A new study has revealed that famous Dutch astronomer Christiaan Huygens was probably nearsighted, which explains why his telescopes weren’t quite as good as his rivals’.
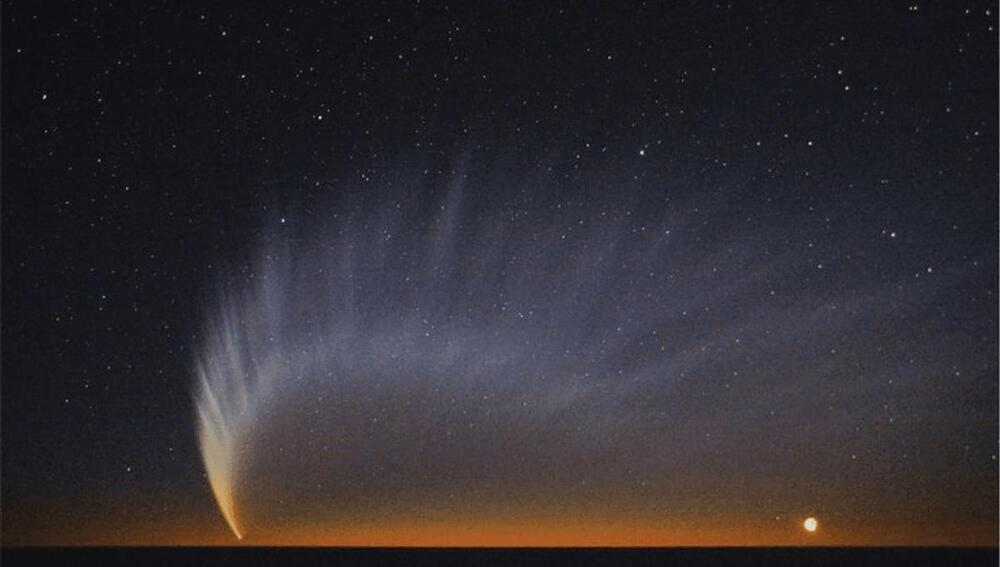



A comet that will make a (somewhat) close approach to the Earth in September 2024 is already creating excitement among amateur astronomers. Comets are unpredictable beasts, and a great many have proven disappointing – but C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan-ATLAS) has many of the characteristics required to put on the best display for at least a decade.
Comets visit the inner solar system quite frequently, but few can be seen with the naked eye. Most are either regular visitors (short period) that have been slowly losing material on previous approaches to the Sun and don’t have enough left to be very bright. Others never get close enough to Earth to put on a show.
Tsuchinshan-ATLAS passes both those tests. Its orbit is so long it there is debate as to whether it visited the inner solar system 80,000 years ago, or if it never has. At closest approach, it will be 58 million kilometers (36 million miles) or just under 0.39 AU (Earth-Sun distance) from the Earth.
The mission to return humans to the Moon is moving on to its next phase, NASA has announced. While reporting the current analysis of the successful uncrewed Artemis I mission, the agency revealed when the first crewed mission will take place.
Artemis I was the first test flight for NASA’s megarocket Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft and spent 25.5 days in space. Artemis II will be the first crewed flight to the Moon before Artemis III actually lands on the lunar surface.
NASA revealed that as the Orion capsule successfully survived Earth reentry without burning up, the next launch is now expected for November 2024. The four-astronaut crew, including one Canadian, will be announced later this year.

Iwas never into house plants until I bought one on a whim—a prayer plant, it was called, a lush, leafy thing with painterly green spots and ribs of bright red veins. The night I brought it home I heard a rustling in my room. Had something scurried? A mouse? Three jumpy nights passed before I realized what was happening: The plant was moving. During the day, its leaves would splay flat, sunbathing, but at night they’d clamber over one another to stand at attention, their stems steadily rising as the leaves turned vertical, like hands in prayer.
“Who knew plants do stuff?” I marveled. Suddenly plants seemed more interesting. When the pandemic hit, I brought more of them home, just to add some life to the place, and then there were more, and more still, until the ratio of plants to household surfaces bordered on deranged. Bushwhacking through my apartment, I worried whether the plants were getting enough water, or too much water, or the right kind of light—or, in the case of a giant carnivorous pitcher plant hanging from the ceiling, whether I was leaving enough fish food in its traps. But what never occurred to me, not even once, was to wonder what the plants were thinking.
To understand how human minds work, he started with plants.
See my site’s section on movies and transhumanism:
http://www.truefreethinker.com/movies.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
You can visit me here:
True Freethinker:
http://www.truefreethinker.com.
Backup video channel:
https://archive.org/details/@ken_ammi.
Facebook:
http://www.facebook.com/pages/True-Freethinker/121114521301654
Twitter:
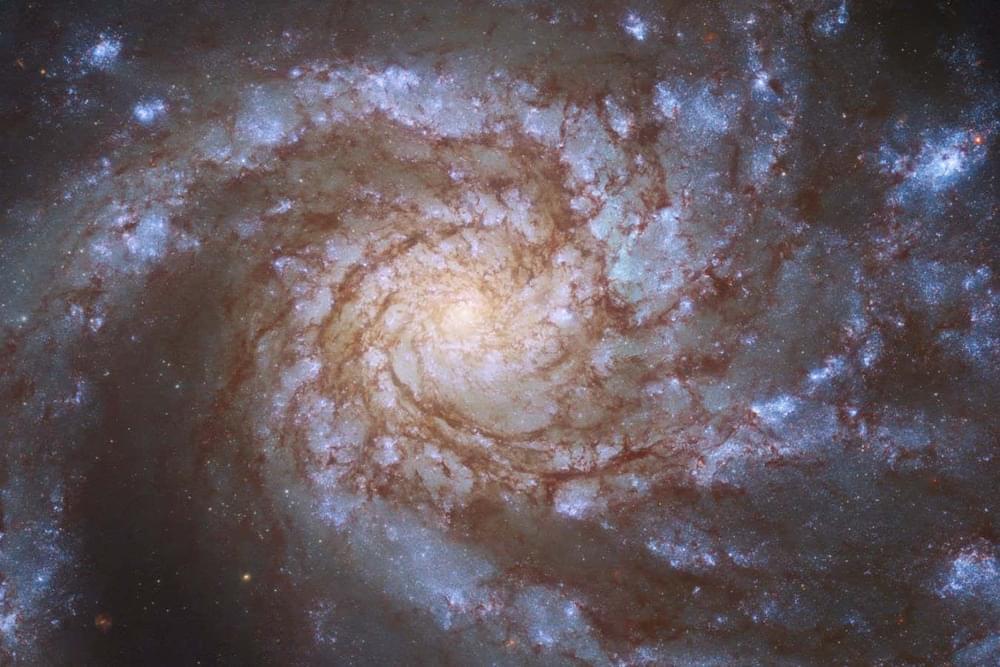

Most galaxies seemed to be missing a huge proportion of the matter we expected them to have – now researchers may have found its hiding spot, but the discovery contradicts accepted models of galaxy formation.
By Leah Crane
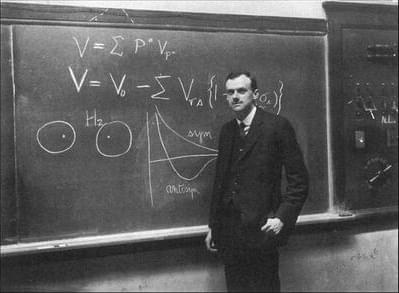

The cosmos is full of mysteries, one of which is the existence of supermassive black holes. Though much effort has been granted to these celestial mysteries, the evolution and formation of such supermassive black holes are quite hard to explain.
Supermassive Black Holes
According to Science Alert, these celestial objects are among the heaviest in the entire universe. In fact, their mass can be up to millions or billions of times that of the sun. They can have the mass of more than 10 billion suns, and this is not just in theory.
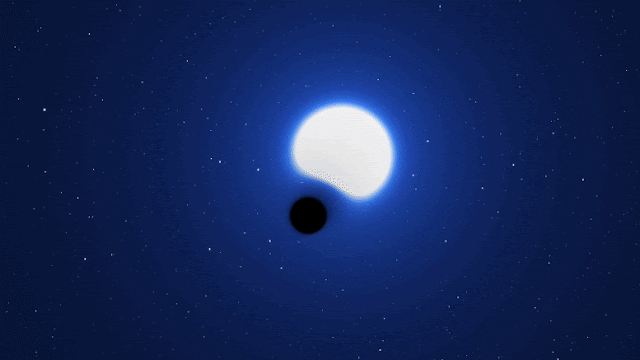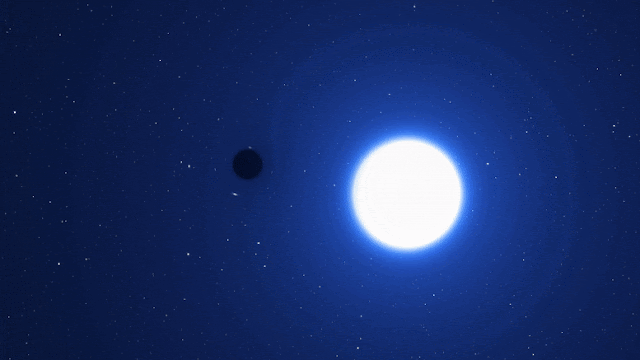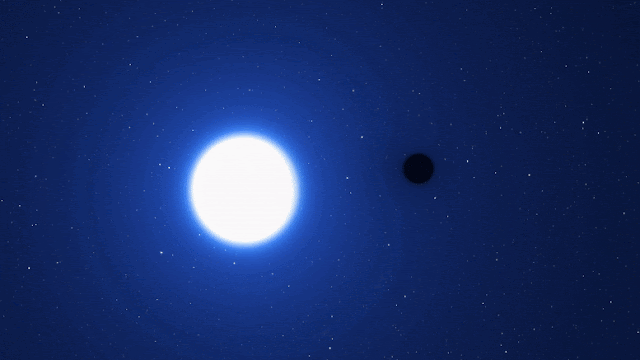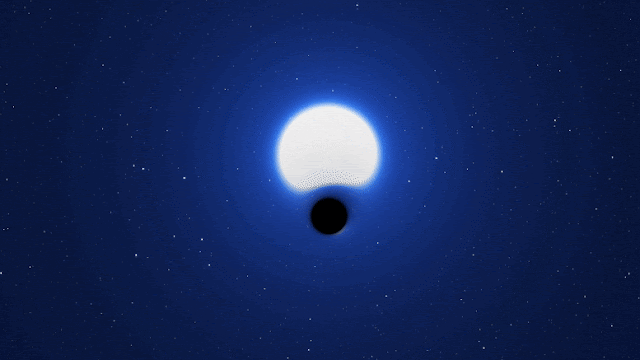
Astronomers have found what they are calling a “cosmic needle in a haystack” in a galaxy next to our Milky Way. It is a dormant black hole that seems to have formed without the explosion of a dead star.
Researchers said on Monday that this black hole is different from all the others that we know of because it is “X-ray quiet.” This means that it doesn’t make a lot of X-ray radiation, which would indicate that it is eating nearby matter with its huge gravitational pull, and that it didn’t form in a supernova.
Black holes are very dense things with so much gravity that not even light can get out.