Views that make you go ‘huh!’ Headlining my weekly posting. Is it “tl;dr”? Sure. So assign your robot to read it. S/he’s in charge, anyway.
https://davidbrin.blogspot.com/2023/05/the-ai-saga-continues.html
Views that make you go ‘huh!’ Headlining my weekly posting. Is it “tl;dr”? Sure. So assign your robot to read it. S/he’s in charge, anyway.
https://davidbrin.blogspot.com/2023/05/the-ai-saga-continues.html

At its I/O developer conference, the search giant needs to rethink its AI strategy if it wants to catch Microsoft. The missing element? Experimentation. Google has had a rough six months. Since ChatGPT launched last November — followed by the new Bing in February and GPT-4 in March — the company has failed to establish its AI credentials. Its own offering, the “experimental” chatbot Bard, compares poorly to rivals, and insider reports have portrayed a company in panic and di… See more.
AI outputs are increasingly defining the cultural moment — just not Google’s.

The demo is clever, questionably real, and prompts a lot of questions about how this device will actually work.
Buzz has been building around the secretive tech startup Humane for over a year, and now the company is finally offering a look at what it’s been building. At TED last month, Humane co-founder Imran Chaudhri gave a demonstration of the AI-powered wearable the company is building as a replacement for smartphones. Bits of the video leaked online after the event, but the full video is now available to watch.
The device appears to be a small black puck that slips into your breast pocket, with a camera, projector, and speaker sticking out the top. Throughout the 13-minute presentation, Chaudhri walks through a handful of use cases for Humane’s gadget: * The device rings when Chaudhri receives a phone call. He holds his hand up, and the device projects the caller’s name along with icons to answer or ignore the call. He then has a brief conversation. (Around 1:48 in the video) * He presses and holds one finger on the device, then asks a question about where he can buy a gift. The device responds with the name of a shopping district. (Around 6:20) * He taps two fingers on the device, says a sentence, and the device translates the sentence into another language, stating it back using an AI-generated clone of his voice. (Around 6:55) * He presses and holds one finger on the device, says, “Catch me up,” and it reads out a summary of recent emails, calendar events, and messages. (At 9:45) * He holds a chocolate bar in front of the device, then presses and holds one finger on the device while asking, “Can I eat this?” The device recommends he does not because of a food allergy he has. He presses down one finger again and tells the device he’s ignoring its advice. (Around 10:55)
Chaudhri, who previously worked on design at Apple for more than two decades, pitched the device as a salve for a world covered in screens. “Some believe AR / VR glasses like these are the answer,” he said, an image of VR headsets behind him. He argued those devices — like smartphones — put “a further barrier between you and the world.”
Humane’s device, whatever it’s called, is designed to be more natural by eschewing the screen. The gadget operates on its own. “You don’t need a smartphone or any other device to pair with it,” he said.

Microsoft isn’t slowing down in its battle with Google for AI features.
Microsoft only just announced a round of new updates to its GPT-4-powered Bing Chat earlier this month, and it’s back today with some big improvements for mobile users. Just days after Google rebranded its AI tools for Docs and Gmail as Duet AI, Microsoft is now focused on mobile with contextual chat for Edge mobile, a Bing widget for iOS and Android, and even continuous Bing Chat conversations between mobile and desktop.
These new mobile-first features arrive just as Microsoft finishes rolling out its new image and video answers, restaurant bookings, and chat history features that were all announced earlier this month. Microsoft only launched Bing Chat nearly 100 days ago, and it’s showing no signs of slowing down with its AI announcements.
Starting today, you’ll now be able to start a Bing Chat conversation on a PC and then pick it up on mobile. Microsoft uses the example of asking Bing Chat to create a recipe for you on a PC and then asking it to provide a substitute on the mobile app when you’re at a grocery store and they’ve run out of an ingredient. This is starting to roll out today and will be available to all iOS and Android users within the next week.
The second big mobile change is contextual chat inside Microsoft Edge on iOS and Android. This is very similar to what exists in the Bing sidebar inside the desktop version of Edge, and it lets the mobile version of the browser read the context of a website you’re on. You can tap the Bing Chat icon at the bottom of Edge and ask it questions about a website you’re viewing or even ask it to summarize an article or document you’re reading.
Edge mobile will also include selected text actions where you can highlight a chunk of text and Bing will explain or summarize it. Microsoft says both of these new Edge features will be rolling out to mobile users “soon.”
Microsoft is also bringing a mobile widget to iOS and Android users that can be pinned to the homescreen for quick access to Bing Chat. The widget includes a Bing icon to get straight into Bing Chat and a microphone icon to ask a question with voice. This will be available on iOS and Android at some point this week, and Microsoft is also improving its language support for voice input.
Stability AI, the AI startup behind the text-to-image model Stable Diffusion, this week announced the release of StableStudio, an open source version of DreamStudio, Stability AI’s commercial AI-powered design suite.
In a blog post, Stability AI writes that it hopes to “foster a project [that] can outpace anything developed by a single company,” alluding to recent investments in the generative AI space from tech giants like Microsoft, Google and Amazon.
“We believe the best way to expand upon that impressive reach is through open, community-driven development rather than a private iteration of a closed-source product,” Stability AI said. “Our goal is to work with the broader community to create a world-class user interface for generative AI [that] users fully control.”
DreamStudio was first imagined as an animation studio for the open source generative AI art model Disco Diffusion. Focus shifted last year toward image generation with the arrival of Stable Diffusion, which brought DreamStudio more in line with rival generative image platforms like MidJourney and Nightcafe.
The differences between StableStudio and DreamStudio are relatively minor. StableStudio doesn’t have DreamStudio branding or Stability-specific account features, like billing and API management, and API calls on the backend have been replaced by a plugin system.
Stability AI stressed that, going forward, DreamStudio will become its preferred, managed instance of StableStudio and stay up to date with StableStudio “whenever possible.”
“The release of StableStudio reiterates Stability AI’s commitment to open-source and transparency,” the company continued. “We’re eager to see what the community will create.”
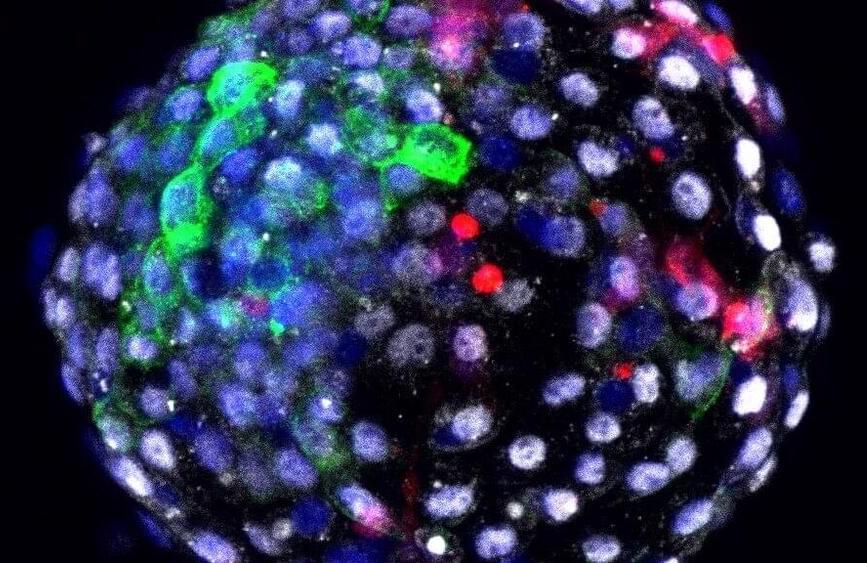
Year 2022
Experiments such as this one cannot be funded with federal research dollars, though they break no U.S. laws. The work was conducted in China, not because it was illegal in the United States, the researchers said, but because the monkey embryos, which are difficult to procure and expensive, were available there. The experiment used a total of 150 embryos, which were obtained without harming the monkeys, “just like in the IVF procedure,” Tan said.
But such experiments, which combine human cells with those of animals, are nevertheless controversial. This work, and other work by Izpisua Belmonte, has moved so rapidly, bioethicists have had trouble keeping up.
“The complicated thing is that we need better models of human disease, but the better those models are, the closer they bring us to the ethical issues we were trying to avoid by not doing experiments in humans,” Farahany said. “Remarkable steps forward require urgent public engagement.”
Two former Apple employees have just unveiled their “iPhone killer” AI-powered wearable that could make smartphones a thing of the past.
What if I told you that some of the minds behind the first iPhone, and many other silicon valley veterans, are now working to replace it?
They believe technology went in the wrong way, and now they want to fix this.
They have yet to show anything to the public, but some investors had many nice things to say about them.
This is Humane, and in this video, I’ll show you my concept of how the hardware and the UI of their device could be.
ChatGPT creator Sam Altman answered questions from congress about the safety and risks of ChatGPT. The topics of discussion included regulation, election integrity the effect of artificial intelligence on jobs.
Never miss a deal again! See CNET’s browser extension 👉 https://bit.ly/3lO7sOU
Follow us on TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@cnetdotcom.
Follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/cnet/
Follow us on Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/cnet.
Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/cnet.
#ai #artificialintelligence #congress

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer — no Kindle device required. Learn more
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.

A pair of harvesting robots are picking raspberries in Portugal, demonstrating the ability of tech to help combat seasonal labor shortages.
Sea of Green is a marijuana growing method in which numerous little plants are produced in close proximity per square meter of area. The advantage of developing this way is that plants spend less time in the vegetation stage while still creating as many bud sites per area volume. Buds mature faster in SOG, resulting in an additional yield yearly.
Furthermore, clones are typically used in SOG. This guarantees that all of the plants have the same characteristics (growing speed and height.) and that your SOG grows to have a lovely even canopy. You can also grow weed seeds for sale; however, only seeds from the same strain should be used. Avoid tall, lanky Sativa if possible. Also, keep your plants at the same level beneath your grow lights to maintain consistent development.
How many plants can you expect to grow per square foot with SOG?
The size of your growing space determines the number of cannabis plants per square foot that SOG can cultivate. After that, you can determine how many plants you want and the size of the containers. Most experts, however, advise growing up to one plant per square foot or two at most. Cultivating one SOG plant per square foot equals 10–11 plants per square meter (1 square meter = roughly 10.75 square feet). You should also avoid using pots with capacities of less than three liters.