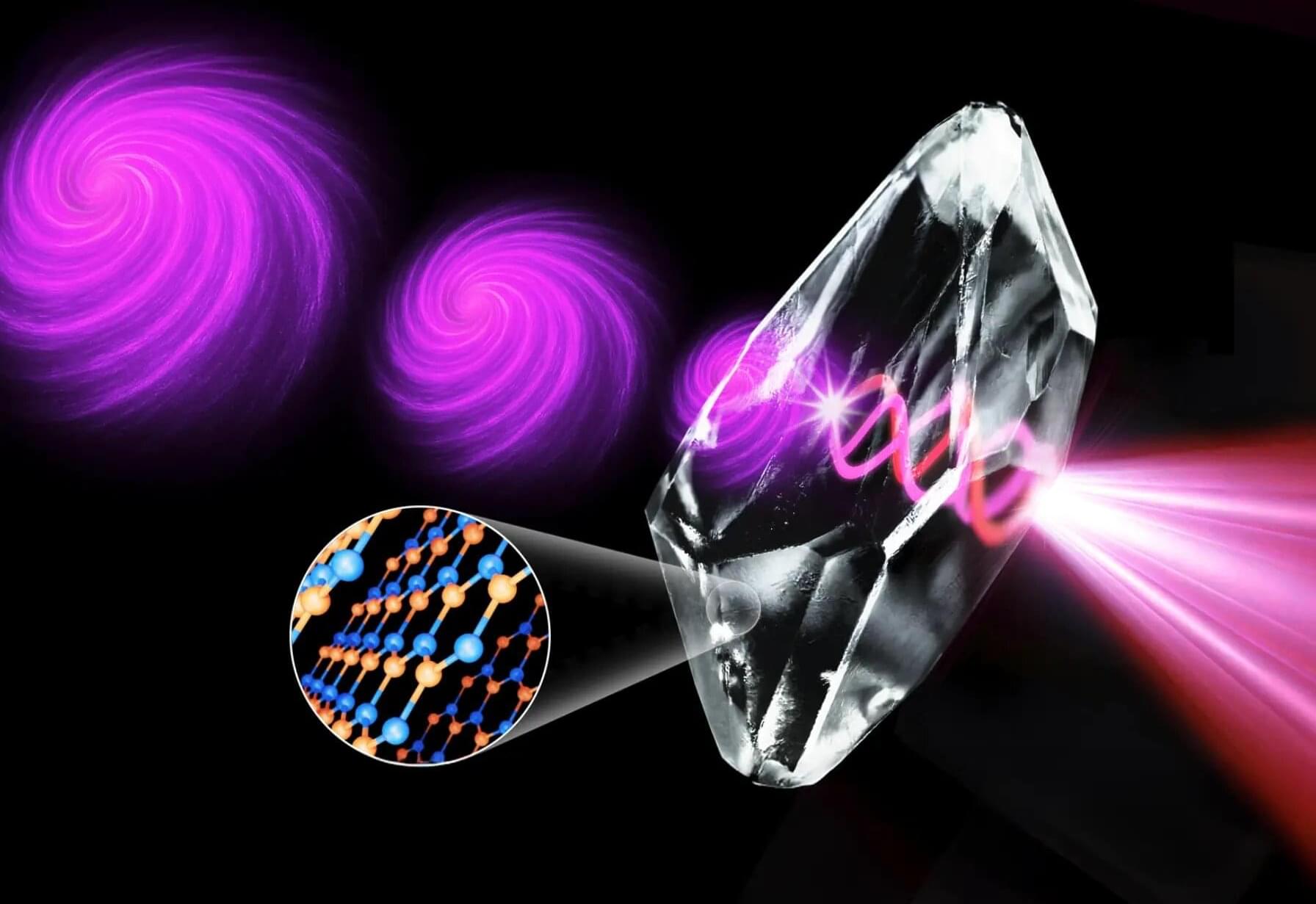
Imagine a whirlpool spinning in a river, or a tornado swirling through the sky. They don’t just spin on the spot: they travel forward while maintaining that spiraling motion inside them. These twisting motions, called vortices, are powerful and organized spirals. Now, imagine light that behaves the same way: a beam of light that spins as it moves forward. This “twisted” light, known as an optical vortex, can carry more information than normal light, opening the door to faster internet and ultra-secure communications.