A simulation of a probe sent to the other side of a wormhole shows it could send speedy messages back before the hole closes and the probe is lost.


OzGrav is turning Albert Einstein’s imagination into reality as they pursue groundbreaking discoveries in the rapidly expanding area of gravitational wave physics. Read the article to find out more.
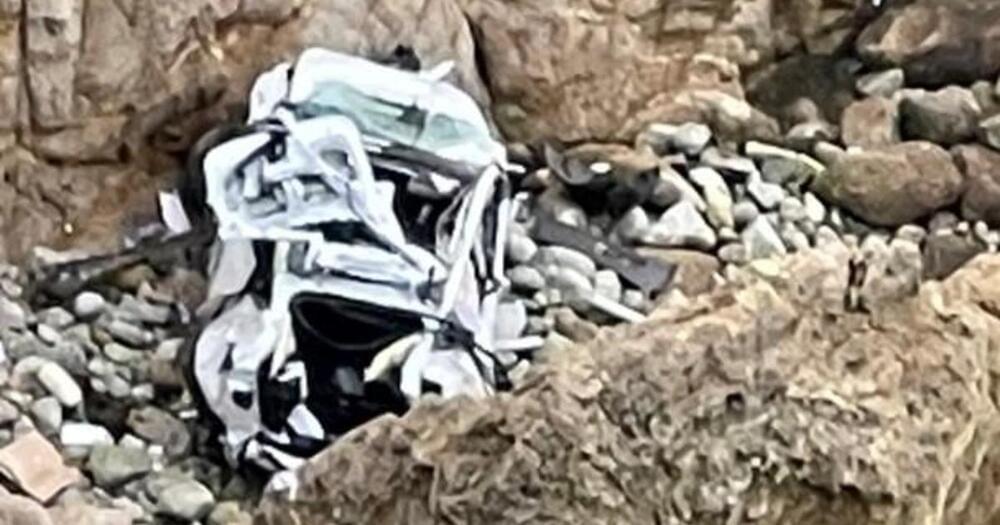

250 feet down a cliff. Notice many of the Musk bashing news outlets are not reporting this. #PleaseShare
Montara, Calif. — A 4-year-old girl, a 9-year-old boy and two adults survived Monday after their car plunged off a Northern California cliff along the Pacific Coast Highway near an area known as Devil’s Slide that’s known for fatal wrecks, officials said.
The Tesla sedan plummeted more than 250 feet from the highway and crashed into a rocky outcropping. It appears to have flipped a few times before landing on its wheels, wedged against the cliff just feet from the surf, according to Brian Pottenger, a battalion chief for Coastside Fire Protection District/Cal Fire.
Crashes along Devil’s Slide, a steep, rocky and winding coastal area about 15 miles south of San Francisco between Pacifica and Montara, rarely end with survivors. On Monday, the victims were initially listed in critical condition but all four were conscious and alert when rescuers arrived.
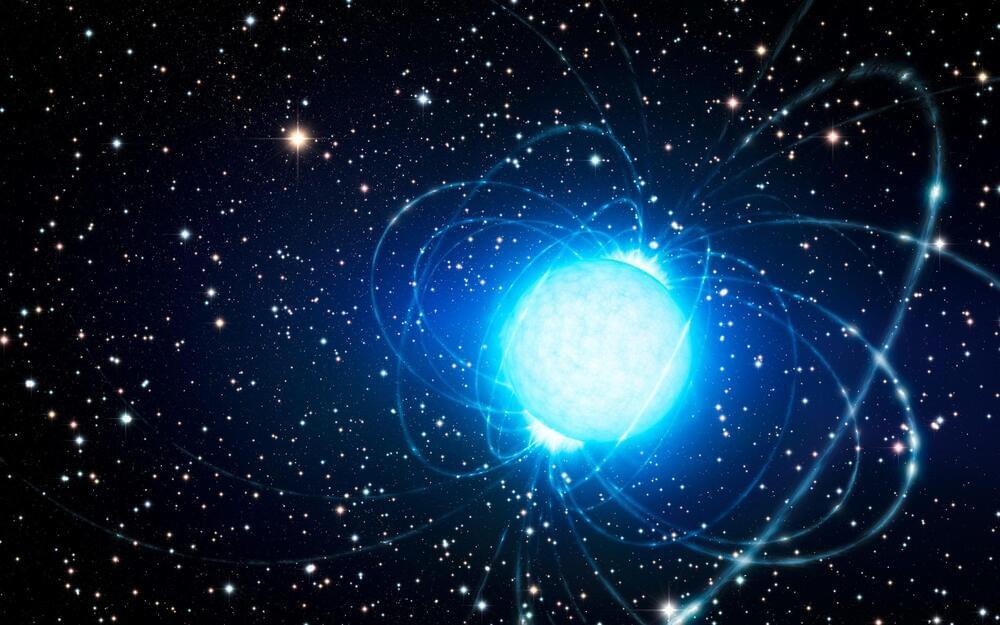
According to a new study the X-ray light emitted by a certain magnetar – a highly magnetized dead star – appears to indicate that the star has a solid surface and no atmosphere.
A study published in the journal Science has used data from NASA
Established in 1958, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is an independent agency of the United States Federal Government that succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). It is responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. Its vision is “To discover and expand knowledge for the benefit of humanity.” Its core values are “safety, integrity, teamwork, excellence, and inclusion.”


Since OpenAI released ChatGPT, there has been a lot of speculation about what its killer app will be. And perhaps topping the list is online search. According to The New York Times, Google’s management has declared a “code red” and is scrambling to protect its online search monopoly against the disruption that ChatGPT will bring.
ChatGPT is a wonderful technology, one that has a great chance of redefining the way we create and interact with digital information. It can have many interesting applications, including for online search.
But it might be a bit of a stretch to claim that it will dethrone Google—at least from what we have seen so far. For the moment, large language models (LLM) have many problems that need to be fixed before they can possibly challenge search engines. And even when the technology matures, Google Search might be positioned to gain the most from LLMs.
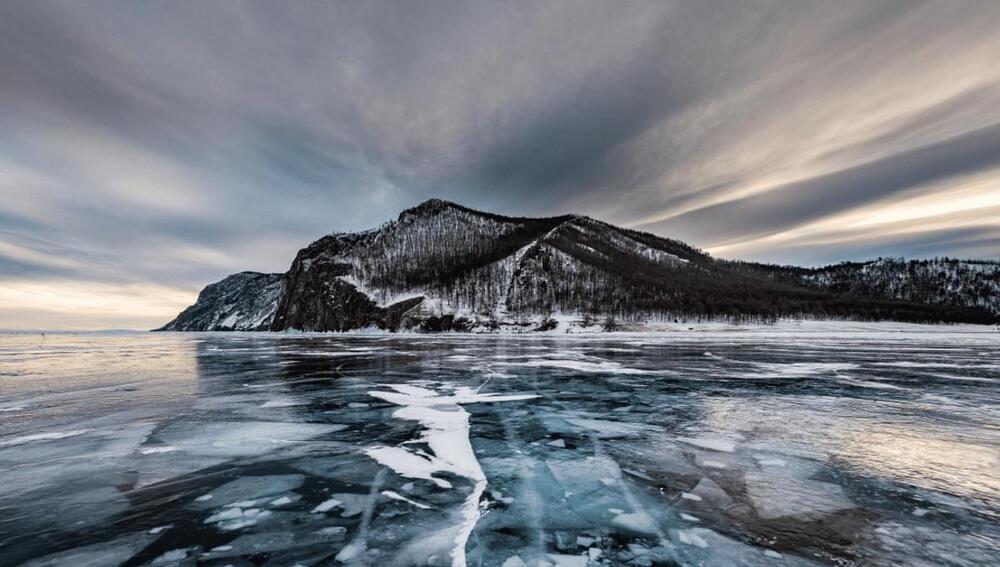



The world’s oldest lake can be found in southeastern Siberia where it’s believed to have existed for around 25 million years. As well as being the great great grandad of lakes, Baikal is also the deepest at 1,700 meters (5,600 feet). The impressive accolade means it’s home to around 20 percent of the world’s unfrozen freshwater reserves, and in a pond that massive you can expect a fish or two.
Lake Baikal is known as the “Galapagos of Russia” for the many weird and diverse species that call it home. Despite being covered by a thick layer of ice for five months each year, the ecosystem that has developed in the lake is astonishing and like few others. It is estimated that 80 percent of plants and animals that live in it are found nowhere else on the planet.
Among them is the Baikal oilfish, also known as the golomyankas. They’re scale-less fish with translucent bodies that can stretch to around 21 centimeters (8.3 inches). There are two species in the Comephorus genus, C. baikalensis and C. dybowski.