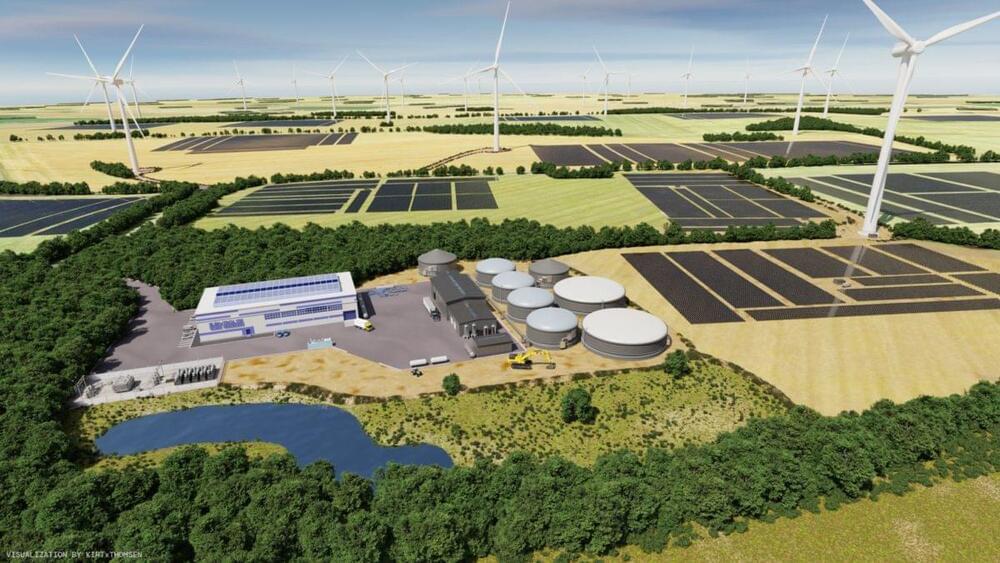
Eurowind Energy is building wind-solar capacity at five onshore energy centers and is also considering hydrogen electrolysis. It says each of the sites will include battery storage to offer grid services.
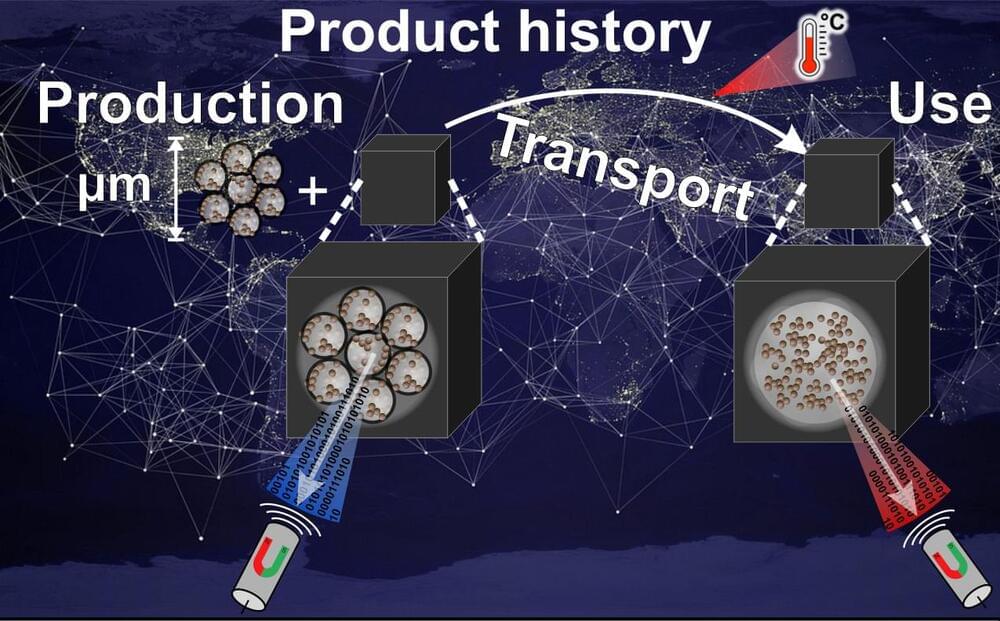
The right temperature ensures the success of technical processes, the quality of food and medicines, or affects the lifetime of electronic components and batteries. Temperature indicators enable to detect (un)desired temperature exposures and irreversibly record them by changing their signal for a readout at any later time.
Of particular interest are small-sized temperature indicators that can be easily integrated into any arbitrary object and subsequently monitor the objects’ temperature history autonomously, i.e. without power supply. Accordingly, the indicators’ signal readout permits to verify successful bonding processes, to uncover temperature peaks in global supply chains, or to localize hot spots in electronic devices.
Prof. Dr. Karl Mandel (Professorship for Inorganic Chemistry) and his research group have succeeded in developing a new type of temperature indicator in the form of a micrometer-sized particle, which differs from previously established, mostly optical indicators mainly due to its innovative magnetic readout method. The results of the research work have now been published in the journal Advanced Materials (“Recording Temperature with Magnetic Supraparticles”).
NASA director Bill Nelson warned that China’s space program was primarily established to be used as an extension of its military rather than for peaceful or scientific purposes.
By Trevor Filseth L
China’s Foreign Ministry issued a condemnation on Monday of reports from the United States that Beijing intends to pursue exclusive control over the Moon in the future, accusing administrators within the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) of ignoring facts and speaking “irresponsibly” about China’s space program.
A group of scientists has developed an entirely new approach to treating eating disorders.
They showed that a group of nerve cells (so-called AgRP, agouti-related peptide neurons) in the hypothalamus control the release of endogenous lysophospholipids, which in turn control the excitability of nerve cells in the cerebral cortex, which stimulates food intake.
In this process, the crucial step of the signaling pathway is controlled by autotaxin, an enzyme that is responsible for the production of lysophosphatidic acid.
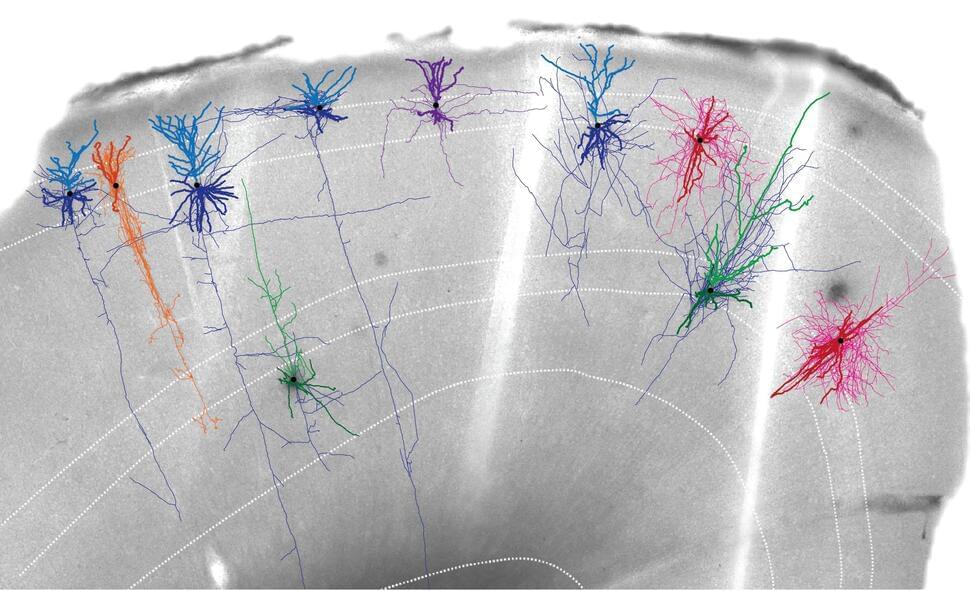
Hundreds of neuroscientists built a ‘parts list’ of the motor cortex, laying groundwork to map the whole brain and better understand brain diseases.
Before you read any further, bring your hand to your forehead.
It probably didn’t feel like much, but that simple kind of motion required the concerted effort of millions of different neurons in several regions of your brain, followed by signals sent at 200 mph from your brain to your spinal cord and then to the muscles that contracted to move your arm.
While we haven’t found any evidence of alien life yet, that doesn’t mean it’s not out there, beyond our reach. Now, a team of researchers has put together a mathematical model showing aliens could potentially be communicating across space – via quantum physics.
Efforts are well underway to make quantum communications a reality here on Earth. The idea is that quantum mechanics provide certain properties that would make information transfer inherently faster and more secure than regular systems… if we can get it to work.
One of the major hurdles to overcome before quantum networks can be established is that they’re very fragile and susceptible to interference. According to this latest study, such networks could fly across space without breaking up.
View insights.
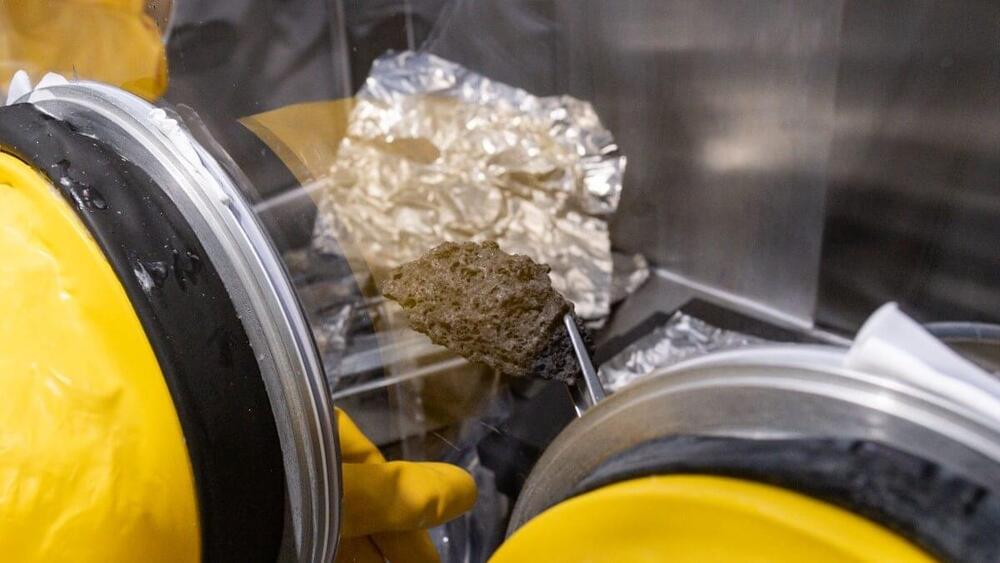
Scientists are finally getting a look at frozen lunar surface samples from the last time that humans walked on the Moon.
The samples were collected during the Apollo 17 mission, which returned to Earth in December 1972.
As NASA gears up for its Artemis program, which aims to return humans to the Moon by 2024, preserved samples from the later Apollo missions are being studied as part of the Apollo Next Generation Samples Analysis Program (ANGSA). Understanding how different storage techniques and the passage of time have affected lunar samples will inform how NASA will treat new samples collected during Artemis missions.
http://2045.com http://gf2045.com.
In February of 2012 the first Global Future 2045 Congress was held in Moscow. There, over 50 world leading scientists from multiple disciplines met to develop a strategy for the future development of humankind. One of the main goals of the Congress was to construct a global network of scientists to further research on the development of cybernetic technology, with the ultimate goal of transferring a human’s individual consciousness to an artificial carrier.
2012–2013. The global economic and social crises are exacerbated. The debates on the global paradigm of future development intensifies.
New transhumanist movements and parties emerge. Russia 2045 transforms into World 2045.
Simultaneously, the 2045.com international social network for open innovation is expanding. Here anyone interested may propose a project, take part in working on it, or fund it, or both. In the network, there are scientists, scholars, researchers, financiers and managers.
2013–2014. New centers working on cybernetic technologies for the development of radical life extension rise. The ‘race for immortality’ starts.
2015–2020. The Avatar is created — A robotic human copy controlled by thought via ‘brain-computer’ interface. It becomes as popular as a car.
View insights.
When it comes to something as complex as space-time, intuition comes in different ways, depending on the level of science you have access to, writes Chanda Prescod-Weinstein.
Quantum collaboration demonstrates in Chicagoland the first steps toward functional long-distance quantum networks over deployed telecom fiber optics, opening the door to scalable quantum computing — https://bit.ly/3QXe780