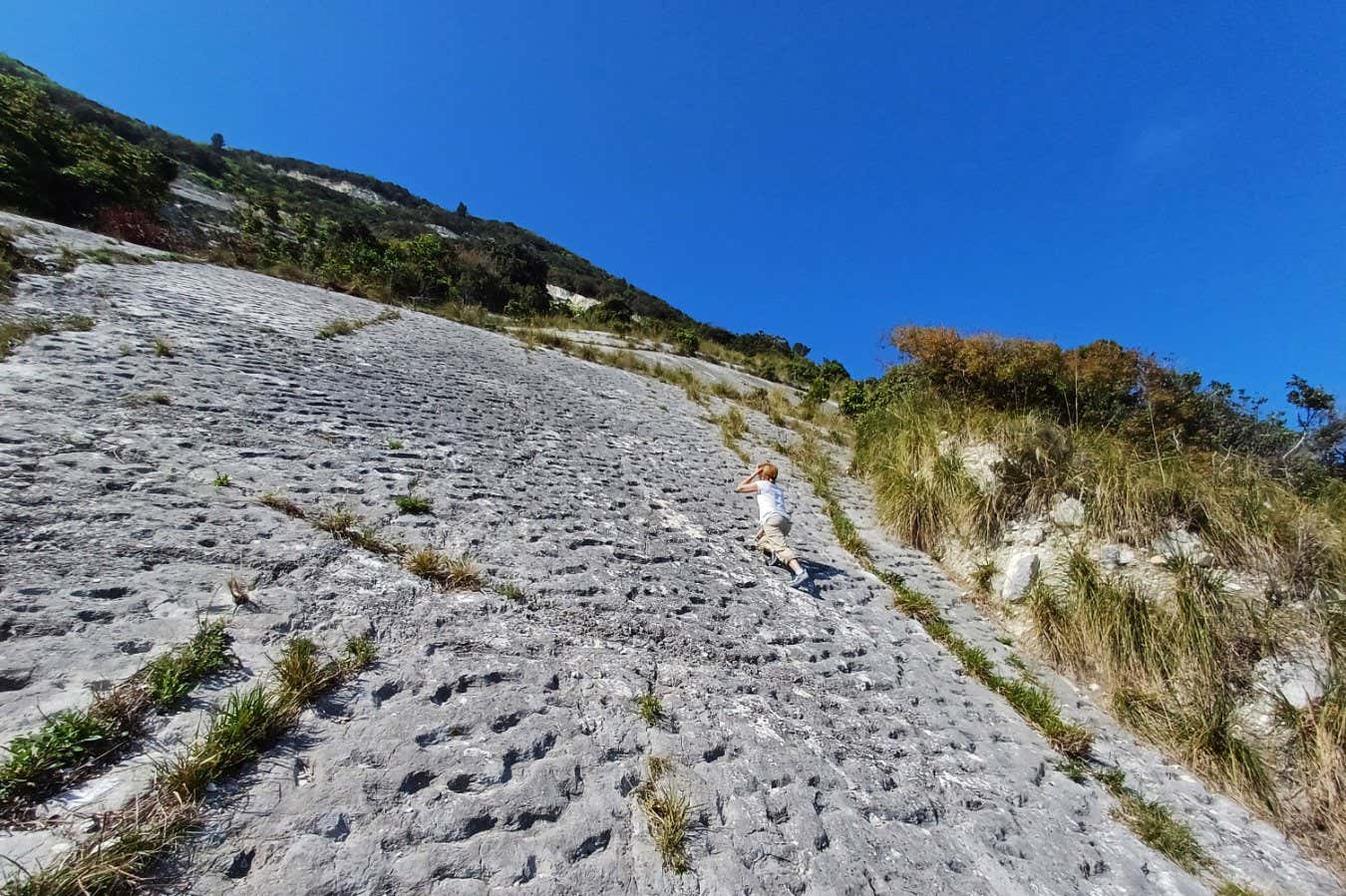
Around 1000 markings on a slab of rock that was once a seafloor during the Cretaceous period may have been made by sea turtle flippers and swiftly buried by an earthquake




Researchers discovered a new way to independently tune a nanoparticle’s speed and direction using different strength electric fields.
The new method could lead to better drug delivery technologies.
Read more.
A new method using a combination of strong and weak electric fields to change nanoparticle speed and direction could improve drug delivery and purification systems.
GLP-1 drugs have been transformative for treating obesity, but about 50 percent of patients who were prescribed this treatment ended up stopping due to severe side effects, such as nausea.
At the 2025 Society for Neuroscience meeting, experts presented new findings on how GLP-1 agonists’ action in the brain produced unwanted side effects and how these discoveries can guide future research.
Read more.
At the 2025 Society for Neuroscience meeting, scientists discussed the adverse side effects of GLP-1 agonists and new directions for future research.

Researchers at the University of Bamberg have traced a darkly intricate form of narcissism in sexually motivated male serial killers, reporting that many offenders combine brittle sensitivity with a craving for admiration and dominance leans on the killers’ own words from confessions and interrogations rather than psychiatric labels alone.
Serial killers have fascinated and frightened audiences for centuries, with media portrayals ranging from monstrous to romanticized. According to the FBI’s Serial Murder Symposium, serial murder involves the unlawful killing of two or more victims by the same offender in separate events.
For decades, many police and forensic teams have grouped serial killers into categories by motive: visionary killers driven by psychosis and hallucinations, thrill killers who pursue excitement and pleasure through killing, mission-oriented offenders who believe they must eliminate specific groups, power/control killers who seek total dominance over their victims, often including sexual abuse, and those whose crimes revolve around lust.
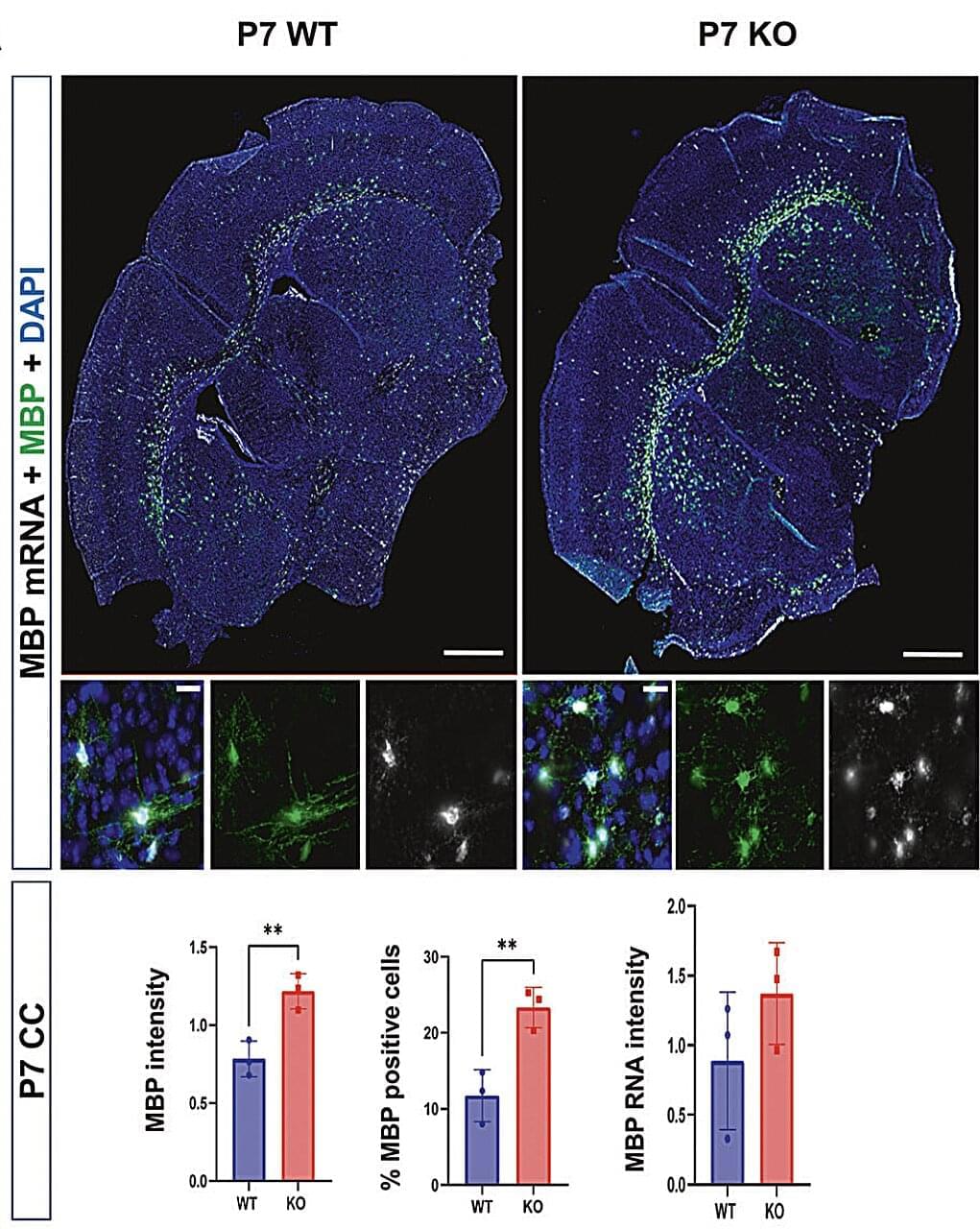
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by differences in communication, behavior and the processing of sensory information. Past research has shown that some individuals diagnosed with ASD exhibit specific genetic variants or differences in the regulation of genes.
In some patients, the Shank3 gene was found to be mutated, partially or fully deleted, or not expressed as much. This gene is known to support the creation of junctions at which connected neurons communicate with each other, known as synapses.
Past findings suggest that people diagnosed with ASD who exhibit variants in Shank3 also present abnormalities in the volume, structure and function of white matter. White matter is a brain region filled with a fatty substance known as myelin, which insulates nerves and allows signals to travel faster within the nervous system.
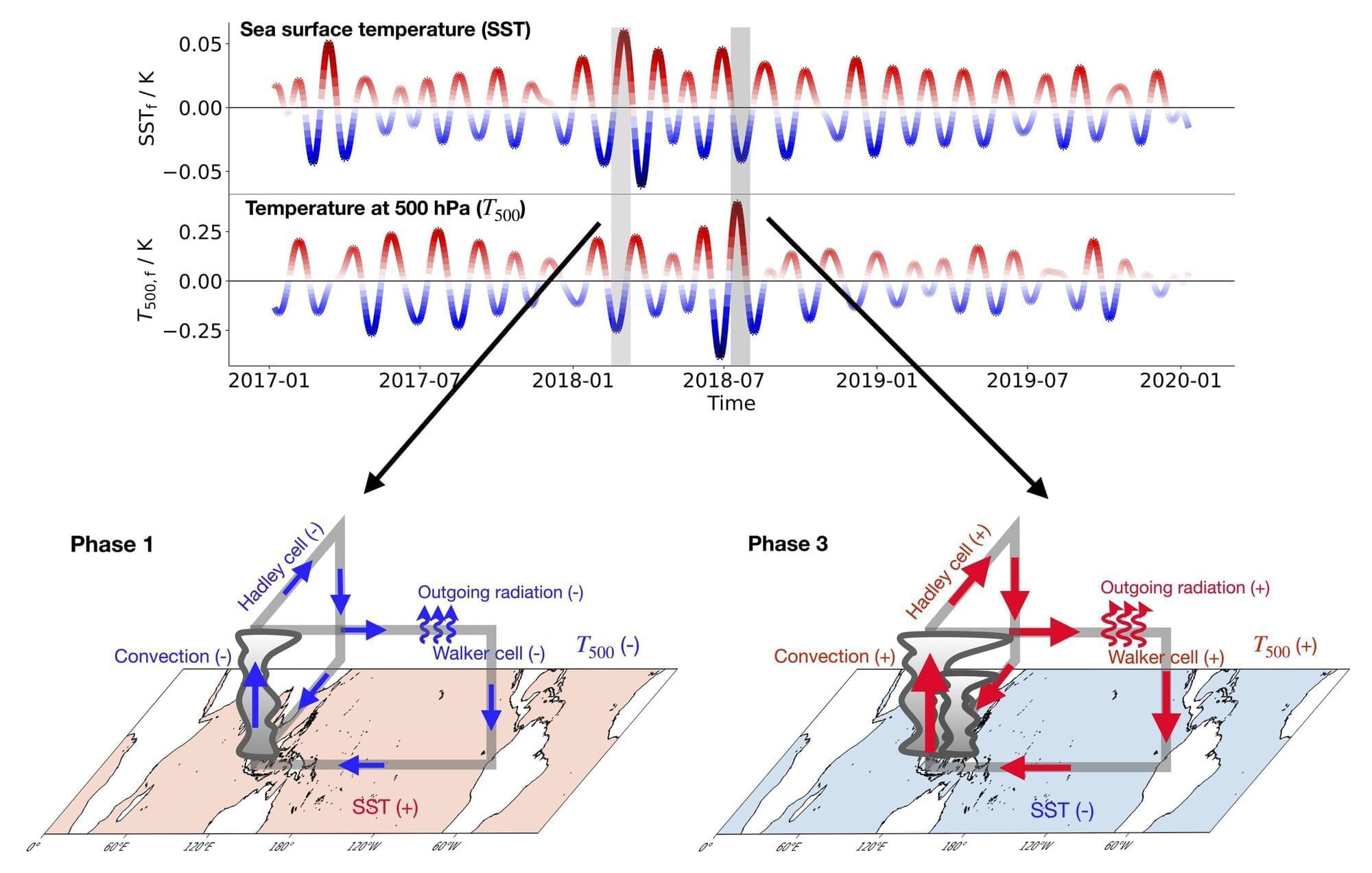
Tropical cyclones can unleash extensive devastation, as recent storms that swept over Jamaica and the Philippines made unmistakably clear. Accurate weather forecasts that buy more time to prepare are crucial for saving lives and are rooted in a deeper understanding of climate systems.
Driving this forward, researchers at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) and others have successfully identified a previously unknown cyclic climate pattern by historical reanalysis of datasets and satellite observations. The findings are published in PNAS.
Jiawei Bao still remembers coming home from middle school to catch the weather forecast on TV. It spanned from China’s northernmost province, Heilongjiang, to the southernmost province and tropical island, Hainan. In winter, the temperature between these regions can range from cold to balmy, varying by a staggering 50 degrees Celsius.

Despite continuous efforts to evaluate and predict changes in Earth’s climate, most models still struggle to accurately simulate extreme precipitation events. Models like the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phases 5 and 6 (CMIP5 and CMIP6) use fairly coarse resolution due to computing constraints, making it a little easier, faster and less expensive to run simulations, while still providing some degree of accuracy.
However, a new study, published in Nature Geoscience, is shedding light on some of the features missed by these coarser resolution models.
The team involved in the study developed a higher resolution model that breaks up the atmosphere into 10–25 km (6–15.5 mile) squares for analysis, instead of 100 km (62 mile) squares. Their high-resolution model is based on the Community Earth System Model v.1.3 (CESM-HR), which looks at the time period between 1920–2100. These results are then compared with the low-resolution version’s (CESM-LR) results.
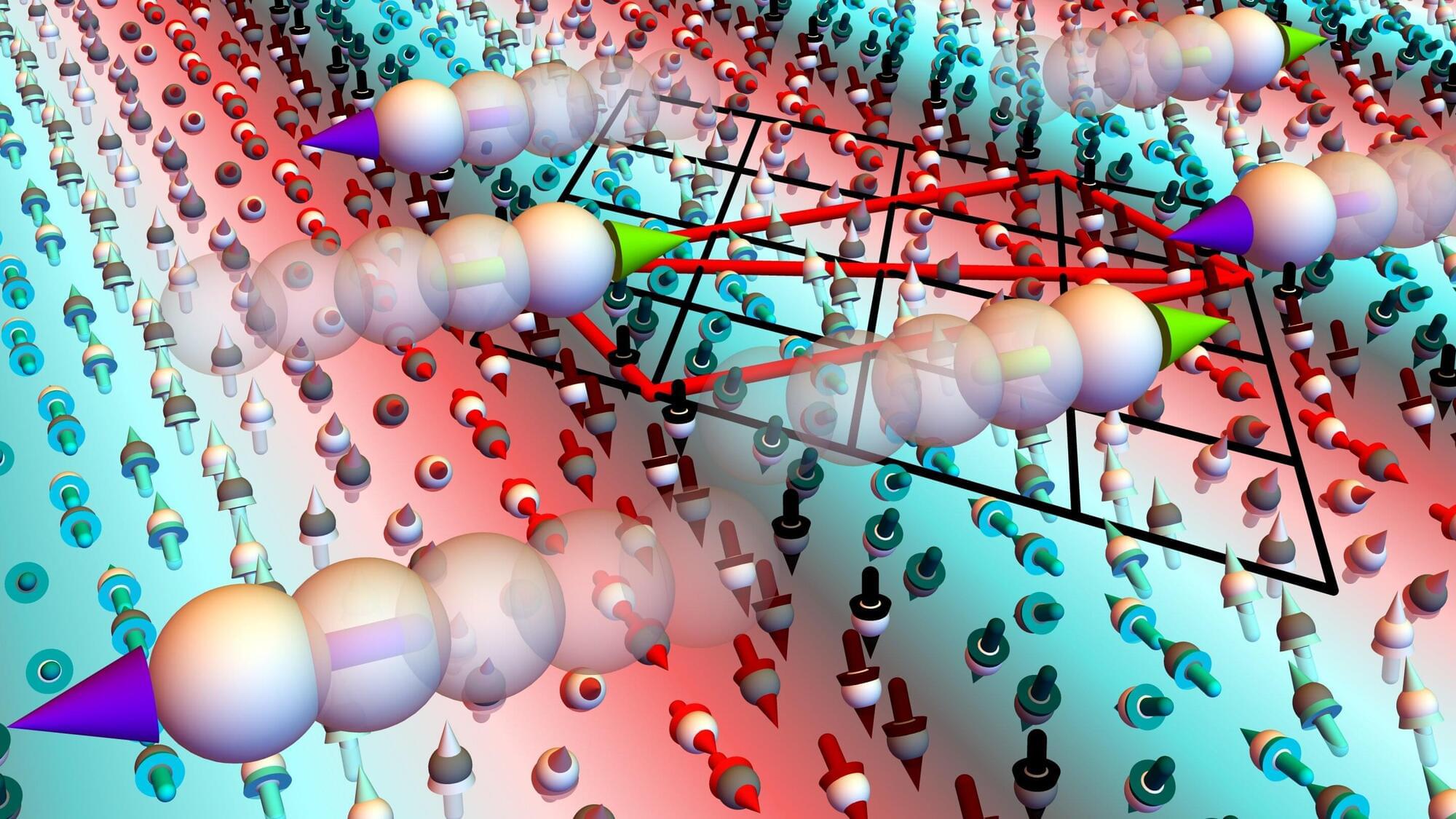
A novel magnetic material with an extraordinary electronic structure might allow for the production of smaller and more efficient computer chips in the future: the p-wave magnet. Researchers from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) were involved in its development.
The magnetic behavior in the interior of this material results from the way the electron spins arrange themselves—in the shape of a helix. Therefore, the electric current flowing through is deflected laterally. The results are published in Nature.
Magnetism, as we experience it every day, makes us usually think of materials such as iron, nickel, or cobalt that generate permanent magnetic fields or are attracted by magnetic forces. In these ferromagnetic materials, the spins, i.e. the moments of all electrons, move in the same direction.
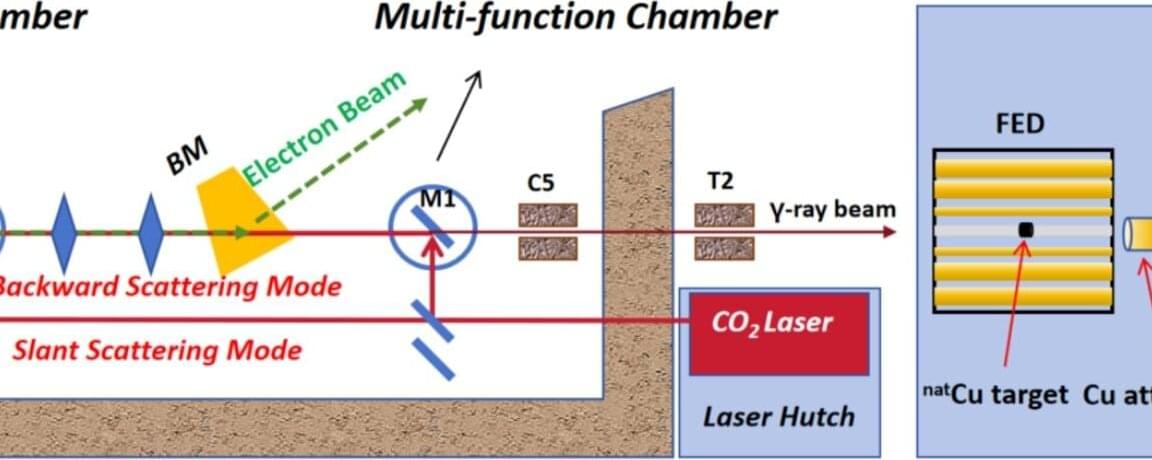
A joint research team has made important progress in the field of photoneutron cross section measurement. The team proposed a substitution measurement method that avoids the use of expensive and hard-to-prepare high-purity isotope targets, successfully measuring the 65 Cu(γ, n)64 Cu reaction cross section with high precision. This method only relies on natural copper (natCu) and previously measured copper-63 (63 Cu) data, without modifying experimental facility parameters, making it simple, efficient, and low-cost.
The related research results have been published in the journal Nuclear Science and Techniques. The team includes researchers from Henan Normal University, Shanghai Advanced Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and other institutions.