Humans are innately able to reason about the behaviors of different physical objects in their surroundings. These physical reasoning skills are incredibly valuable for solving everyday problems, as they can help us to choose more effective actions to achieve specific goals.
Some computer scientists have been trying to replicate these reasoning abilities in artificial intelligence (AI) agents, to improve their performance on specific tasks. So far, however, a reliable approach to train and assess the physical reasoning capabilities of AI algorithms has been lacking.
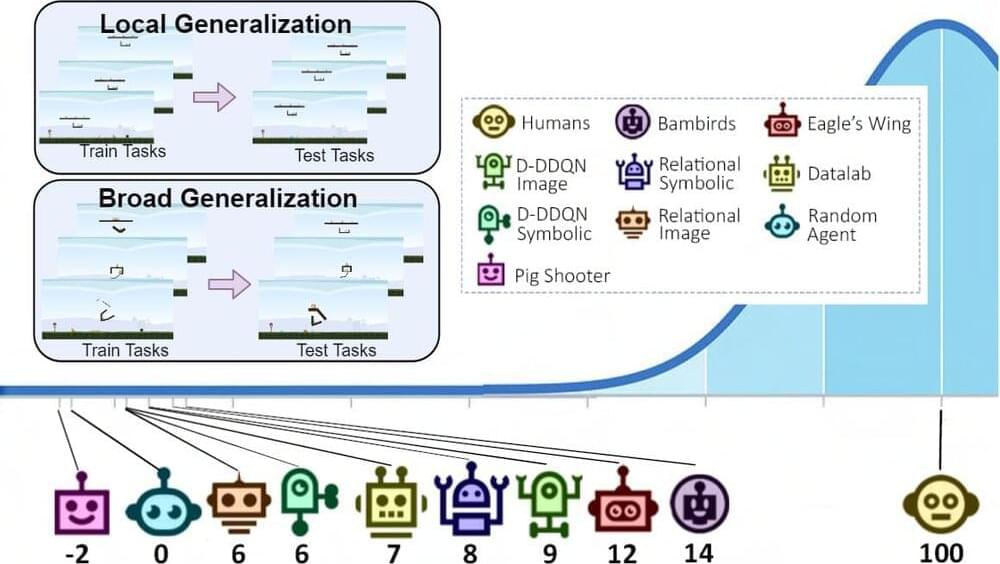
Cheng Xue, Vimukthini Pinto, Chathura Gamage, and colleagues, a team of researchers at the Australian National University, recently introduced Phy-Q, a new testbed designed to fill this gap in the literature. Their testbed, introduced in a paper in Nature Machine Intelligence, includes a series of scenarios that specifically assess an AI agent’s physical reasoning capabilities.