The hNSCs used in the study have been produced and characterised in the Cell Factory and Biobank of Santa Maria Hospital (Terni, Italy), authorised by the Italian Medicine Agency (AIFA) for the production of hNSCs to be used for clinical trials (aM 54/2018). The methodology applied to isolate, expand, characterise and cryopreserve the lines is based on the Neurosphere Assay26,41,54, and has been used for the production of the cells utilised in phase I trials for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis patients (NCT0164006723) and for Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis patients (NCT03282760, ongoing).
The entire production process, starting from tissue procurement to cryopreservation is compliant to cGMP guidelines and approved by AIFA. The hNSCs are obtained from foetal brain tissue derived from fetuses that underwent miscarriage or natural in utero death upon receiving the signed informed consent from the mother. Forty-eight hours prior to implantation, hNSCs were plated in the growth medium at a concentration of 10,000 cells/cm2. On the day of surgery, hNSCs were collected by centrifugation, viable cells were counted by Trypan blue exclusion criteria, and the correct number of cells were re-suspended in HBSS for the transplant.
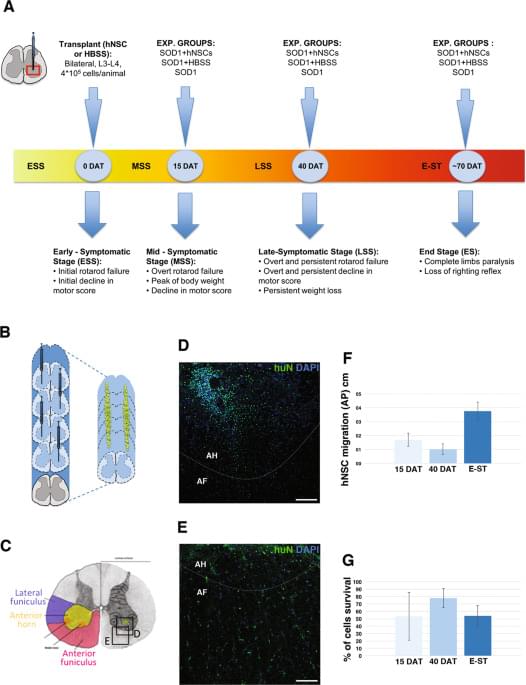
SOD1 transgenic male rats were randomly divided into three experimental groups: (i) transplanted with hNSCs (hNSC rats, n = 15); (ii) treated with HBSS (HBSS rats, n = 15) and (iii) untreated (CTRL rats, n = 22). An additional group of non-transgenic littermates (wild-type, WT, n = 9) were used as controls for symptomatic evaluation of the colony. Tacrolimus (FK506) and cyclosporine (cyclosporin A) are the principal immunosuppressive drugs that have been applied for solid organ transplantation55,56 and have been translated to stem cell treatments for PD57 and ALS22. In animal models, despite differences in potency, both drugs showed excellent survival rates for grafts across many comparative studies58,59. Our previous results44,45 showed that hNSCs can survive—without signs of rejection—in the rat brain up to 6 months under transient immunosuppression treatment, with cyclosporin A. On the bases of these results, we applied the same immunosuppressive treatment with administration of cyclosporine A (15 mg/kg/day subcutaneous; Sandimmne, Novartis) that was initiated on the day of transplantation and continued for 15 days after surgery (for all animal groups).