Is this a sign of nuclear escalation?
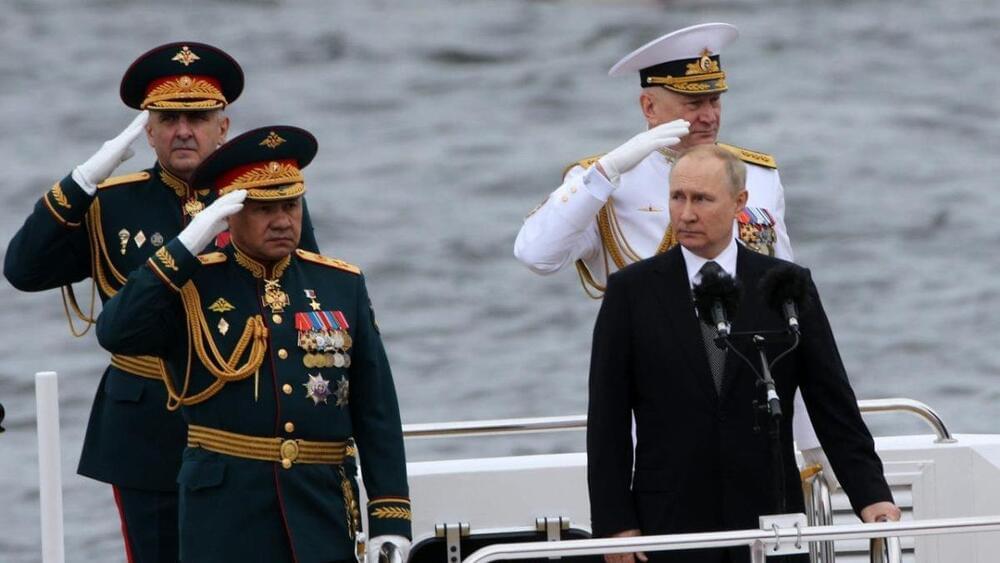
A top-of-the-line Russian nuclear-powered submarine has gone missing from its harbor in the Arctic along with its rumored “doomsday weapon,” according to multiple reports.
NATO has reportedly warned members that Russia’s Belgorod submarine no longer appeared to be operating out of its White Sea base, where it has been active since July. Officials warned that Russia may plan to test Belgorod’s “Poseidon” weapons system, a drone equipped with a nuclear bomb that Russia has claimed is capable of creating a “radioactive tsunami,” according to Italian media.
The drone can be deployed from the submarine at any time and detonated at a depth of 1 kilometer near a coastal city. Russian state media has claimed the device can create a 1,600-ft. wave that smashes into the coast and irradiates it.