If it’s true that robots are taking our jobs, they should also be able to take out the trash and clean the bathroom for us.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Origins of Life: Inevitable or a Toss of the Dice?
How can we start with a mix of rocks, gases, and water and end up with life?Speaker: Dr. Zachary Adam, Kacar Research Group, Univ. of Wisconsin-Madison.

Through the eye of the beholder: Researchers find people with autism process illusory shapes differently
There is this picture—you may have seen it. It is black and white and has two silhouettes facing one another. Or maybe you see the black vase with a white background. But now, you likely see both.
It is an example of a visual illusion that reminds us to consider what we did not see at first glance, what we may not be able to see, or what our experience has taught us to know—there is always more to the picture or maybe even a different image to consider altogether. Researchers are finding the process in our brain that allows us to see these visual distinctions may not be happening the same way in the brains of children with autism spectrum disorder. They may be seeing these illusions differently.
“How our brain puts together pieces of an object or visual scene is important in helping us interact with our environments,” said Emily Knight, MD, Ph.D., assistant professor of Neuroscience and Pediatrics at the University of Rochester Medical Center, and first author on a study out today in the Journal of Neuroscience. “When we view an object or picture, our brains use processes that consider our experience and contextual information to help anticipate sensory inputs, address ambiguity, and fill in the missing information.”
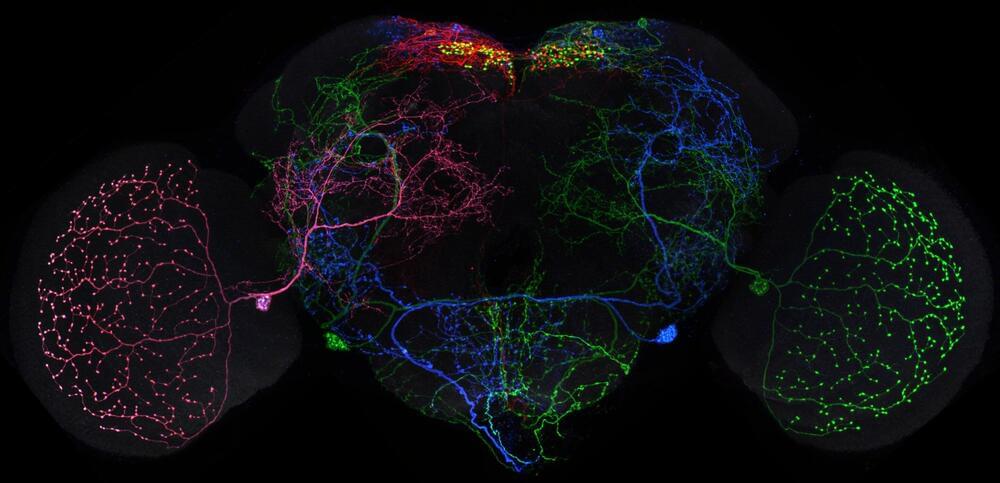
Team releases 74,000 fruit fly brain images for neuroscience research
Neuroscience research just got a little bit easier, thanks to the release of tens of thousands of images of fruit fly brain neurons generated by Janelia’s FlyLight Project Team.
Over eight years, the FlyLight Project Team and collaborators dissected, labeled, and imaged the neurons of more than 74,000 fruit fly brains, taken from more than 5,000 different genetically modified fly strains.
Now, these images are being made freely available, enabling scientists to quickly and easily find the neurons they need to test theories about how the nervous system works.
Just when we thought we were safe, ChatGPT is coming for our graphics cards
This sounds a lot like cryptomining but it also doesn’t. Cryptomining has nothing to do with machine learning algorithms and, unlike machine learning, cryptomining’s only value is producing a highly speculative digital commodity called a token that some people think is worth something and so are willing to spend real money on it.
This gave rise to a cryptobubble that drove a shortage of GPUs over the past two years when cryptominers bought up all the Nvidia Ampere graphics cards from 2020 through 2022, leaving gamers out in the cold. That bubble has now popped, and GPU stock has now stabilized.
But with the rise of ChatGPT, are we about to see a repeat of the past two years? It’s unlikely, but it’s also not out of the question either.
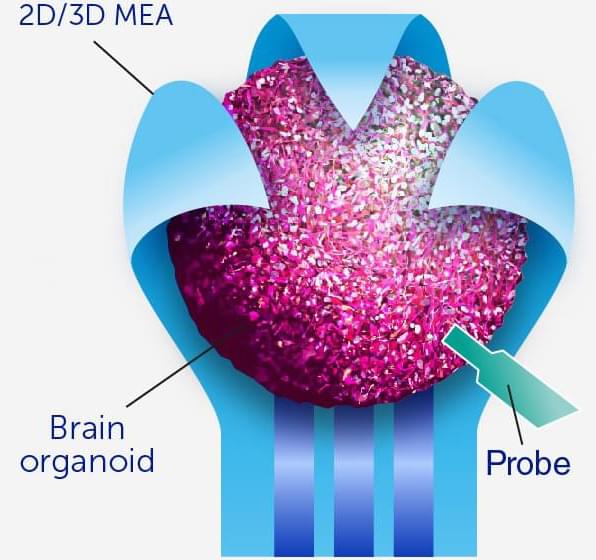
Organoid intelligence could greatly boost AI processing power with human brain cells
Everyone is now scrambling to integrate AI with as many facets of human life as possible. Neural nets and machine learning can offer greatly improved processing speeds, yet these aspects still rely on digital pathways that may never fully mimic the biological structure of the human brain. The next step in AI improvement would be to combine the best of both the digital world and the biological world. Some scientists are already experimenting with this possibility, as a new article published in the academic journal Frontiers of Science is deep diving into the realm of biocomputers and organoid intelligence (OI).
All AI applications today rely on computing power provided by powerful CPUs or GPUs. OI, on the other hand, is seeking to bring “unprecedented advances in computing speed, processing power, data efficiency and storage capabilities” by harnessing the complexity of lab-grown cell-cultures repurposed from adult skin cells that consist of 3D clusters of neurons and other brain cells.
From physics to mind — Prof. Michael Levin
From physics to mind: the journey of cognition seen through the lens of embryonic development // Prof. Michael Levin (Tufts University)
Life Perceives is a symposium bringing together scientists and artists for an open exploration of how “perception” can be understood as a phenomenon that does not only belong to humans, or even the so-called “higher organisms”, but exists across the entire spectrum of life in a myriad of forms.
The programme can be found here: https://lifeperceives.org/programme.
The symposium invites leading practitioners from the arts and sciences to present unique insights through short talks, open discussions, and artistic interventions that bring us slightly closer to the life worlds of plants and fungi, microbial communities and immune systems, cuttlefish and crows.
What do we mean when we talk about perception in other species? Do other organisms have an experience of the world? Or does our human-centred perspective make understanding other forms of life on their own terms an impossible dream? Whatever your answers to these questions may be, we hope to unsettle them, and leave you more curious than when you arrived.
The symposium will be accompanied by a photography exhibition by award-winning photographer Irina Petrova Adamatzky, and an installation, The Sentinel Self, by Danish artist Sissel Marie Tonn in the Jane Attenborough Studio.
Physics of Superpropulsion: Super-Fast Sharpshooter Insect Urination Using a “Butt Flicker”
Tiny insects known as sharpshooters excrete by catapulting urine drops at incredible accelerations. Their excretion is the first example of superpropulsion discovered in a biological system.
Saad Bhamla was in his backyard when he noticed something he had never seen before: an insect urinating. Although nearly impossible to see, the insect formed an almost perfectly round droplet on its tail and then launched it away so quickly that it seemed to disappear. The tiny insect relieved itself repeatedly for hours.
It’s generally taken for granted that what goes in must come out, so when it comes to fluid dynamics in animals, the research is largely focused on feeding rather than excretion. But Bhamla, an assistant professor in the School of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the Georgia Institute of Technology (Georgia Tech), had a hunch that what he saw wasn’t trivial.
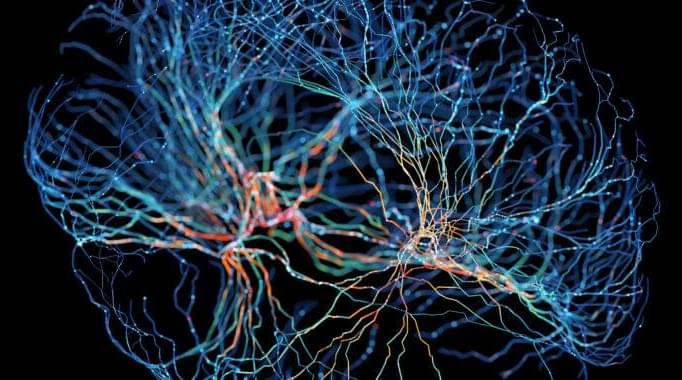
Is the future of computing biological?
Trying to make computers more like human brains isn’t a new phenomenon. However, a team of researchers from Johns Hopkins University argues that there could be many benefits in taking this concept a bit more literally by using actual neurons, though there are some hurdles to jump first before we get there.
In a recent paper, the team laid out a roadmap of what’s needed before we can create biocomputers powered by human brain cells (not taken from human brains, though). Further, according to one of the researchers, there are some clear benefits the proposed “organoid intelligence” would have over current computers.
“We have always tried to make our computers more brain-like,” Thomas Hartung, a researcher at Johns Hopkins University’s Environmental Health and Engineering department and one of the paper’s authors, told Ars. “At least theoretically, the brain is essentially unmatched as a computer.”