Today we’ll take a look at Tesla’s AI Day and the real star of the show. But first…
Musk and Twitter are set to go to Delaware Chancery Court in mid-October over the Tesla CEO’s attempt to get out of his $44 billion deal to buy the company.
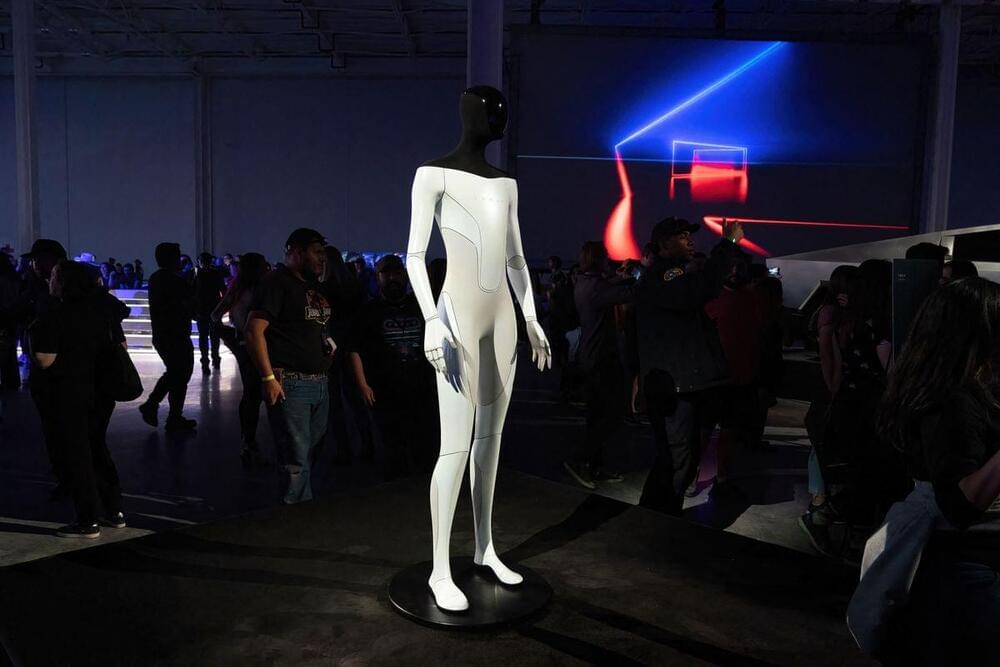
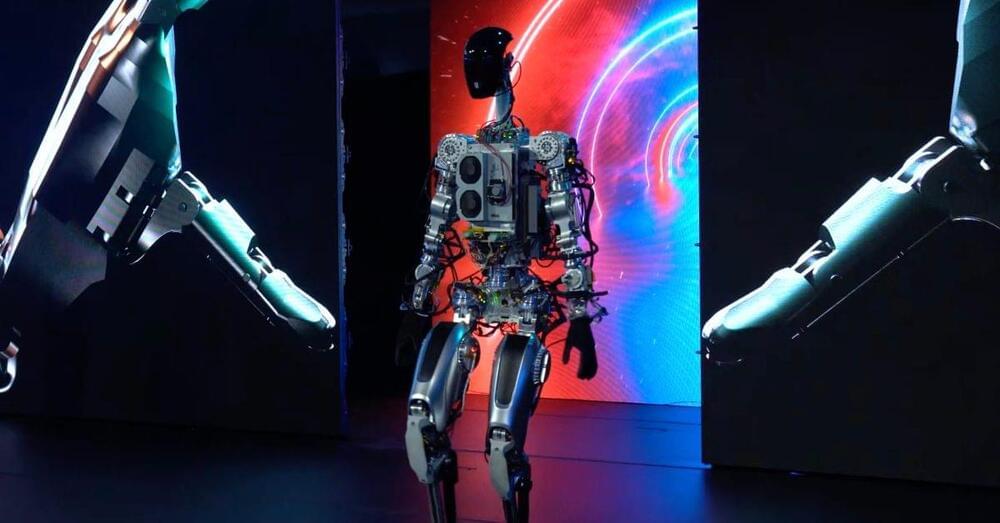
Tesla has unveiled its Optimus humanoid robot at its AI Day 2022 today and Elon Musk believes Tesla can bring it to market for “less than $20,000”.
As expected, the event started with Tesla unveiling a working prototype of its humanoid robot – a project first announced at Tesla’s AI day in 2021.
There were two prototypes unveiled at the event.
PITTSBURGH (KDKA) — Move over, BA-4 and BA-5, there’s a new COVID-19 variant that’s spreading even as the push is on for the current round of boosters.
The word from the experts is to get the booster and don’t let your guard down. KDKA’s John Shumway spoke with CBS News medical expert Dr. David Agus — and some of what he had to say is a bit disconcerting.
Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Omicron, BA-4, BA-5, and now comes BF-7.
There needs to be a radical change to biological wetware in order to handle viruses. What is needed is either nanoparticles or an immunity to all diseases. Crispr is the main path for the biological singularity but it needs to be perfected first as the human body is still a black box due to restrictions. I do believe that mass spectrometry will essentially be key to see the inner world of human biology. Then crispr can make new parts essentially to evolve past our current limits. But either way the biological singularity is needed for survival of human beings for better health.
The coronavirus revealed flaws in the nation’s pandemic plans. The spread of monkeypox shows that the problems remain deeply entrenched.
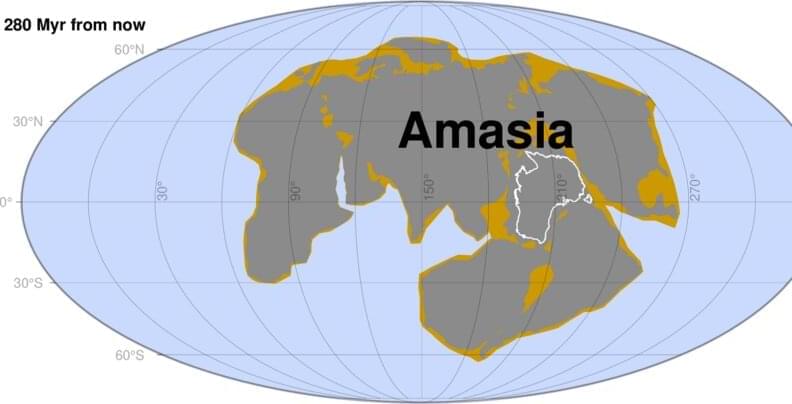
New Curtin University-led research has found that the world’s next supercontinent, Amasia, will most likely form when the Pacific Ocean closes in 200 to 300 million years.
Published in National Science Review, the research team used a supercomputer to simulate how a supercontinent forms and found that because the Earth has been cooling for billions of years, the thickness and strength of the plates under the oceans reduce with time, making it difficult for the next supercontinent to assemble by closing the “young” oceans, such as the Atlantic or Indian oceans.
Lead author Dr. Chuan Huang, from Curtin’s Earth Dynamics Research Group and the School of Earth and Planetary Sciences, said the new findings were significant and provided insights into what would happen to Earth in the next 200 million years.
Foresight Biotech & Health Extension Meeting sponsored by 100 Plus Capital.
Program & apply to join: https://foresight.org/biotech-health-extension-program/
Jennifer Garrison, Buck Institute.
Reframing Health and Aging through the Lens of Reproduct.
Jennifer Garrison is an assistant professor at the Buck Institute for Research on Aging and also holds appointments in the Department of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology at University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) and the Davis School of Gerontology at the University of Southern California. During her doctoral studies at UCSF with Jack Taunton, she discovered the molecular target of a natural product and elucidated a novel mechanism by which small molecules can regulate protein biogenesis.
Join us:
► Twitter: https://twitter.com/foresightinst.
► Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/foresightinst.
► Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/existentialhope/
► LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/foresight-institute.
If you enjoy what we do please support us via Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/foresightinstitute.
If you’re interested in joining these meetings consider donating through our donation page: https://foresight.org/donate/
Foresight Institute advances technologies for the long-term future of life, focusing on molecular machine nanotechnology, biotechnology, and computer science.
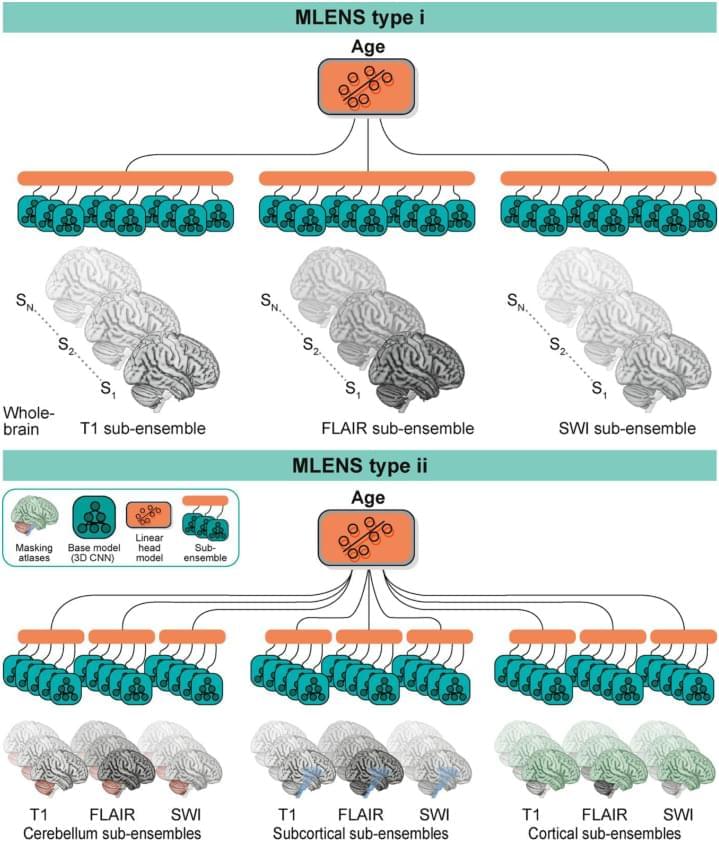
Brain-age (BA) estimates based on deep learning are increasingly used as neuroimaging biomarker for brain health; however, the underlying neural features have remained unclear. We combined ensembles of convolutional neural networks with Layer-wise Relevance Propagation (LRP) to detect which brain features contribute to BA. Trained on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data of a population-based study (n = 2,637, 18–82 years), our models estimated age accurately based on single and multiple modalities, regionally restricted and whole-brain images (mean absolute errors 3.37–3.86 years). We find that BA estimates capture ageing at both small and large-scale changes, revealing gross enlargements of ventricles and subarachnoid spaces, as well as white matter lesions, and atrophies that appear throughout the brain. Divergence from expected ageing reflected cardiovascular risk factors and accelerated ageing was more pronounced in the frontal lobe. Applying LRP, our study demonstrates how superior deep learning models detect brain-ageing in healthy and at-risk individuals throughout adulthood.
Researchers have just discovered a unique and novel intelligence property of hackmanite called gamma exposure memory. The mineral could be used in radiation detection applications.
CHICAGO, Sept 30 (Reuters) — Clear evidence this week that Eisai (4523.T) and Biogen’s (BIIB.O) drug lecanemab slows cognitive decline in early stage dementia has galvanized efforts among Alzheimer’s researchers toward a tantalizing goal — preventing dementia even before symptoms start.
Lecanemab is an antibody that targets and removes toxic clumps of a protein called amyloid beta that accumulate in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s. Results from the companies’ 1,800-patient trial released on Tuesday showed convincingly that doing so also slows the advance of the mind-robbing disease.
In volunteers with mild cognitive impairment and early stage dementia, the drug showed a 27% reduction in cognitive decline after 18 months compared with those who got a placebo.