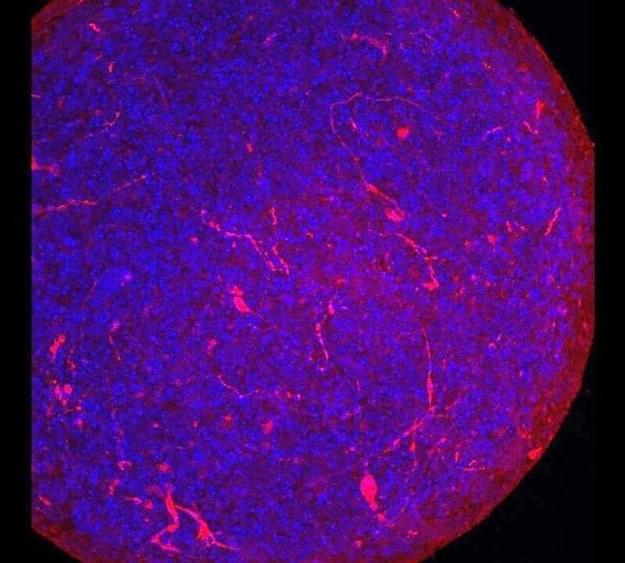
A multidisciplinary team from two Johns Hopkins University institutions, including neurotoxicologists and virologists from the Bloomberg School of Public Health and infectious disease specialists from the school of medicine, has found that organoids (tiny tissue cultures made from human cells that simulate whole organs) known as “mini-brains” can be infected by the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19.
The results, which suggest that the virus can infect human brain cells, were published online June 26, 2020, in the journal ALTEX: Alternatives to Animal Experimentation.
Early reports from Wuhan, China, the origin of the COVID-19 pandemic, have suggested that 36% of patients with the disease show neurological symptoms, but it has been unclear whether or not the virus infects human brain cells. In their study, the Johns Hopkins researchers demonstrated that certain human neurons express a receptor, ACE2, which is the same one that the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses to enter the lungs. Therefore, they surmised, ACE2 also might provide access to the brain.