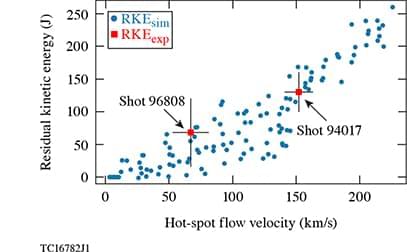
Multidimensional effects degrade the neutron yield and the compressed areal density of laser-direct-drive inertial confinement fusion implosions of layered deuterium–tritium cryogenic targets on the OMEGA Laser System with respect to 1D radiation-hydrodynamic simulation predictions. A comprehensive physics-informed 3D reconstruction effort is under way to infer hot-spot and shell conditions at stagnation from four x-ray and seven neutron detectors distributed around the OMEGA target chamber. Neutron diagnostics, providing measurements of the neutron yield, hot-spot flow velocity, and apparent ion-temperature distribution, are used to infer the mode-1 perturbation at stagnation. The x-ray imagers record the shape of the hot-spot plasma to diagnose mode-1 and mode-2 perturbations. A deep-learning convolutional neural network trained on an extensive set of 3D radiation-hydrodynamic simulations is used to interpret the x-ray and nuclear measurements to infer the 3D profiles of the hot-spot plasma conditions and the amount of laser energy coupled to the hot-spot plasma. A 3D simulation database shows that larger mode-1 asymmetries are correlated with higher hot-spot flow velocities and reduced laser-energy coupling and neutron yield. Three-dimensional hot-spot reconstructions from x-ray measurements indicate that higher amounts of residual kinetic energy are correlated with higher measured hot-spot flow velocities, consistent with 3D simulations.
Three-dimensional reconstruction of inertial confinement fusion hot-spot plasma from x-ray and nuclear diagnostics on OMEGA
Posted in nuclear energy, robotics/AI | Leave a Comment on Three-dimensional reconstruction of inertial confinement fusion hot-spot plasma from x-ray and nuclear diagnostics on OMEGA