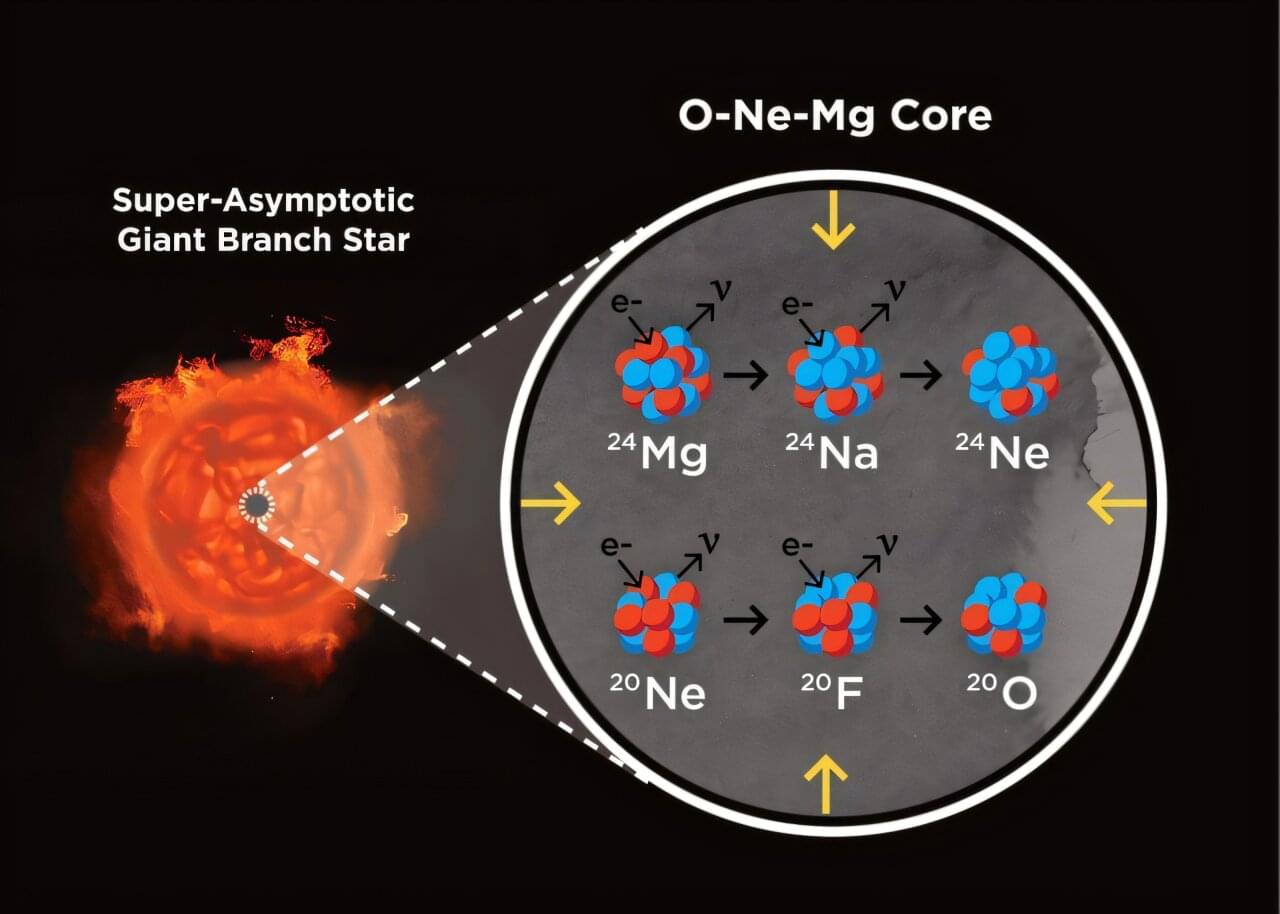
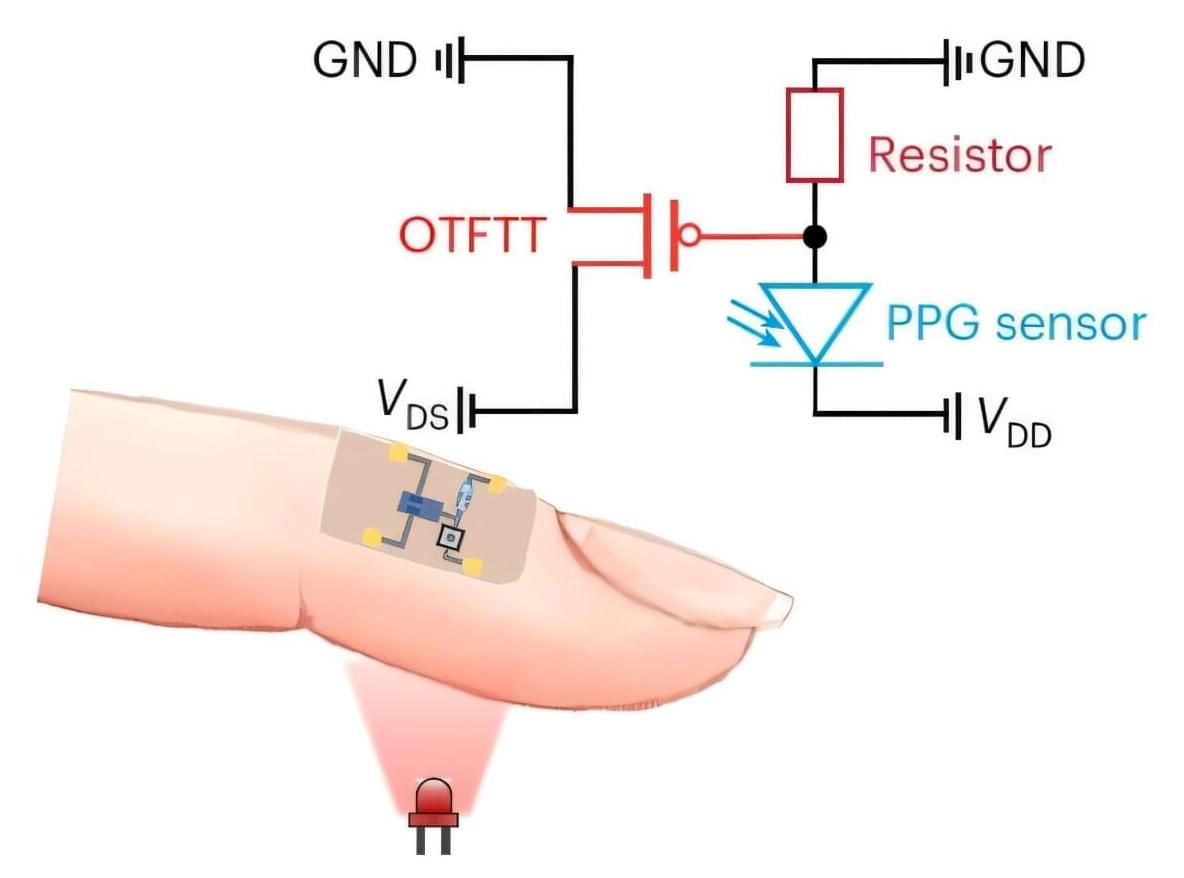
To meet the growing demands of flexible and wearable electronic systems, such as smart watches and biomedical sensors, electronics engineers are seeking high-performance transistors that can efficiently modulate electrical current while maintaining mechanical flexibility.
Thin-film transistors (TFTs), which are comprised of thin layers of conducting, semiconducting and insulating materials, have proved to be particularly promising for large-area flexible and wearable electronics, while also enabling the creation of thinner displays and advanced sensors.
Despite their potential, the energy-efficiency with which these transistors can switch electrical current has proved difficult to improve. This is due to the so-called thermionic limit, a theoretical threshold that delineates the lowest possible voltage required for a transistor to boost electrical current by a factor of 10 at room temperature when switching between “off” and “on” states.