Micron just unveiled specs for its new high-bandwidth memory for AI, which appears to one-up the fastest HBM on the market.


As ive said before we should at least attempt to reverse engineer brains of: mice, lab rats, crows, octupi, pigs, chimps, and end on the… human brain. it would be messy and expensive, and animal activsts would be runnin around it.
Lurking just below the surface of these concerns is the question of machine consciousness. Even if there is “nobody home” inside today’s AIs, some researchers wonder if they may one day exhibit a glimmer of consciousness—or more. If that happens, it will raise a slew of moral and ethical concerns, says Jonathan Birch, a professor of philosophy at the London School of Economics and Political Science.
As AI technology leaps forward, ethical questions sparked by human-AI interactions have taken on new urgency. “We don’t know whether to bring them into our moral circle, or exclude them,” said Birch. “We don’t know what the consequences will be. And I take that seriously as a genuine risk that we should start talking about. Not really because I think ChatGPT is in that category, but because I don’t know what’s going to happen in the next 10 or 20 years.”
In the meantime, he says, we might do well to study other non-human minds—like those of animals. Birch leads the university’s Foundations of Animal Sentience project, a European Union-funded effort that “aims to try to make some progress on the big questions of animal sentience,” as Birch put it. “How do we develop better methods for studying the conscious experiences of animals scientifically? And how can we put the emerging science of animal sentience to work, to design better policies, laws, and ways of caring for animals?”

BEIJING (AP) — China imposed restrictions Monday on exports of long-range civilian drones, citing Russia’s war in Ukraine and concern that drones might be converted to military use.
Chinese leader Xi Jinping’s government is friendly with Moscow but says it is neutral in the 17-month-old war. It has been stung by reports that both sides might be using Chinese-made drones for reconnaissance and possibly attacks.
Export controls will take effect Tuesday to prevent use of drones for “non-peaceful purposes,” the Ministry of Commerce said in a statement. It said some drone exports still will be allowed.
O.o!!!
This holographic concept could explain a mystery about black holes, but the math may not represent reality.
There is typically no discomfort or sensation during the actual radiation treatment. Most pediatric patients have few, or very mild, side effects from proton therapy. If your child does experience any side effects, they can be managed with medications in most cases. Depending on your child’s diagnosis, treatments are usually given five days a week for a period of four to eight weeks.
The time spent actually delivering the protons to the tumor is about one minute, but a pediatric cancer treatment session can range from 20 to 90 minutes, depending on the patient’s needs. Sedation is available if needed to help keep your child still during the treatment. Most children are able to participate in normal activities before and after treatment.
Learn more about what to expect when getting treated with proton therapy.

UCLA Health researchers have published the largest-ever study of families with at least two children with autism, uncovering new risk genes and providing new insights into how genetics influence whether someone develops autism spectrum disorder.
The new study, published July 28 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, also provides genetic evidence that language delay and dysfunction should be reconsidered as a core component of autism.
Most genetic studies of autism have focused on families with one child affected by the neurodevelopmental disorder, sometimes excluding families with multiple affected children. As a result, few studies have examined the role of rare inherited variation or its interaction with the combined effect of multiple common genetic variations that contribute to the risk of developing autism.
Every person starts as just one fertilized egg. By adulthood, that single cell has turned into roughly 37 trillion cells, many of which keep dividing to create the same amount of fresh human cells every few months.
But those cells have a formidable challenge. The average dividing cell must copy — perfectly — 3.2 billion base pairs of DNA, about once every 24 hours. The cell’s replication machinery does an amazing job of this, copying genetic material at a lickety-split pace of some 50 base pairs per second.
The STAR party’s vision for Canada includes the research and development of self sustainable Mobile Airborne Cities; or Airborne Arcologies. Being an obviously semi-long term goal, the objective would be to at first, allocate budgeting towards research and development of components to build this project in a phased manner… and the scaling of the project as technology allows for it.
Phase I: research and development of scalable micro-prototypes.
Phase II: multiple prototype development / testing stages.
Phase III: Final modifications, and testing of Finished Model.
Phase IV: aircity one digital-testing / infrastructure development.
Phase V: aircity production facility development.
Phase VI:… More
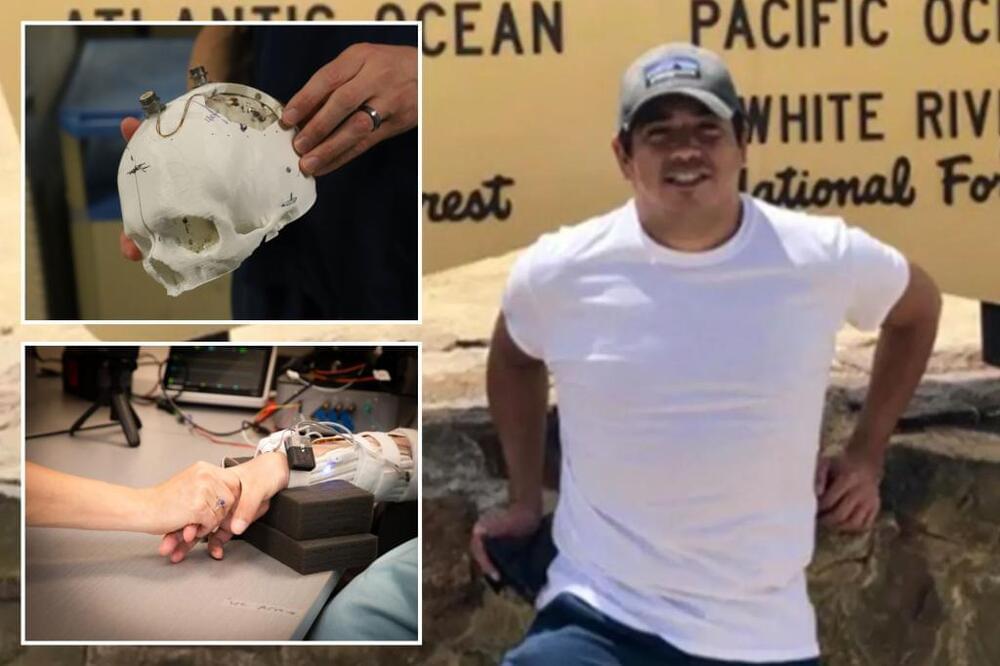
A Long Island man who was paralyzed in a diving accident has regained motion and feeling in his body after a breakthrough, machine learning-based surgery that successfully “connected a computer to his brain” through microelectrode implants.
Now, the successful case of Massapequa’s Keith Thomas, 45, is being heralded throughout the medical world as a “pioneer” case for AI-infused surgeries to treat or cure impassible illnesses like blindness, deafness, ALS, seizures, cerebral palsy and Parkinson’s, experts at Manhasset’s Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research boast.
“This is the first time a paralyzed person is regaining movement and sensation by having their brain, body and spinal cord electronically linked together,” Chad Bouton, a professor at Feinstein’s Institute of Bioelectronic Medicine, told The Post.