A groundbreaking study shows that the human hippocampus continues producing new neurons well into late adulthood.


In this article I list 45 AI tools across 20 different categories. After exploring all the available options in each category, I’ve carefully selected the best tools based on my personal experience. This ensures that the recommendations come from real, practical use, so you can trust that they’re grounded in what actually works.
For each tool, I focus on its best use cases, explaining when and how it can be most useful. I also share what I love about each one, as well as any downsides I’ve encountered during my experience. Additionally, I provide information on the free version and premium pricing plans for each tool.
An in-depth guide to the 40 best AI tools including the best AI assistants, video generators, automation tools, app builders, and more.

Last video: The Tesla Robotaxi Just TOOK OVER Austin Texas!
► Support the channel by becoming a member: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCJjAIBWeY022ZNj_Cp_6wAw/join.
►The Tesla Space Merch Store Is Live! Shop our newest release while quantities last: https://shop.theteslaspace.com/
► Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/theteslaspace.
► Join Our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/zfMNSnuRQN
► Subscribe to our other channel, The Space Race: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCeMcDx6-rOq_RlKSPehk2tQ
► Subscribe to The Tesla Space newsletter: https://www.theteslaspace.com.
► Use my referral link to purchase a Tesla product and get up to $1,300 off and other exclusive benefits. https://ts.la/satinder184250
Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCJjAIBWeY022ZNj_Cp_6wAw?sub_confirmation=1
Welcome to the Tesla Space, where we share the latest news, rumors, and insights into all things Tesla, Space X, Elon Musk, and the future! We’ll be showing you all of the new details around the Tesla Model 3 2023, Tesla Model Y 2023, along with the Tesla Cybertruck when it finally arrives, it’s already ordered!
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/TheTeslaSpace.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/TheTeslaSpace.
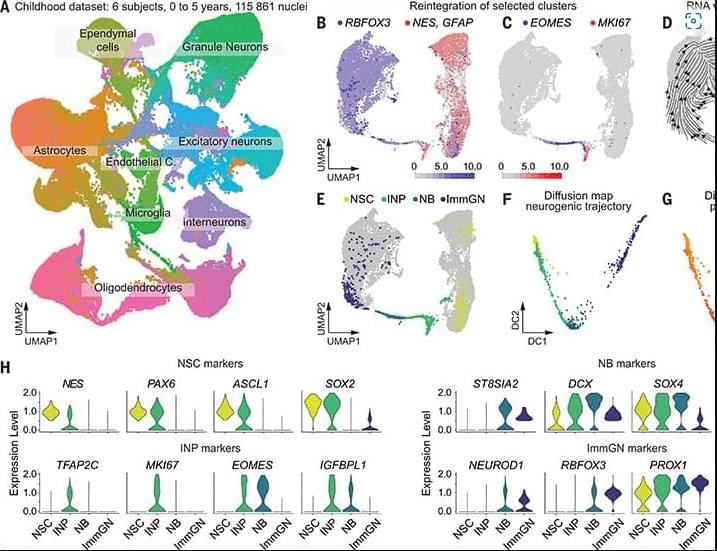
Continuous adult hippocampal neurogenesis is involved in memory formation and mood regulation but is challenging to study in humans. Difficulties finding proliferating progenitor cells called into question whether and how new neurons may be generated. We analyzed the human hippocampus from birth through adulthood by single-nucleus RNA sequencing. We identified all neural progenitor cell stages in early childhood. In adults, using antibodies against the proliferation marker Ki67 and machine learning algorithms, we found proliferating neural progenitor cells. Furthermore, transcriptomic data showed that neural progenitors were localized within the dentate gyrus. The results contribute to understanding neurogenesis in adult humans.

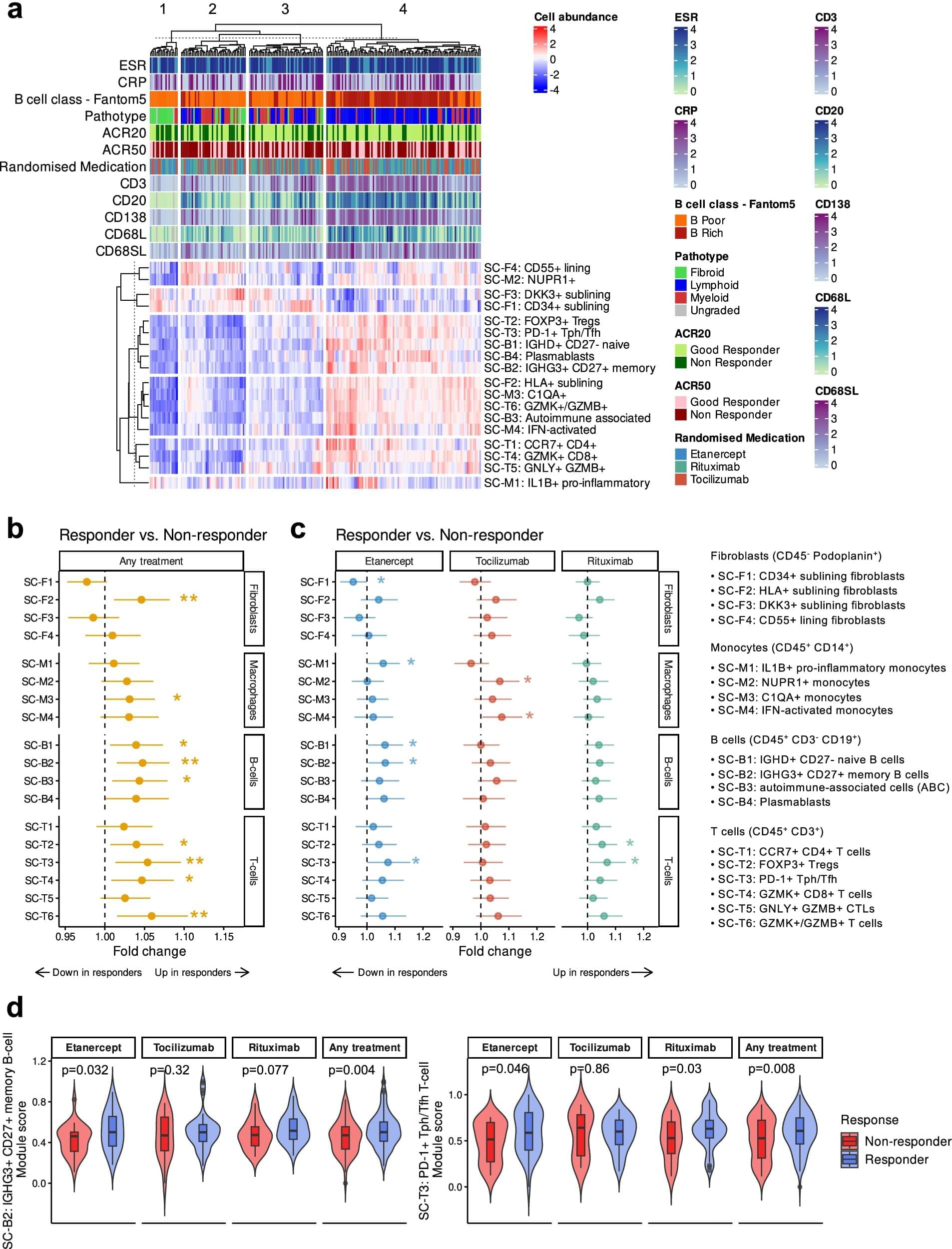
1 in 100 people in Britain today live with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Unlike osteoarthritis (OA), RA is caused not by wear and tear but by the body’s immune system attacking its own joints. RA can strike quickly at any age—but is most common for people aged 40–60.
Biological therapies are the leading treatment. Clinicians use engineered proteins made from living cells to slow the disease by targeting the specific parts of the immune system that are going rogue. Over the past 20 years they have led to major improvements in helping patients to live with RA.
However, different patients will react differently to different biological therapies depending upon their genetics. This means individual therapies have a failure rate of approximately 40%.


