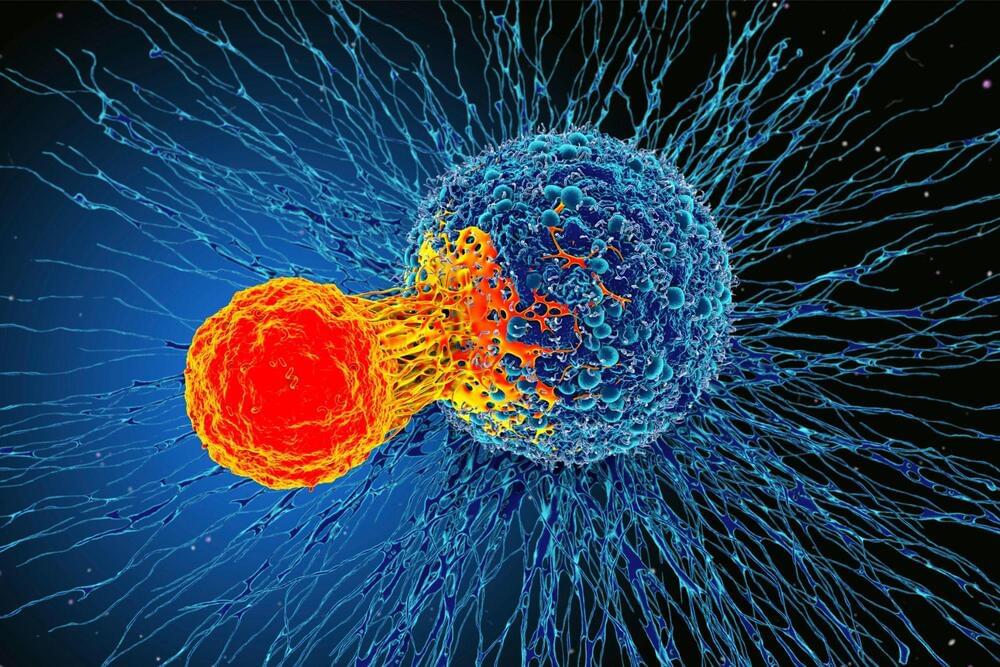
Scientists at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) and IBM Research have created a virtual library of thousands of “command sentences” for cells using machine learning. These “sentences” are based on combinations of “words” that direct engineered immune cells to find and continuously eliminate cancer cells.
This research, which was recently published in the journal Science, is the first time that advanced computational techniques have been applied to a field that has traditionally progressed through trial-and-error experimentation and the use of pre-existing molecules rather than synthetic ones to engineer cells.
The advance allows scientists to predict which elements – natural or synthesized – they should include in a cell to give it the precise behaviors required to respond effectively to complex diseases.