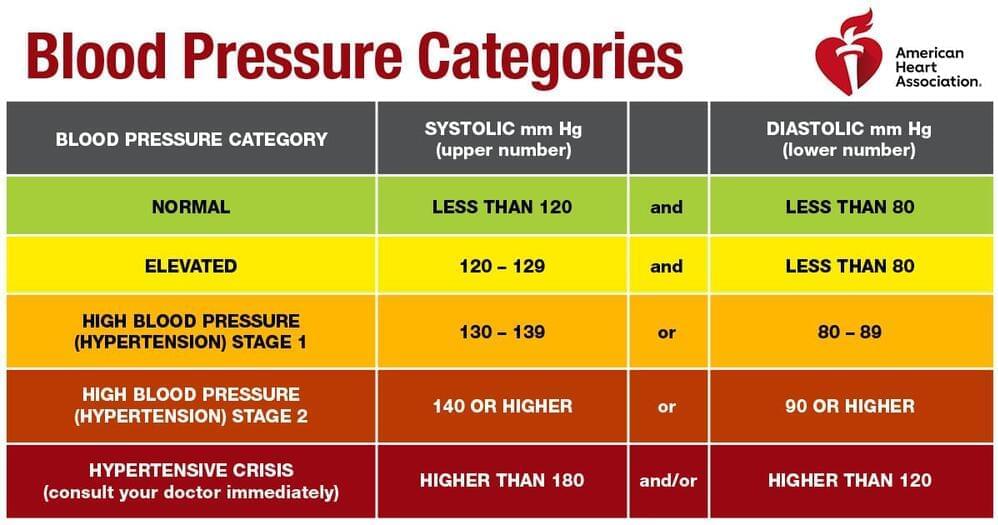
Ideal blood pressure may remodel brain clearance pathways linked to brain health, dementia
𝐈𝐝𝐞𝐚𝐥 𝐛𝐥𝐨𝐨𝐝 𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐮𝐫𝐞 𝐦𝐚𝐲 𝐫𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐝𝐞𝐥 𝐛𝐫𝐚𝐢𝐧 𝐜𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐚𝐧𝐜𝐞 𝐩𝐚𝐭𝐡𝐰𝐚𝐲𝐬 𝐥𝐢𝐧𝐤𝐞𝐝 𝐭𝐨 𝐛𝐫𝐚𝐢𝐧 𝐡𝐞𝐚𝐥𝐭𝐡, 𝐝𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐢𝐚
𝘾𝙡𝙤𝙨𝙚 𝙧𝙚𝙫𝙞𝙚𝙬 𝙤𝙛 𝙈𝙍𝙄 𝙨𝙘𝙖𝙣𝙨 𝙛𝙤𝙪𝙣𝙙 𝙢𝙤𝙧𝙚 𝙞𝙣𝙩𝙚𝙣𝙨𝙞𝙫𝙚 𝙝𝙞𝙜𝙝 𝙗𝙡𝙤𝙤𝙙 𝙥𝙧𝙚𝙨𝙨𝙪𝙧𝙚 𝙩𝙧𝙚𝙖𝙩𝙢𝙚𝙣𝙩 (𝙩𝙖𝙧𝙜𝙚𝙩𝙚𝙙 𝙩𝙤 𝙖𝙘𝙝𝙞𝙚𝙫𝙚 𝙖 𝙨𝙮𝙨𝙩𝙤𝙡𝙞𝙘 𝙥𝙧𝙚𝙨𝙨𝙪𝙧𝙚 𝙡𝙚𝙨𝙨 𝙩𝙝𝙖𝙣 120 𝙢𝙢 𝙃𝙜) 𝙬𝙖𝙨 𝙢𝙤𝙧𝙚 𝙚𝙛𝙛𝙚𝙘𝙩𝙞𝙫𝙚 𝙩𝙝𝙖𝙣 𝙖 𝙡𝙚𝙨𝙨-𝙞𝙣𝙩𝙚𝙣𝙨𝙚 𝙩𝙧𝙚𝙖𝙩𝙢𝙚𝙣𝙩 𝙜𝙤𝙖𝙡 𝙤𝙛 140 𝙢𝙢 𝙃𝙜 𝙨𝙮𝙨𝙩𝙤𝙡𝙞𝙘 𝙞𝙣 𝙖𝙘𝙝𝙞𝙚𝙫𝙞𝙣𝙜 𝙖 𝙥𝙤𝙨𝙞𝙩𝙞𝙫𝙚 𝙨𝙩𝙧𝙪𝙘𝙩𝙪𝙧𝙖𝙡 𝙘𝙝𝙖𝙣𝙜𝙚 𝙞𝙣 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙗𝙧𝙖𝙞𝙣’𝙨 𝙥𝙚𝙧𝙞𝙫𝙖𝙨𝙘𝙪𝙡𝙖𝙧 𝙨𝙥𝙖𝙘𝙚𝙨: 𝙥𝙖𝙩𝙝𝙬𝙖𝙮𝙨 𝙩𝙝𝙖𝙩 𝙖𝙧𝙚 𝙞𝙢𝙥𝙤𝙧𝙩𝙖𝙣𝙩 𝙩𝙤 𝙘𝙡𝙚𝙖𝙧𝙞𝙣𝙜 𝙩𝙤𝙭𝙞𝙣𝙨 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙤𝙩𝙝𝙚𝙧 𝙗𝙮𝙥𝙧𝙤𝙙𝙪𝙘𝙩𝙨.
𝙄𝙛 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙗𝙧𝙖𝙞𝙣 𝙘𝙖𝙣𝙣𝙤𝙩 𝙥𝙧𝙤𝙥𝙚𝙧𝙡𝙮 𝙘𝙡𝙚𝙖𝙧 𝙢𝙚𝙩𝙖𝙗𝙤𝙡𝙞𝙘 𝙗𝙮𝙥𝙧𝙤𝙙𝙪𝙘𝙩𝙨, 𝙩𝙝𝙚𝙮 𝙖𝙘𝙘𝙪𝙢𝙪𝙡𝙖𝙩𝙚 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙢𝙖𝙮 𝙘𝙤𝙣𝙩𝙧𝙞𝙗𝙪𝙩𝙚 𝙩𝙤 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙙𝙚𝙫𝙚𝙡𝙤𝙥𝙢𝙚𝙣𝙩 𝙤𝙛 𝙙𝙚𝙢𝙚𝙣𝙩𝙞𝙖, 𝙧𝙚𝙨𝙚𝙖𝙧𝙘𝙝𝙚𝙧𝙨 𝙨𝙖𝙞𝙙.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET, Thursday, Feb. 2, 2023
(NewMediaWire) — February 2, 2023 — DALLAS Among people who received more intensive treatment for high blood pressure, evaluations of MRI scans indicated a positive change in brain structures involved in its ability to clear toxins and other byproducts, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference 2023. The meeting, held in person in Dallas and virtually, Feb. 8–10, 2023, is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health.
The study is the first to examine whether intensive blood pressure treatment may slow, or reverse structural changes related to the volume of the brain’s perivascular spaces, areas of the brain around the blood vessels that are involved in the clearance of toxins and other byproducts. These areas tend to enlarge as people get older or have more cardiovascular risk factors.

This genius student uses the power of AI and a 3D printer to ‘handwrite’ their homework
As technology advances, you can always count on one thing: students will use it to avoid doing homework. One industrious student not only got an AI chatbot to do their homework assignment, but they also rigged it to a 3D printer to write it out on pen and paper, expending the maximum amount of effort required to do the minimum amount of homework. Bravo!
TikTok user 3D_printer_stuff (opens in new tab) shared a series of videos on how they programmed a 3D printer to produce homework with the answers that ChatGPT (opens in new tab) wrote.
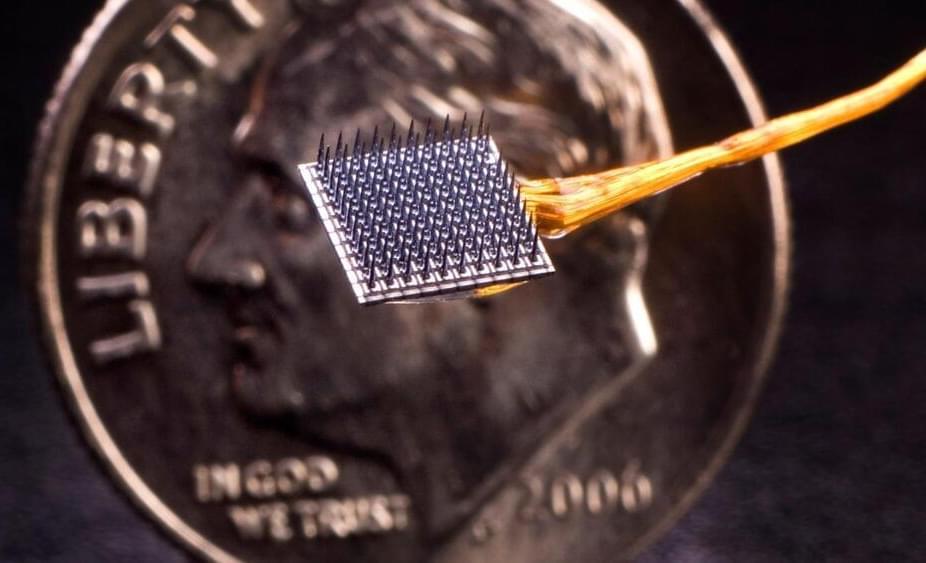
Clinical trials show encouraging safety profile for brain-computer interface turning thoughts into action
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — More than two decades ago, a team of Brown University researchers set out with an ambitious goal to provide people with paralysis a revolutionary neurotechnology capable of turning thoughts about movement into actual action, using a tiny device that would one day be implanted in the surface of the brain. Their work led to an ongoing, multi-institution effort to create the BrainGate brain-computer interface, designed to allow clinical trial participants with paralysis to control assistive devices like computers or robotic limbs just by thinking about the action they want to initiate.
Open Access Paper:
https://n.neurology.org/content/early/2023/01/13/WNL.
In an important step toward a medical technology that could help restore independence of people with paralysis, researchers find the investigational BrainGate neural interface system has low rates of associated adverse events.