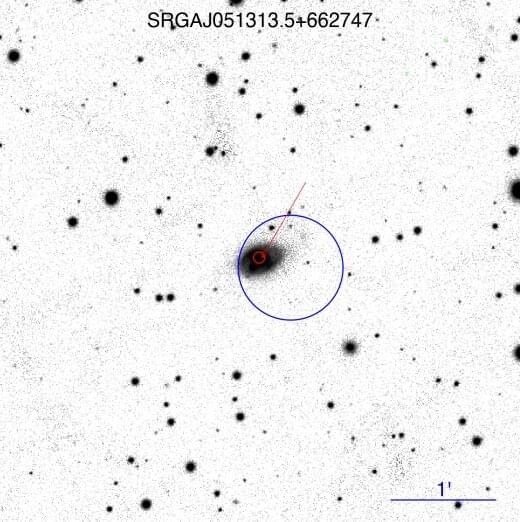
Using the Spectrum–RG (SRG) spacecraft and two ground-based telescopes, Russian astronomers have observed X-ray sources in the eastern Galactic sky. The observational campaign resulted in the detection of 14 new active galactic nuclei. The findings were presented June 6 in the journal Astronomy Letters.
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy, more luminous than the surrounding galaxy light. AGNs are very energetic due either to the presence of a black hole or star formation activity at the core of the galaxy.
Astronomers generally divide AGNs into two groups based on emission line features. Type 1 AGNs show broad and narrow emission lines, while only narrow emission lines are present in Type 2 AGNs.