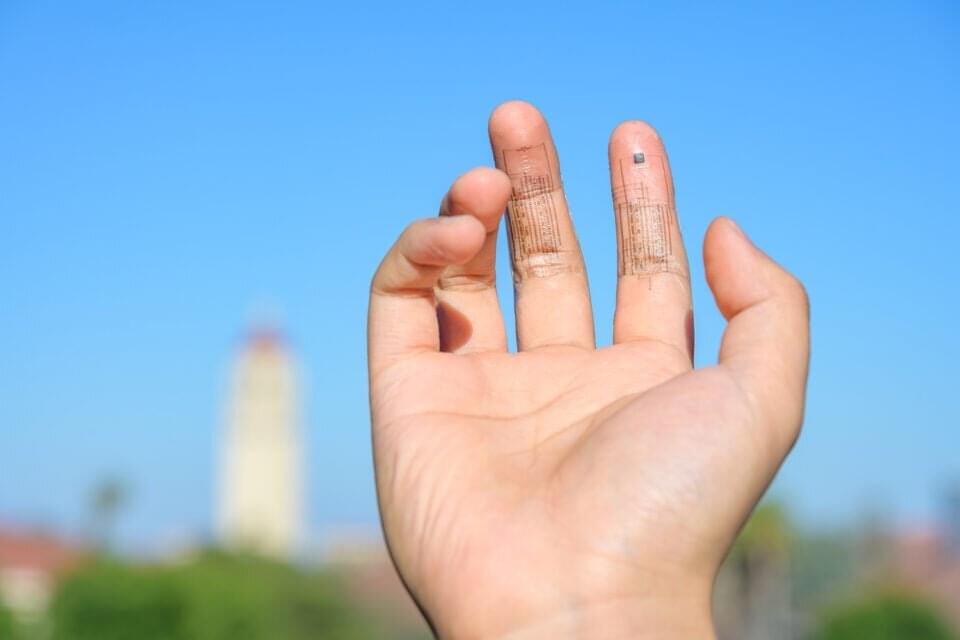
On Saturday, leaders of the Group of Seven (G7) nations made some public calls for the development and adoption of technical standards to keep artificial intelligence (AI) “trustworthy.” They added that they feared that governance of the technology has not kept pace with its growth.
This is according to a report by the Financial Post published on Saturday.
The leaders from the U.S., Japan, Germany, Britain, France, Italy, Canada and the EU said in a statement that while approaches to “the common vision and goal of trustworthy AI may vary,” the rules for digital technologies like AI should be “in line with our shared democratic values.”