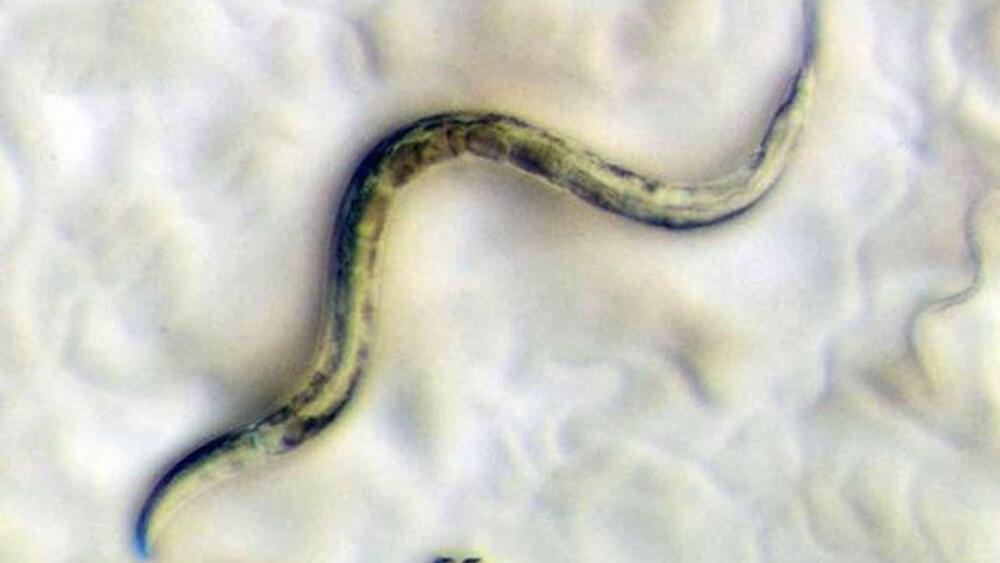
“Decreased mitochondrial membrane potential is an attractive explanation for the complex dysfunctions of aging.”
University of Washington School of Medicine researchers’ experiment on C.elegans.
Roundworms, which have an average lifespan of just two to three weeks, are frequently used in aging studies… More.
National Science Foundation.
As part of their research on aging, the team is interested in learning how to modulate mitochondrial activity directly. The energy centers inside living cells are called mitochondria. Among their numerous essential roles, they are vital for cellular respiration and energy production, as per the release.