This is one type of problem that researchers think quantum computers will be better at compared to classical: simulating molecules.

COVID-19 is spreading in China at an alarming rate, infecting a massive number of people and causing numerous suspected deaths that can’t be verified by official sources. What the public can sense is that crematoriums in major cities are overwhelmed.
Have questions? Do you have something to share with us about China? We want to hear from you!
Email: [email protected].
Facebook www.facebook.com/EyesOnChina.
Your support allows us to produce more high-quality videos.
Consider donating at https://www.paypal.com/paypalme/ChinaInsights.
Copyright @ China Insights 2021. Any illegal reproduction of this content in any form will result in immediate action against the person(s) concerned.
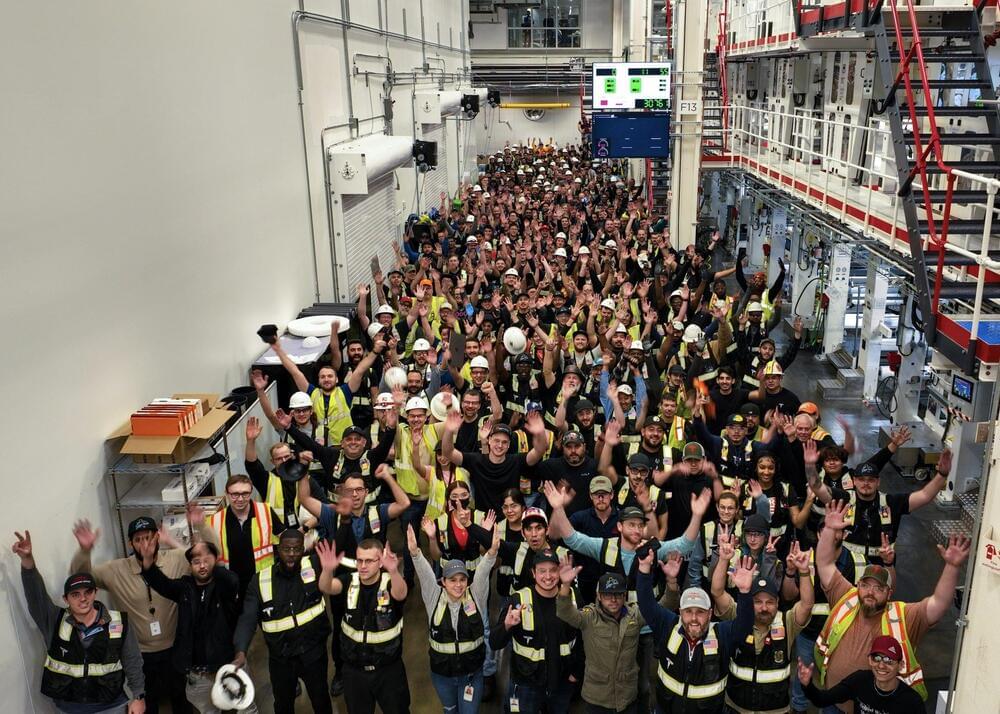

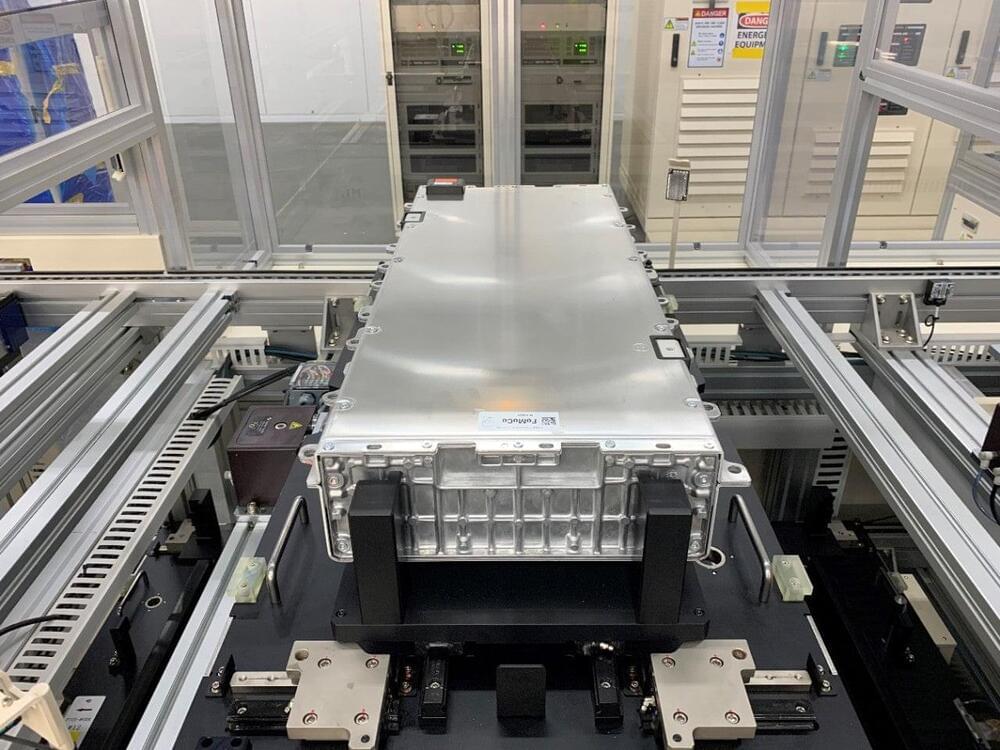
It appears that Tesla’s 4,680 battery cell production line is hitting its rhythm. As recently announced by the company, its 4,680 team has managed to build 868,000 cells in the last seven days. That’s roughly equal to the battery packs of over 1,000 electric vehicles.
Tesla announced the milestone on its official Twitter account. The EV maker highlighted its appreciation for its 4,680 team in its post, while also including a couple of photos of the teams behind the milestone. “Congrats to the 4,680 cell team on achieving 868k cells built in the last 7 days—equal to 1k+ cars!” Tesla wrote.
While producing enough cells for over 1,000 electric cars may seem like a minor achievement considering the scale of Tesla’s overall operations, the accomplishment was likely achieved with just the company’s initial 4,680 production lines. Tesla currently produces 4,680 cells in its pilot line at Kato Road, close to the Fremont Factory. Giga Texas also has a 4,680 line.
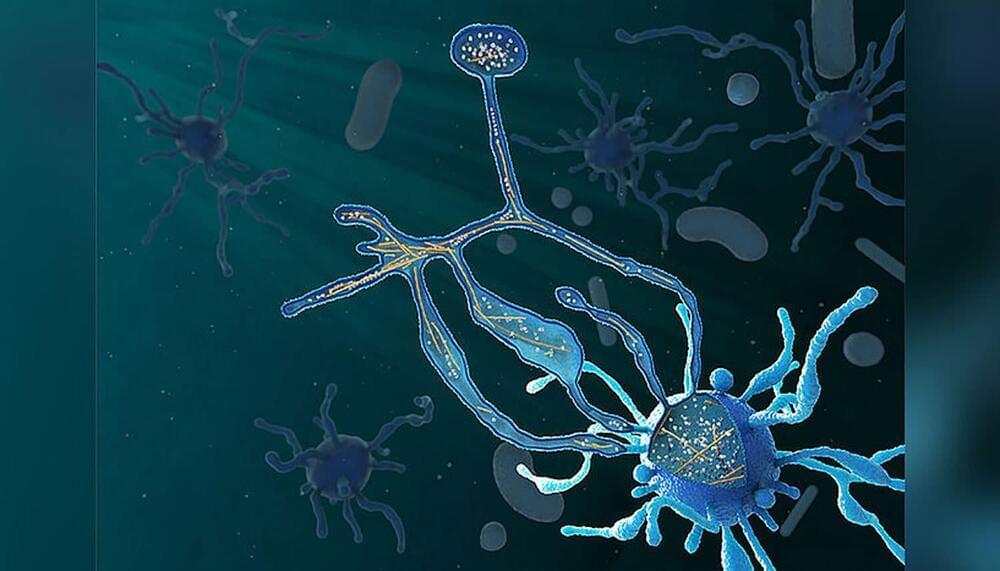
The Asgard archaea are thought to be the eukaryotes’ nearest living relatives. In their genomes, numerous eukaryotic signature proteins (ESPs) have sparked theories about how eukaryotic cells evolved. Although never proven, ESPs may play a part in developing intricate cytoskeletons and complicated cellular structures.
A collaboration between the working groups of Christa Schleper at the University of Vienna and Martin Pilhofer at ETH Zurich – shed light on the origin of the complex organisms on Earth. Scientists have successfully cultivated a special archaeon and characterized it more precisely using microscopic methods. This Asgard archaea member demonstrates distinct cellular traits and might serve as an evolutionary “missing link” to more complex living forms like mammals and plants.
Most current theories presuppose that archaea and bacteria were crucial in the development of eukaryotes. It is thought that a close relationship between archaea and bacteria about two billion years ago led to the evolution of the first eukaryotic primordial cell. On 2015, the so-called “Asgard archaea,” which in the tree of life represent the closest ancestors of eukaryotes, were found through genomic analyses of deep-sea environmental samples. A Japanese study revealed the first pictures of Asgard cells in 2020 using enrichment cultures.

Yet the notion that we inhabit a space with any mathematical structure is a radical innovation of Western culture, necessitating an overthrow of long-held beliefs about the nature of reality. Although the birth of modern science is often discussed as a transition to a mechanistic account of nature, arguably more important – and certainly more enduring – is the transformation it entrained in our conception of space as a geometrical construct.
Over the past century, the quest to describe the geometry of space has become a major project in theoretical physics, with experts from Albert Einstein onwards attempting to explain all the fundamental forces of nature as byproducts of the shape of space itself. While on the local level we are trained to think of space as having three dimensions, general relativity paints a picture of a four-dimensional universe, and string theory says it has 10 dimensions – or 11 if you take an extended version known as M-Theory. There are variations of the theory in 26 dimensions, and recently pure mathematicians have been electrified by a version describing spaces of 24 dimensions. But what are these ‘dimensions’? And what does it mean to talk about a 10-dimensional space of being?

After the release of The Jazz Singer in 1927, all bets were off for live musicians who played in movie theaters. Thanks to synchronized sound, the use of live musicians was unnecessary — and perhaps a larger sin, old-fashioned. In 1930 the American Federation of Musicians formed a new organization called the Music Defense League and launched a scathing ad campaign to fight the advance of this terrible menace known as recorded sound.
The evil face of that campaign was the dastardly, maniacal robot. The Music Defense League spent over $500,000, running ads in newspapers throughout the United States and Canada. The ads pleaded with the public to demand humans play their music (be it in movie or stage theaters), rather than some cold, unseen machine. A typical ad read like this one from the September 2, 1930 Syracuse Herald in New York:
Tho’ the Robot can make no music of himself, he can and does arrest the efforts of those who can.

We live in an amazing age. New medicines, therapies, and treatments come out every day that help people live happier, more meaningful lives. Things are moving so fast it can be hard to keep up. That’s why I follow futurists like Ray Kurzweil who sift through all these innovations. They make it easier for regular people like me to live happier and healthier lives.
Learn from Ray Kurzweil how to easily improve your health and increase your productive lifespan so you can be happier and more fulfilled.

Movie plots often use holograms to give the scene a scientific or cooler essence. However, researchers have made these futuristic scenes a reality. According to reports, Scientists in China showcased a laser that can create Chinese characters out of thin air.
Although lasers often have a long-range, you can only see them when the light lands on a surface. However, dust particles made an exception. But this is entirely different and looks like something out of a sci-fi movie.
Scientists have already used lasers to create a range of optical illusions. However, it required mediums like dust and clouds to do so. But according to reports, with the new device, researchers are able to draw patterns using ultra-short laser pulses.