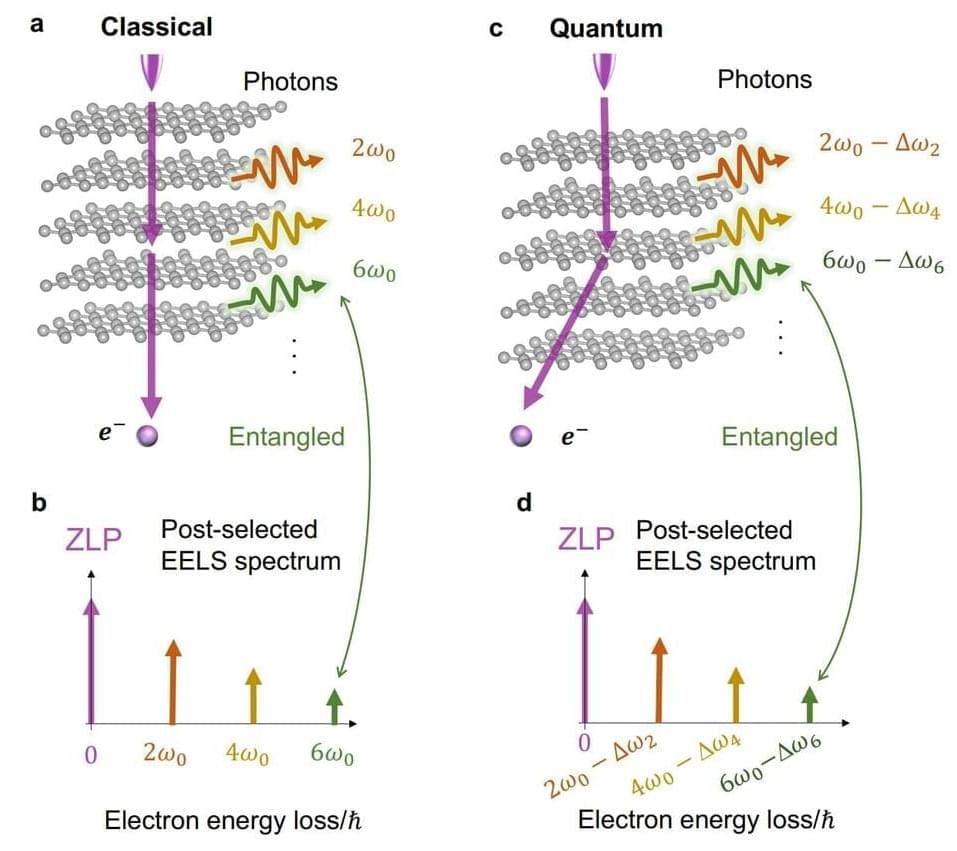
For the first time since it was proposed more than 80 years ago, scientists from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have demonstrated the phenomenon of “quantum recoil,” which describes how the particle nature of light has a major impact on electrons moving through materials. The research is published online today (January 19) in the journal Nature Photonics.
Making quantum recoil a practical reality should eventually allow businesses to more accurately produce X-rays of specific energy levels, leading to superior accuracy in healthcare and manufacturing applications such as medical imaging and flaw detection in semiconductor chips.
Quantum recoil was theorized by Russian physicist and Nobel laureate Vitaly Ginzburg in 1940 to accurately account for radiation emitted when charged particles like electrons move through a medium, such as water, or materials with repeated patterns on the surface, including those on butterfly wings and graphite.