The gamma ray burst is the brightest ever detected in X-rays, according to scientists, and could shed light on the most energetic phenomena in space.
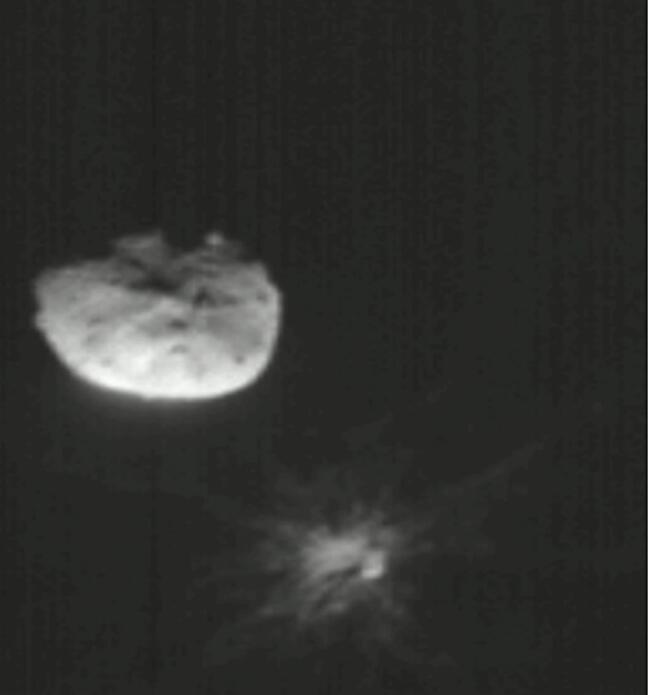
Analysis of data obtained over the past two weeks by NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) investigation team shows the spacecraft’s kinetic impact with its target asteroid, Dimorphos, successfully altered the asteroid’s orbit. This marks humanity’s first time purposely changing the motion of a celestial object and the first full-scale demonstration of asteroid deflection technology. Images such as the below helped scientists understand the orbit change resulting from DART’s impact.
Bull’s-eye: NASA’s DART craft successfully changed the orbit of the asteroid Dimorphos by colliding into the rocky body two weeks ago, according to the space agency.
The test shows humanity has the capability to stop an asteroid from hitting the planet, NASA administrator Bill Nelson said in a Tuesday press conference (Opens in a new window). “If an Earth-threatening asteroid was discovered, and we can see it far enough away, this technique could be used to deflect it,” he added.
The DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) was a spacecraft about the size of a refrigerator. When it collided with Dimorphos on September 26th, it was traveling at 14,000 miles per hour, which caused a noticeable impact that telescopes and radar images were able to capture.
Scientists ‘Blown Away’
Posted in genetics, neuroscience
The brain’s ability to adapt and rewire itself throughout life continues to surprise neuroscientists. Researchers have found a way to restore sight in adult mice with a form of congenital blindness, in spite of the rodents’ relative maturity.
The mice were modeling a rare human disorder of the eye’s retina, called leber congenital amaurosis (LCA), which often causes blindness or severe visual impairment at birth.
This inherited condition seems to be caused by a mutation in any one of dozens of genes associated with the retina and its light-sensing abilities.
QNTYM Railway is a ‘software level’ application that can be deployed on current hardware meaning there will be no need for changes in physical network infrastructure (hardware). The QNTYM Railway is an inherently quantum secure, self-defending, resilient, digital infrastructure capable of lightning-fast speed with a significant sustainability proposition. From a command & control standpoint, the QNTYM Railway is also integrated with leading vendors where users can benefit from having threat intel, vulnerability, device & incident response management capabilities all automated and in one place, hence reducing complexity.
In terms of speed, the QNTYM Railway has demonstrated consistent throughput speeds of 350+ Mbit/s, (and above). The QNTYM Railway provides integration and interoperability that is in a class of its own allowing technology to reach new levels. For the past year, QDEx Labs has been stress-assessing the QNTYM Railway across three interconnected cloud environments (AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure); they found that not only are they consistently experiencing the minimum requirement of 250 Mbit/s for 8k video streaming, but they are also, in fact, recording data streams reaching 3 to 4 times that amount with little to no processor load and added latencies in the microsecond (NOT millisecond) range.
The bottom line is that this architecture has now proven capable of hosting an ultra-realistic 3D metaverse. Results like these are something that Web3 and Metaverse projects currently lack and will require.
Michael Levin is a developmental and synthetic biologist at Tufts University, where he is the Vannevar Bush Distinguished Professor of biology. He is a director of the Allen Discovery Center, director at the Tufts Center for Regenerative and Developmental Biology, and principal investigator at the Levin Lab.
0:00 intro.
1:38 bioelectricity and developmental biology.
7:56 memory and conditioning in GRNs.
11:50 is there a privileged cognitive substrate?
13:55 Godel type limits.
15:45 multi-scale competency architecture.
25:12 intelligence.
27:00 conceptual framework for cognition.
29:45 does cognition bottom out somewhere?
36:47 synthetic cognition.
39:23 sci-fi that captures this well.
45:16 consciousness, hard problem, and the consciousness of development.
51:09 where does the self come from?
54:06 how do different emergent levels interact.
56:50 top-down causality.
1:02:28 where do goals come from?
1:07:06 balancing conceptual and empirical work.
Michael Levin’s Website:
https://ase.tufts.edu/biology/labs/levin/
Podcast.
Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/0dUBLTl6qzOfA0xMndLFzq.
Google: https://www.google.com/podcasts?feed=aHR0cHM6Ly9mZWVkcy5yZWR…FhMw%3D%3D
Apple: https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast/thing-in-it-self/id1616881426
Amazon: https://music.amazon.ca/podcasts/9c6c08b2-e975-47d6-a897…in-it-self.
Social.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/thinginitself__
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/thinginitself.pod/
Humans managed to alter an asteroid’s path through space.
NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) successfully moved an asteroid, space agency officials confirmed on Tuesday, October 11.
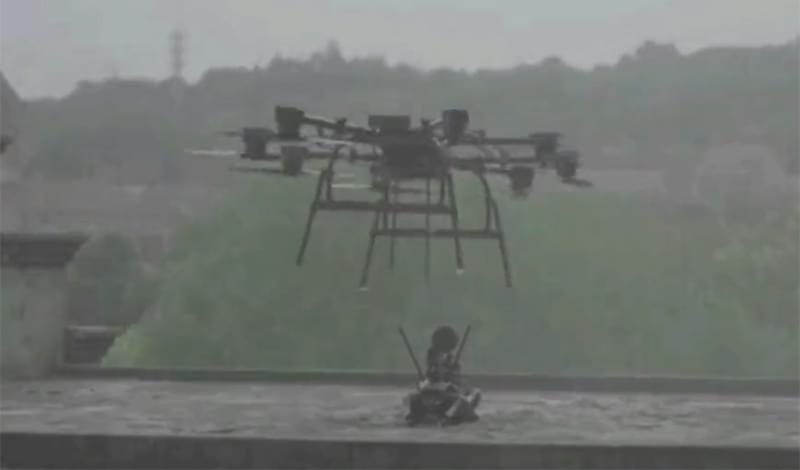
It’s unclear what “Blood-Wing” in the top-right corner refers to, but the drone itself is called Red Wing. According to the description, this small aerial vehicle could travel to a weak point behind the enemy lines and perform a “surprise attack” by deploying the robot dog. In one envisioned scenario, this four-legged machine “can be placed on the roof of the enemy to occupy the commanding heights to suppress firepower.”
Mounted on its back is what appears to be a Chinese QBB-97 (designated as Type 95 LGM in the United States). This 5.8 mm light support weapon can fire up to 650 rounds a minute.
No further specifications have been made available, but the drone and robodog pairing seems designed primarily for use in urban environments that are notoriously difficult for human foot soldiers to infiltrate. It could, for example, be used to scout ahead, take out hard-to-access targets or create a diversion. Kestrel Defence explains that ground troops, supported from above, could conduct “a three-dimensional pincer attack on the enemy in the building.”
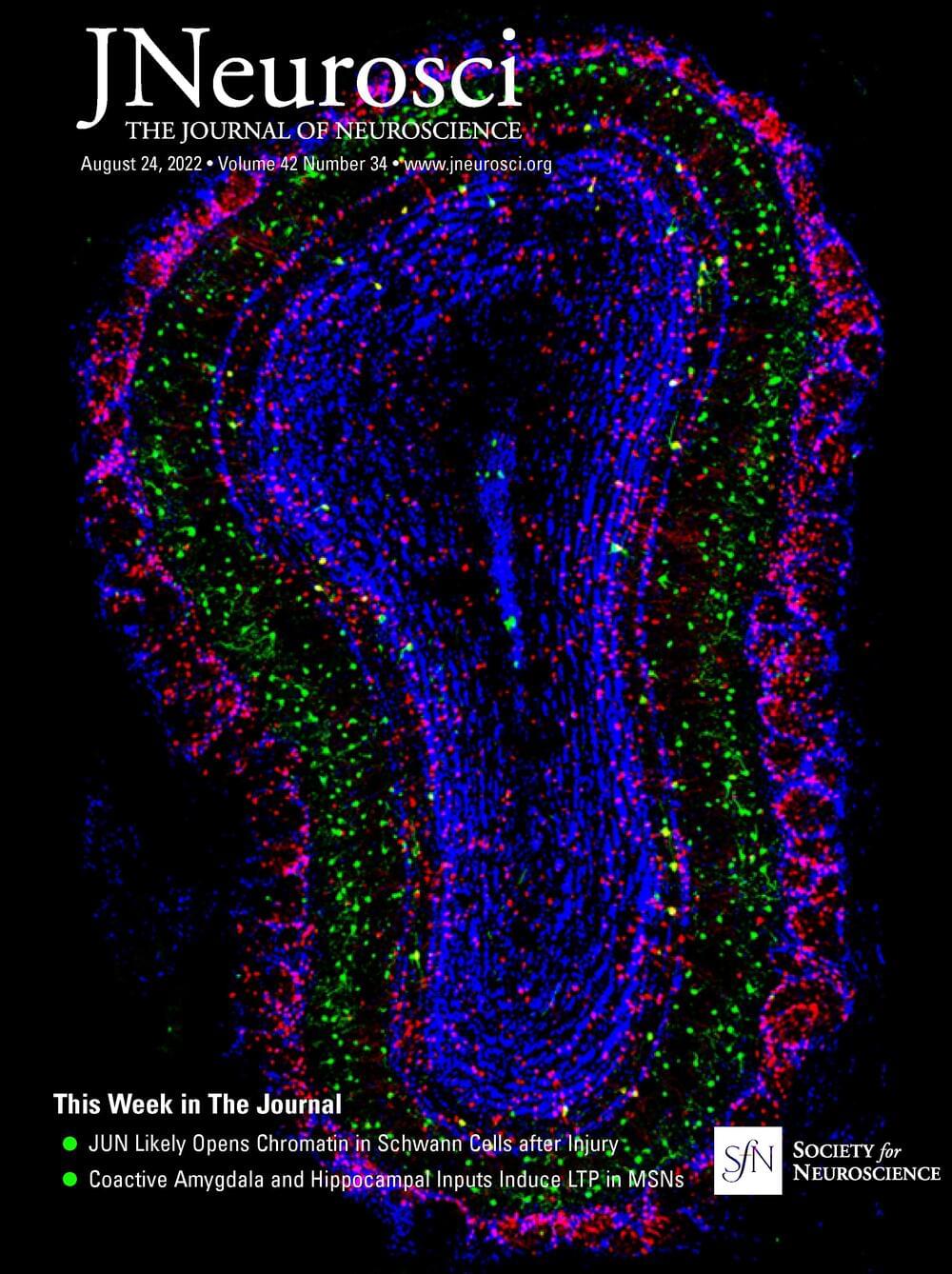
Large glutamatergic, somatic synapses mediate temporally precise information transfer. In the ventral nucleus of the lateral lemniscus, an auditory brainstem nucleus, the signal of an excitatory large somatic synapse is sign inverted to generate rapid feedforward inhibition with high temporal acuity at sound onsets, a mechanism involved in the suppression of spurious frequency information. The mechanisms of the synaptically driven input–output functions in the ventral nucleus of the lateral lemniscus are not fully resolved. Here, we show in Mongolian gerbils of both sexes that, for stimulation frequencies up to 200 Hz, the EPSC kinetics together with short-term plasticity allow for faithful transmission with only a small increase in latency. Glutamatergic currents are exclusively mediated by AMPARs and NMDARs. Short-term plasticity is frequency-dependent and composed of an initial facilitation followed by depression. Physiologically relevant output generation is limited by the decrease in synaptic conductance through short-term plasticity (STP). At this endbulb synapse, STP acts as a low pass filter and increases the dynamic range of the conductance dependent input–output relation, while NMDAR signaling slightly increases the sensitivity of the input–output function. Our computational model shows that STP-mediated filtering limits the intensity dependence of the spike output, thus maintaining selectivity to sound transients. Our results highlight the interaction of cellular features that together give rise to the computations in the circuit.
SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Auditory information processing in the brainstem is a prerequisite for generating our auditory representation of the environment. Thereby, many processing steps rely on temporally precise filtering. Precise feedforward inhibition is a key motif in auditory brainstem processing and produced through sign inversion at several large somatic excitatory synapses. A particular feature of the ventral nucleus of the lateral lemniscus is to produce temporally precise onset inhibition with little temporal variance independent of sound intensity. Our cell-physiology and modeling data explain how the synaptic characteristics of different current components and their short-term plasticity are tuned to establish sound intensity-invariant onset inhibition that is crucial for filtering out spurious frequency information.
Did you miss a session from MetaBeat 2022? Head over to the on-demand library for all of our featured sessions here.
The software supply chain is not linear or simplistic: It is made up of many different components introduced at different times and in different phases.
And, today’s software supply chains only continue to grow in complexity — a mix of proprietary, open-source and third-party code, configurations, binaries, libraries, plugins and other dependencies.