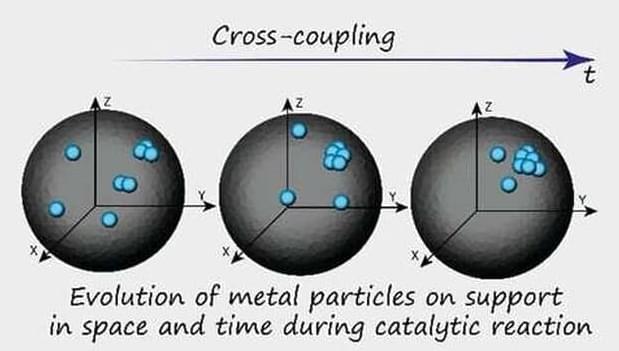
A small team of chemists at the Russian Academy of Sciences, has found that metal atoms, not nanoparticles, play the key role in catalysts used in fine organic synthesis. In the study, reported in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, the group used multiple types of electron microscopy to track a region of a catalyst during a reaction to learn more about how it was proceeding.
Prior research has shown that there are two main methods for studying a reaction. The first is the most basic: As ingredients are added, the reaction is simply observed and/or measured. This can be facilitated through use of high-speed cameras. This approach will not work with nanoscale reactions, of course. In such cases, chemists use a second method: They attempt to capture the state of all the components before and after the reaction and then compare them to learn more about what happened.
This second approach leaves much to be desired, however, as there is no way to prove that the objects under study correspond with one another. In recent years, chemists have been working on a new approach: Following the action of a single particle during the reaction. This new method has proven to have merit but it has limitations as well—it also cannot be used for reactions that occur in the nanoworld. In this new effort, the researchers used multiple types of electron microscopy coupled with machine-learning algorithms.