Year 2017 😗😁
Artificial-intelligence program AlphaGo Zero trained in just days, without any human input.
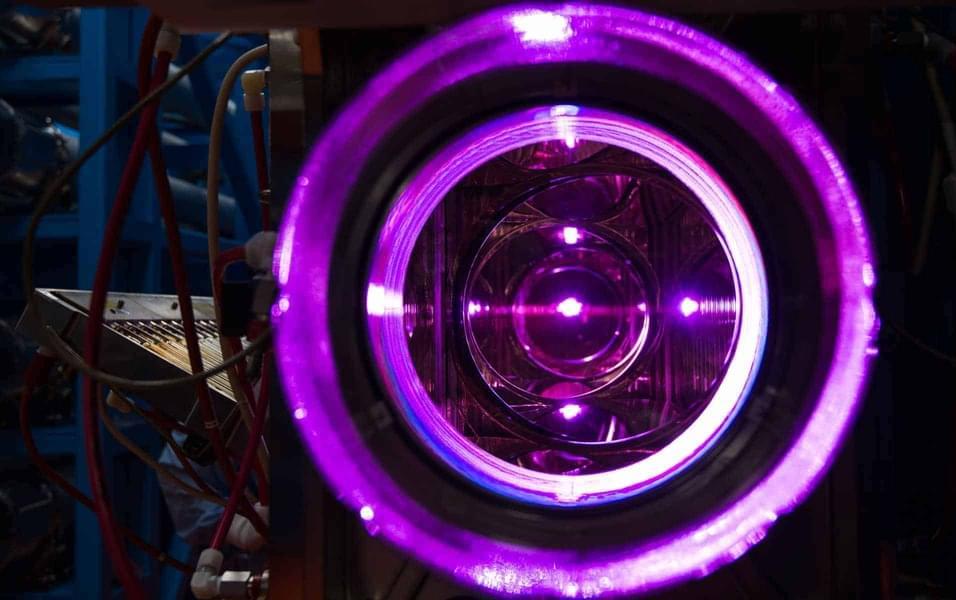



Scientists achieved ignition at the National Ignition Facility at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in December 2022. However, there are still many obstacles to overcome before fusion energy is technically and economically feasible for widespread production and use.
Researchers at the University of Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE) have, for the first time, experimentally demonstrated a method called dynamic shell formation, which may help achieve the goal of creating a fusion power plant.

Physicists at Harvard University in the US have created a novel strongly interacting quantum liquid known as a Laughlin state in a gas of ultracold atoms for the first time. The state, which is an example of a fractional quantum Hall (FQH) state, had previously been seen in condensed-matter systems and in photons, but observations in atoms had been elusive due to stringent experimental requirements. Because atomic systems are simpler than their condensed-matter counterparts, the result could lead to fresh insights into fundamental physics.
“Some of the most intriguing phenomena in condensed-matter physics emerge when you confine electrons in two dimensions and apply a strong magnetic field,” explains Julian Léonard, a postdoctoral researcher in the Rubidium Lab at Harvard and the lead author of a paper in Nature on the new work. “For example, the particles can behave collectively as if they have a charge that is only a fraction of the elementary charge – something that does not occur anywhere else in nature and is even ruled out by the Standard Model for all fundamental particles.”
The way in which such fractional charges arise is still not fully understood because it is difficult to study solid-state systems at an atomic scale. This is why it is so desirable to study the behaviour of FQHs in synthetic quantum systems such as cold atoms, which act as quantum simulators for more complex condensed-matter phenomena.
Flying cars are becoming closer to reality than what sci-fi movies may lead you to believe. Another electric flying car “took flight” this week in the US. CEO Doron Merdinger of Miami-based Doroni Aerospace successfully piloted a two-seater personal vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft that fits in your garage.
Electric flying cars are all of a sudden taking the US by storm. Last month, California-based Alef Aeronautics revealed its 100% electric flying car, “Model A,” the first of its kind to receive legal approval to fly from the US government.
According to Alef, the Model A has a 200-mile driving range and can fly for 110 miles. The company says it had gathered over 440 orders for its $300K electric flying car within three months.

Our universe could be twice as old as current estimates, according to a new study that challenges the dominant cosmological model and sheds new light on the so-called “impossible early galaxy problem.”
The work is published in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
“Our newly-devised model stretches the galaxy formation time by a several billion years, making the universe 26.7 billion years old, and not 13.7 as previously estimated,” says author Rajendra Gupta, adjunct professor of physics in the Faculty of Science at the University of Ottawa.
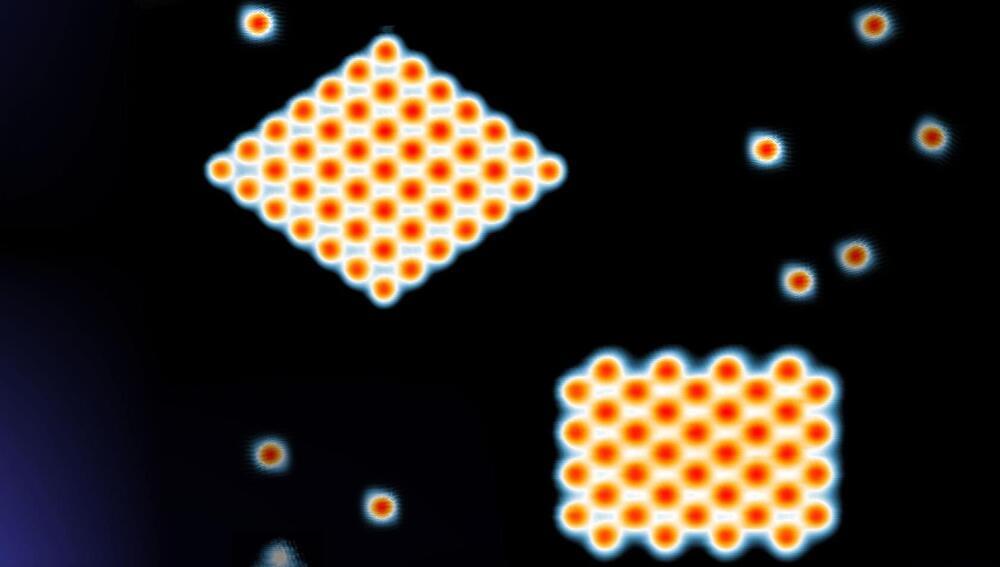
The future of electronics will be based on novel kinds of materials. Sometimes, however, the naturally occurring topology of atoms makes it difficult for new physical effects to be created. To tackle this problem, researchers at the University of Zurich have now successfully designed superconductors one atom at a time, creating new states of matter.
What will the computer of the future look like? How will it work? The search for answers to these questions is a major driver of basic physical research. There are several possible scenarios, ranging from the further development of classical electronics to neuromorphic computing and quantum computers.
The common element in all these approaches is that they are based on novel physical effects, some of which have so far only been predicted in theory. Researchers go to great lengths and use state-of-the-art equipment in their quest for new quantum materials that will enable them to create such effects. But what if there are no suitable materials that occur naturally?

The Death of Death: The Scientific Possibility of Physical Immortality and its Moral Defense (Copernicus Books) — Kindle edition by Cordeiro, José, Wood, David. Download it once and read it on your Kindle device, PC, phones or tablets. Use features like bookmarks, note taking and highlighting while reading The Death of Death: The Scientific Possibility of Physical Immortality and its Moral Defense (Copernicus Books).
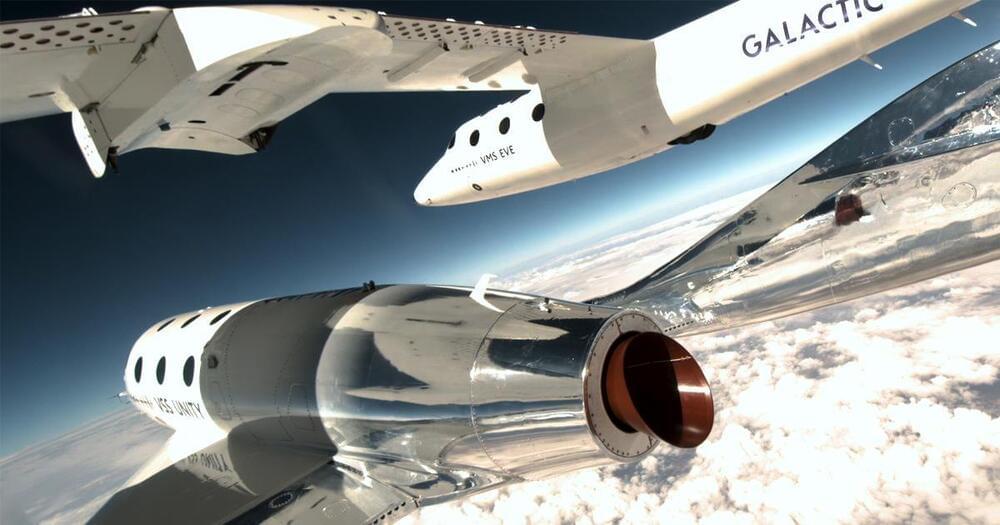

Now that Virgin Galactic has flown its first commercial spaceflight, it’s ready to take civilians aboard. The company now expects to launch its first private passenger flight, Galactic 2, as soon as August 10th. Virgin isn’t yet revealing the names of everyone involved, but there will be three passengers alongside the usual crew. You can watch a live stream on the company website.
The inaugural commercial flight, Galactic 1, flew in late June. However, all three passengers were Italian government workers (two from the Air Force and one research council member) conducting microgravity studies. While it’s not clear what 02’s civilian crew will do, they can be tourists this time around.
The firm has been ramping up its operations in recent months after numerous delays from previous years. While Galactic 2 is just Virgin’s seventh spaceflight of any kind, it’s the third in 2023. The company says it’s establishing a “regular cadence” of flights, and you can expect them to become relatively routine if this voyage goes as planned.