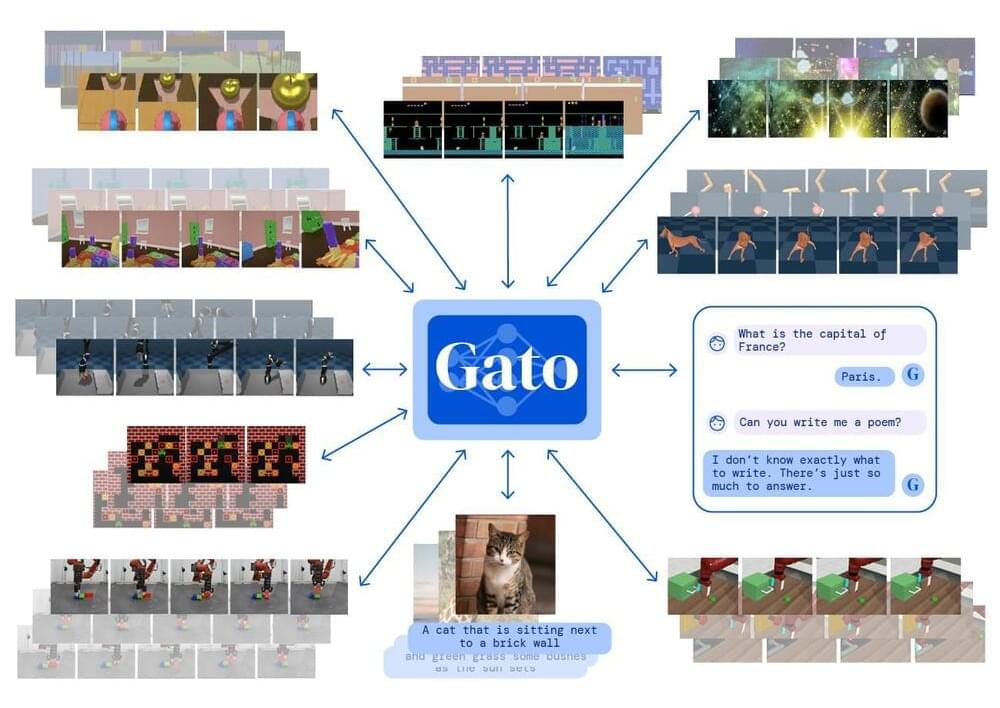
Inspired by progress in large-scale language modelling, we apply a similar approach towards building a single generalist agent beyond the realm of text outputs. The agent, which we refer to as Gato, works as a multi-modal, multi-task, multi-embodiment generalist policy. The same network with the same weights can play Atari, caption images, chat, stack blocks with a real robot arm and much more, deciding based on its context whether to output text, joint torques, button presses, or other tokens.
During the training phase of Gato, data from different tasks and modalities are serialised into a flat sequence of tokens, batched, and processed by a transformer neural network similar to a large language model. The loss is masked so that Gato only predicts action and text targets.
When deploying Gato, a prompt, such as a demonstration, is tokenised, forming the initial sequence. Next, the environment yields the first observation, which is also tokenised and appended to the sequence. Gato samples the action vector autoregressively, one token at a time.