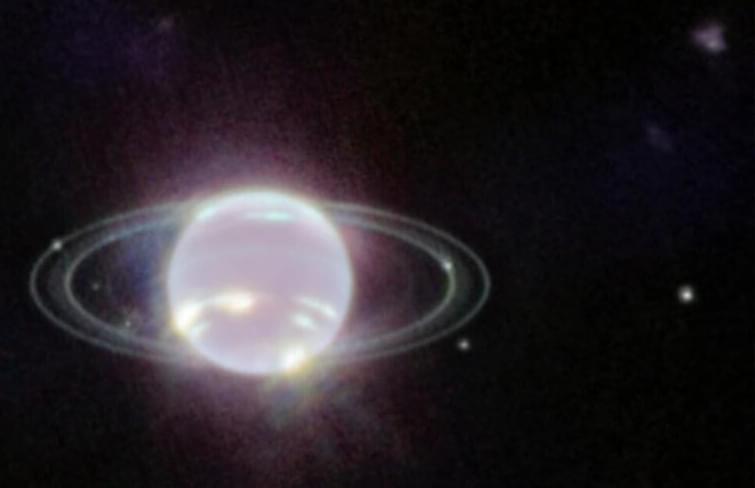
The NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope is showing off its capabilities closer to home with its first image of Neptune. Not only has Webb captured the clearest view of this peculiar planet’s rings in more than 30 years, but its cameras are also revealing the ice giant in a whole new light.
Most striking about Webb’s new image is the crisp view of the planet’s dynamic rings — some of which haven’t been seen at all, let alone with this clarity, since the Voyager 2 flyby in 1989. In addition to several bright narrow rings, the Webb images clearly show Neptune’s fainter dust bands. Webb’s extremely stable and precise image quality also permits these very faint rings to be detected so close to Neptune.
Neptune has fascinated and perplexed researchers since its discovery in 1846. Located 30 times farther from the Sun than Earth, Neptune orbits in one of the dimmest areas of our Solar System. At that extreme distance, the Sun is so small and faint that high noon on Neptune is similar to a dim twilight on Earth.