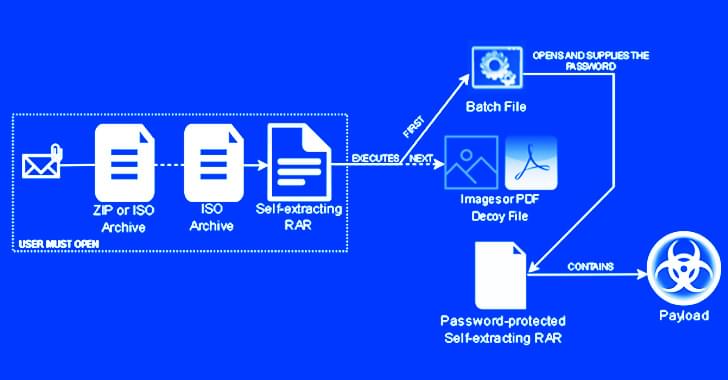
The notorious Emotet botnet has been linked to a new wave of malspam campaigns that take advantage of password-protected archive files to drop CoinMiner and Quasar RAT on compromised systems.
In an attack chain detected by Trustwave SpiderLabs researchers, an invoice-themed ZIP file lure was found to contain a nested self-extracting (SFX) archive, the first archive acting as a conduit to launch the second.
While phishing attacks like these traditionally require persuading the target into opening the attachment, the cybersecurity company said the campaign sidesteps this hurdle by making use of a batch file to automatically supply the password to unlock the payload.