Like, Subscribe and be Notified, to inspire and feed creativity.
Check out the Strange Worlds channel for more videos:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCFEqV4wpdLLslZc-9ugeuyA
Like, Subscribe and be Notified, to inspire and feed creativity.
Check out the Strange Worlds channel for more videos:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCFEqV4wpdLLslZc-9ugeuyA
More cool designs are on Amazon: https://amzn.to/3wDGy2i.
Alternatively, PayPal donations can be sent here: http://paypal.me/whatdamath.
Hello and welcome! My name is Anton and in this video, we will talk about bizarre quantum effects discovered in the last few months.
Links:
https://news.uchicago.edu/story/uchicago-scientists-observe-…laboratory.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-023-02139-8
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-05727-z.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s42005-022-00881-8
#quantum #quantumphysics #quantummechanics.
0:00 Evidence for quantum superchemistry.
3:40 Solar fusion is quantum and not classical.
5:20 Quantum tunneling and microscopy.
7:00 Tunneling causes chemistry.
7:40 Tunneling affects DNA and causes mutation.
Support this channel on Patreon to help me make this a full time job:
https://www.patreon.com/whatdamath.
Bitcoin/Ethereum to spare? Donate them here to help this channel grow!
bc1qnkl3nk0zt7w0xzrgur9pnkcduj7a3xxllcn7d4
or ETH: 0x60f088B10b03115405d313f964BeA93eF0Bd3DbF
Space Engine is available for free here: http://spaceengine.org.
Enjoy and please subscribe.
Life runs on ribosomes. Every cell across the globe requires ribosomes to convert genetic data into the vital proteins required for the organism’s operation, and, subsequently, for the production of more ribosomes. However, scientists still lack a clear understanding of how these essential nanomachines are assembled.
Now, new high-resolution images of the large ribosomal subunit are shedding light on how arguably nature’s most fundamental molecule coalesces in human cells. The findings, published in Science, bring us one step closer to a complete picture of ribosome assembly.
“We now have a pretty good idea of how the large ribosomal subunit is assembled in humans,” says Rockefeller’s Sebastian Klinge. “We still have quite a few gaps in our understanding, but we certainly now have a much better idea than we had before.”

Over the past few decades, material scientists and chemists have been working on designing increasingly sophisticated materials for a wide range of technological and scientific applications. These materials include synthetic polymers and hydrogels that could be introduced inside the human body as part of medical interventions.
Researchers at the Leibniz Institute of Polymer Research Dresden, Technische Universität Dresden and other institutes in Germany recently designed new fully synthetic materials with a dynamic DNA-crosslinked matrix that could prove useful for the creation of organoids (artificial organs) and other bio-mimetic systems. These materials, introduced in Nature Nanotechnology, are versatile, programmable and relatively inexpensive, making them advantageous for medical and biological research.
“Polymer chemistry can create materials with wonderful properties,” Elisha Krieg, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Phys.org. “Think of everyday products like toys and packaging, but also bullet-proof vests, parachutes, medical implants, etc. But these materials are very static—it is not easy to change their properties, once broken they cannot heal themselves, and their characteristics are difficult to predict. Our group tries to make materials that are more akin to living matter: adaptive, self-healing, and programmed to fulfill specific functions.”
By: Vikas Datta/IANS
Bali (Indonesia): It is not new technology, but Artificial Intelligence (AI) is now raising concerns with the advent of generative AI tools like ChatGPT, which may have significant repercussions across the cyber landscape, as they foster phenomenon like “suffering distancing syndrome”, “responsibility delegation”, and “AI hallucination” for those simply using it to find or validate information, says a senior Kaspersky Labs cyberthreat expert.
Future computers could be built smaller than ever before using the tiny biological skeletons that hold our cells together.
That’s according to one team of scientists, who have devised a way to make computer chips using cytoskeletons — protein scaffolds that give cells their shape.
They claim that the silicon chips that brought computers to the masses in the 1980s are soon to be a thing of the past.
Subscribe here: https://goo.gl/9FS8uF
Check out the previous episode: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X5lpOskKF9I
Become a Patreon!: https://www.patreon.com/ColdFusion_TV
Here it is, the bio computer. A new type of parallel computing method that could rival the infamous quantum computer at a much lower price while being more practical to boot.
Hi, welcome to ColdFusion (formally known as ColdfusTion).
Experience the cutting edge of the world around us in a fun relaxed atmosphere.
Sources:
http://www.mind.ilstu.edu/curriculum/nature_of_computers/computer_types.php.
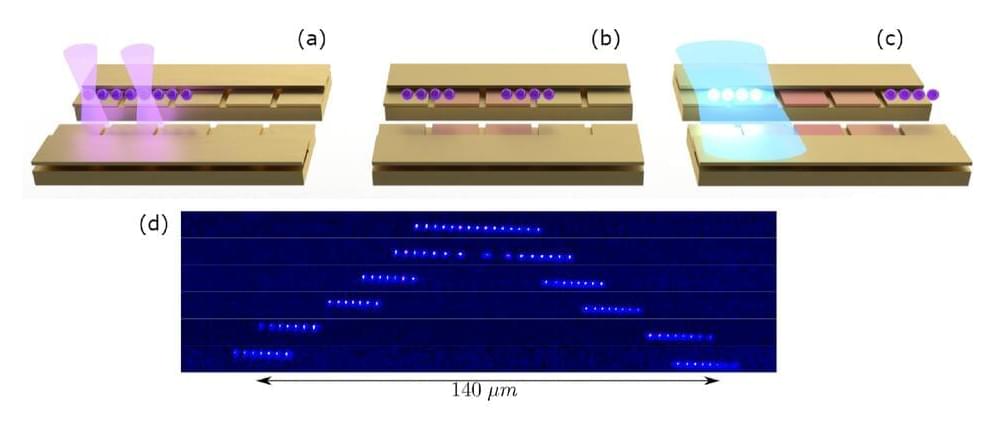
Quantum computers, devices that perform computations by exploiting quantum mechanical phenomena, have the potential to outperform classical computers on some tasks and optimization problems. In recent years, research teams at both academic institutions and IT companies have been trying to realize this predicted better performance for specific problems, which is broadly known as “quantum advantage.”
To reliably demonstrate that a quantum computer performs better than a classical computer, one should, among other things, collect precise measurements inside the computer and compare them to those collected in classical computers. Doing this, however, can sometimes be challenging, due to the distinct nature of these two types of devices.
Researchers at NIST/University of Maryland, UC Berkeley, Caltech and other institutes in the United States recently introduced and tested a new protocol that could help to reliably validate the advantage of quantum computers. This protocol, introduced in Nature Physics, relies on mid-circuit measurements and a cryptographic technique.