Hear the biggest stories from the world of science | 10 May 2023.



A study of the mechanical forces in certain immune cells may give new insights into how organisms deal with ever-evolving pathogens.
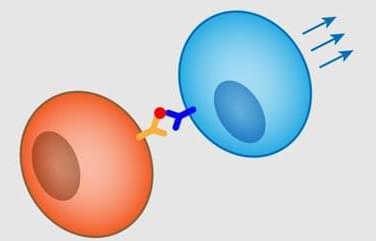
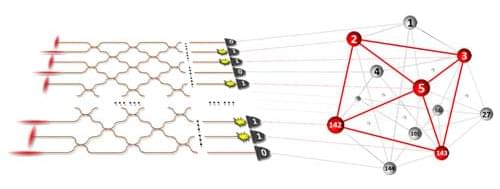
To fight disease, many organisms have an adaptive immune system, which learns the molecular shapes of foreign elements (antigens) and remembers them to mount a defense against future infections. In vertebrates, the learning stage involves a remarkable cycle of evolution within an individual animal—a cycle called affinity maturation, which involves a type of immune cell called a B cell (Fig. 1). In this process, B cells are selected to have receptors that bind strongly to specific antigens. However, if these cells become too specialized, they risk becoming unresponsive to slightly mutated pathogens. Fortunately, the immune system can limit affinity maturation to retain a range of specificities for target pathogens. Just how the immune system is able to do that is the subject of a fascinating new study by Hongda Jiang and Shenshen Wang from the University of California, Los Angeles [1].
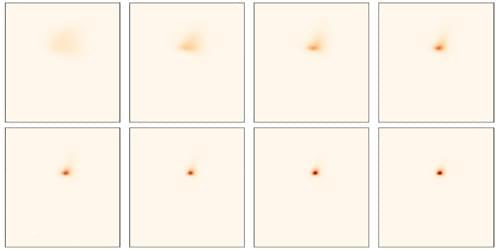
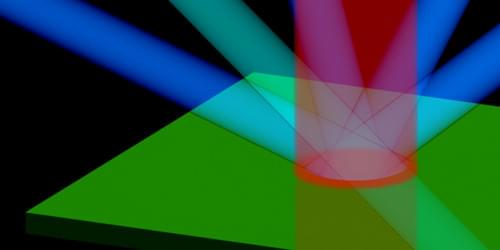
Experiments probing quasiparticles in semiconductor microcavities offer unprecedented insights into the dynamics of quantum fluids of light.
Superfluidity [1, 2], the ability of a fluid to flow without friction, isn’t restricted to systems described by hydrodynamics. Over a decade ago, optics researchers started to take an interest in superfluids and other quantum fluids [3], driven by the realization that light propagating in a nonlinear medium can exhibit quantum hydrodynamics features [4]. Two platforms emerged for the study of these “fluids of light”: semiconductor microcavities in which photons are confined [5] and propagating geometries in which photons travel in a bulk medium [6–8]. Both configurations allow photons to acquire an effective mass and experience an effective mutual interaction—properties that can lead them to collectively behave as a quantum fluid.

For the first time, astronomers have spotted an evolving star engulfing an orbiting planet.
When our Sun nears the end of its life, it will start to swell. During this expansion, which is expected to happen in some 6 billion years, the dying Sun will engulf our Solar System’s inner planets, including Earth. Though scientists are certain of Earth’s far-future fate, no direct observation had been made of a dying star swallowing an orbiting planet, until now [1].
The unique observation comes from Kishalay De of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and his colleagues. The team found the planet-eating star in data taken as part of the Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF), a large-area optical survey of the night sky. While comparing a few weeks’ worth of consecutive ZTF scans—a new survey of the sky is performed every 48 hours—a brightening star 12,000 light-years from Earth caught De’s attention, he says.
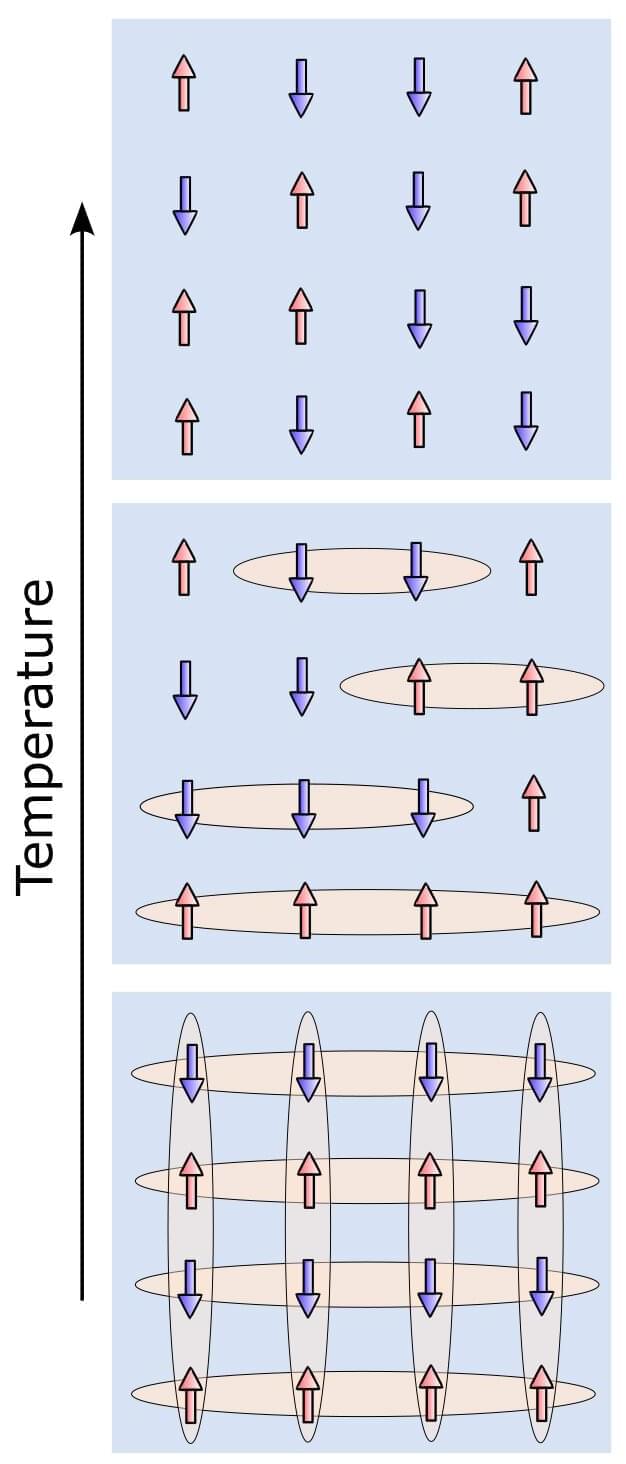
Physicists have discovered “stacked pancakes of liquid magnetism” that may account for the strange electronic behavior of some layered helical magnets.
The materials in the study are magnetic at cold temperatures and become nonmagnetic as they thaw. Experimental physicist Makariy Tanatar of Ames National Laboratory at Iowa State University noticed perplexing electronic behavior in layered helimagnetic crystals and brought the mystery to the attention of Rice theoretical physicist Andriy Nevidomskyy, who worked with Tanatar and former Rice graduate student Matthew Butcher to create a computational model that simulated the quantum states of atoms and electrons in the layered materials.
Magnetic materials undergo a “thawing” transition as they warm up and become nonmagnetic. The researchers ran thousands of Monte Carlo computer simulations of this transition in helimagnets and observed how the magnetic dipoles of atoms inside the material arranged themselves during the thaw. Their results were published in a recent study in Physical Review Letters.