😗
Not to mention the potential for cost-savings. If you have been severely sick, you will have felt the unfairness of the high cost of drugs. The latest drugs for cancer, cardiovascular or gastrointestinal diseases, nervous disorders, and rare conditions are so costly that even selling an expensive car won’t cover a year’s supply of them.
The most poignant example is that of cancer drugs, whose approval is by far the most wasteful process of all drug types: The FDA approves less than four percent of cancer drugs, meaning 96 percent of them spend more than a decade being tested in petri dishes, mice, and a small set of patients, before scientists finally realize that they aren’t suitable for human use. Each drug in the four percent that does get approved bears an average price tag of more than a billion dollars, a bill passed down to you, the patient-customer.
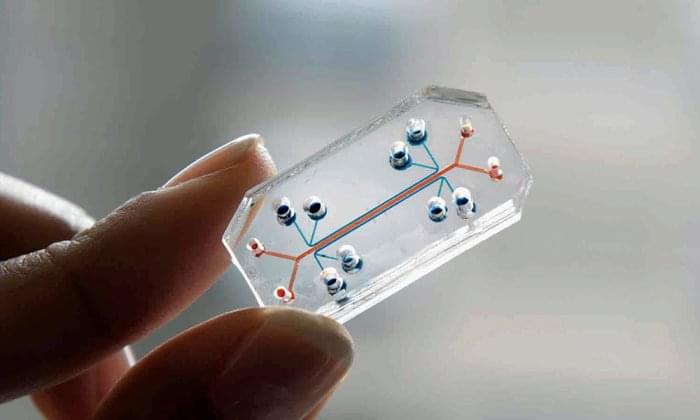
Given what is at stake, it is not surprising that a growing number of companies are offering their organs-on-chips to pharma, each with a different technology, patented chip design, or organ. The three oldest companies in this space — Hurel Corporation, Hepregen, and Organovo, founded in 2007 — are all from the United States. InSphero (Switzerland, 2009), TissUse (Germany, 2010), and Mimetas (Netherlands, 2011) were started shortly afterward. Nortis (Seattle, 2012) and Emulate (Boston, 2013, by Don Ingber) followed, and after them half a dozen startup companies are fighting to grow in this exciting cauldron. Thanks to the organs-on-chips pioneered by Grotberg, Huh, and Takayama, the day when most new drugs will be developed and tested directly (and only) using human tissues is fast approaching.