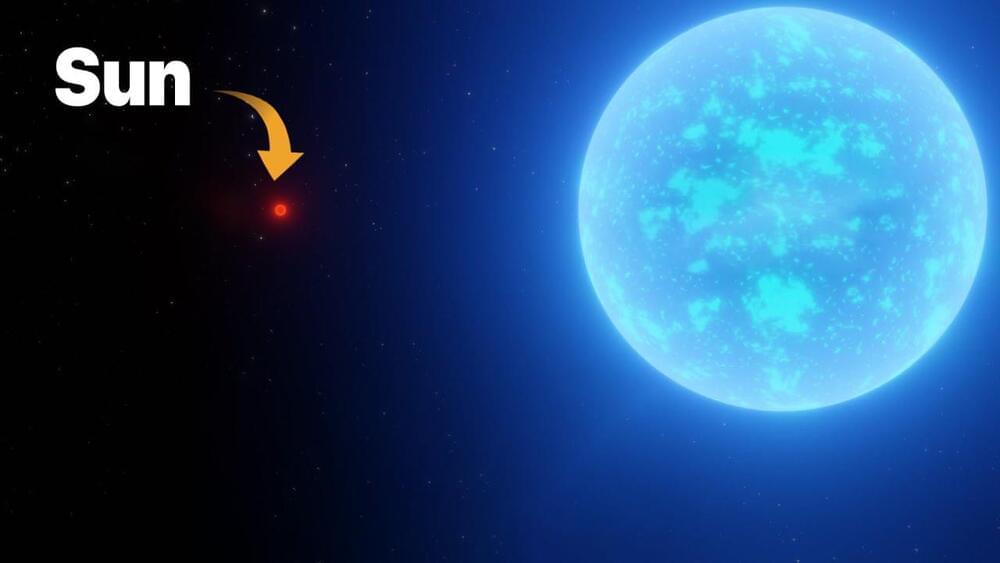
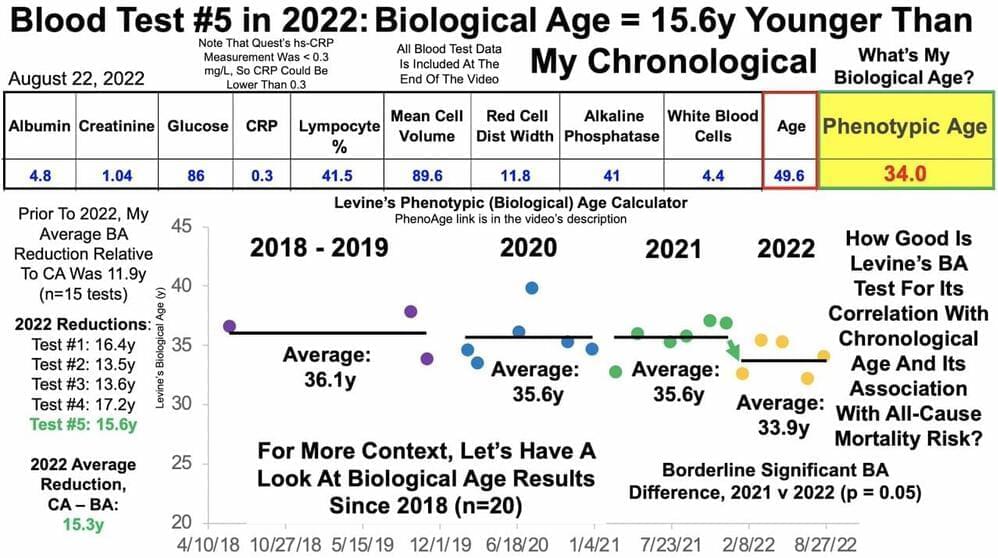
The most massive star known by astronomers is truly of gargantuan proportions. Dubbed R136a1, this is the most massive and luminous star ever discovered in the cosmos. Additionally, it belongs to the Large Magellanic Cloud and is one of the hottest stars out there, and it is very, very different than our Sun.
Astronomers have obtained the sharpest image ever of star R136a1, the most massive known star in the Universe, with the 8.1-meter Gemini South telescope in Chile, part of the International Gemini Observatory operated by NSF’s NOIRLab. Researchers at NOIRLab, led by Venu Kalari, challenge our understanding of the most massive stars and suggest their mass may be lower than previously believed.
The formation of the biggest stars – those with 100 times the mass of the Sun – is still a mystery to astronomers. Observing these giants, which normally reside within dust-shrouded star clusters, is challenging. A giant star’s fuel reserves are depleted in less than a million years. Compared with our Sun, which has a lifespan of about 10 billion years, ours is less than halfway through. Individual massive stars in clusters are difficult to distinguish due to their densely packed nature, short lifetimes, and vast astronomical distances.