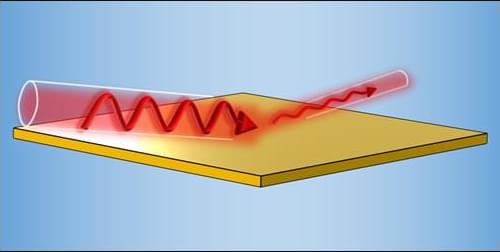
Light grazing an ultrathin conductive film can be absorbed much more strongly than previously thought.


Entanglement and so-called magic states have long been viewed as the key resources for quantum error correction. Now contextuality, a hallmark of quantum theory, joins them as a complementary resource.
Machines make mistakes, and as they scale up, so too do the opportunities for error. Quantum computers are no exception; in fact, their errors are especially frequent and difficult to control. This fragility has long been a central obstacle to building large-scale devices capable of practical, universal quantum computation. Quantum error correction attempts to circumvent this obstacle, not by eliminating sources of error but by encoding quantum information in such a way that errors can be detected and corrected as they occur [1]. In doing so, the approach enables fault-tolerant quantum computation. Over the past few decades, researchers have learned that this robustness relies on intrinsically quantum resources, most notably, entanglement [2] and, more recently, so-called magic states [3].
Researchers from the Institute of Metal Research (IMR) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a new ferroelectric ultraviolet photodetector material that overcomes the long-standing performance limitations of conventional photodetectors.
This breakthrough, published in Nature Communications, promises to enable next-generation optical detection with ultra-fast speed, high sensitivity, and low noise across a wide range of applications.
Photodetectors convert light signals into electrical currents and are fundamental to modern optoelectronics. They are essential for technologies such as high-speed optical communications, environmental monitoring, and space exploration. However, creating a material that possesses all three of these qualities has been a significant challenge.

Mark Thomson, the new head of Europe’s physics laboratory CERN, voiced confidence Tuesday about raising the billions of dollars needed to build by far the world’s biggest particle accelerator.
CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, seeks to unravel what the universe is made of and how it works.
The planned Future Circular Collider (FCC) would be an electron-positron collider ring with a circumference of 91 kilometers and an average depth of 200 meters.
Ordinary matter, when cooled, transitions from a gas into a liquid. Cool it further still, and it freezes into a solid. Quantum matter, however, can behave very differently. In the early 20th century, researchers discovered that when helium is cooled, it transitions from a seemingly ordinary gas into a so-called superfluid. Superfluids flow without losing any energy, among other quantum quirks, like an ability to climb out of containers.
What happens when you cool a superfluid down even more? The answer to this question has eluded physicists since they first started asking it half a century ago.
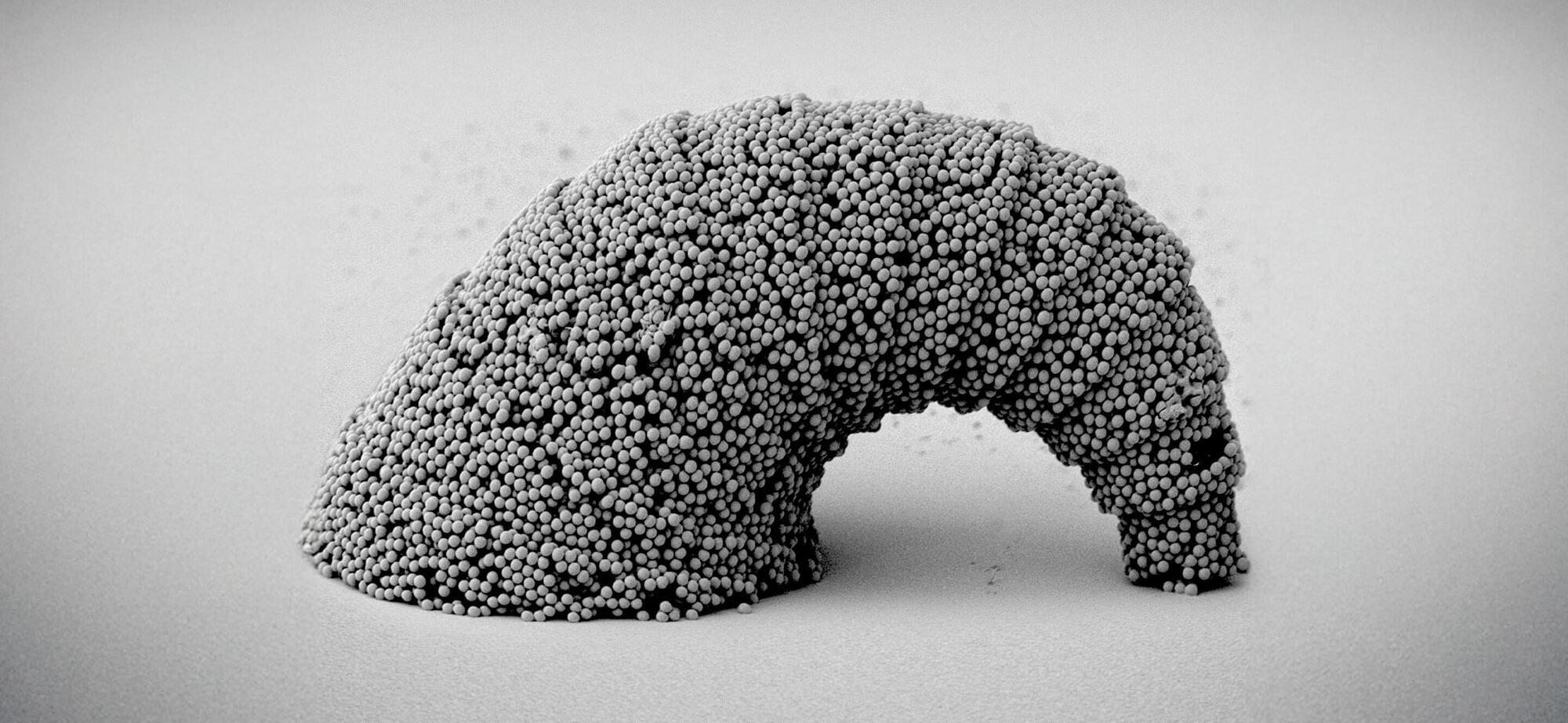

Building things so small that they are smaller than the width of a human hair was previously achieved by using a method called two-photon polymerization, also known as 2PP—today’s state-of-the-art in 3D micro- and nanofabrication. Tiny sculptures such as a miniature replica of the Eiffel Tower or the Taj Mahal made the headlines.
Researchers from the Institute of Cosmos Sciences of the University of Barcelona (ICCUB) and the Institute of Space Studies of Catalonia (IEEC), in collaboration with the Institute of Astrophysics of the Canary Islands (IAC), have led the most extensive observational study to date of runaway massive stars, which includes an analysis of the rotation and binarity of these stars in our galaxy.
This study, published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics, sheds new light on how these stellar “runaways” are ejected into space and what their properties reveal about their fascinating origins.
Runaway stars are stars that move through space at unusually high speeds, drifting away from the places where they were born. For a long time, the way massive runaway stars acquire these high velocities has remained a mystery to astronomers, who have considered two main scenarios: a violent kick when a companion explodes as a supernova in a binary system, or a gravitational ejection during close encounters in dense, young star clusters.
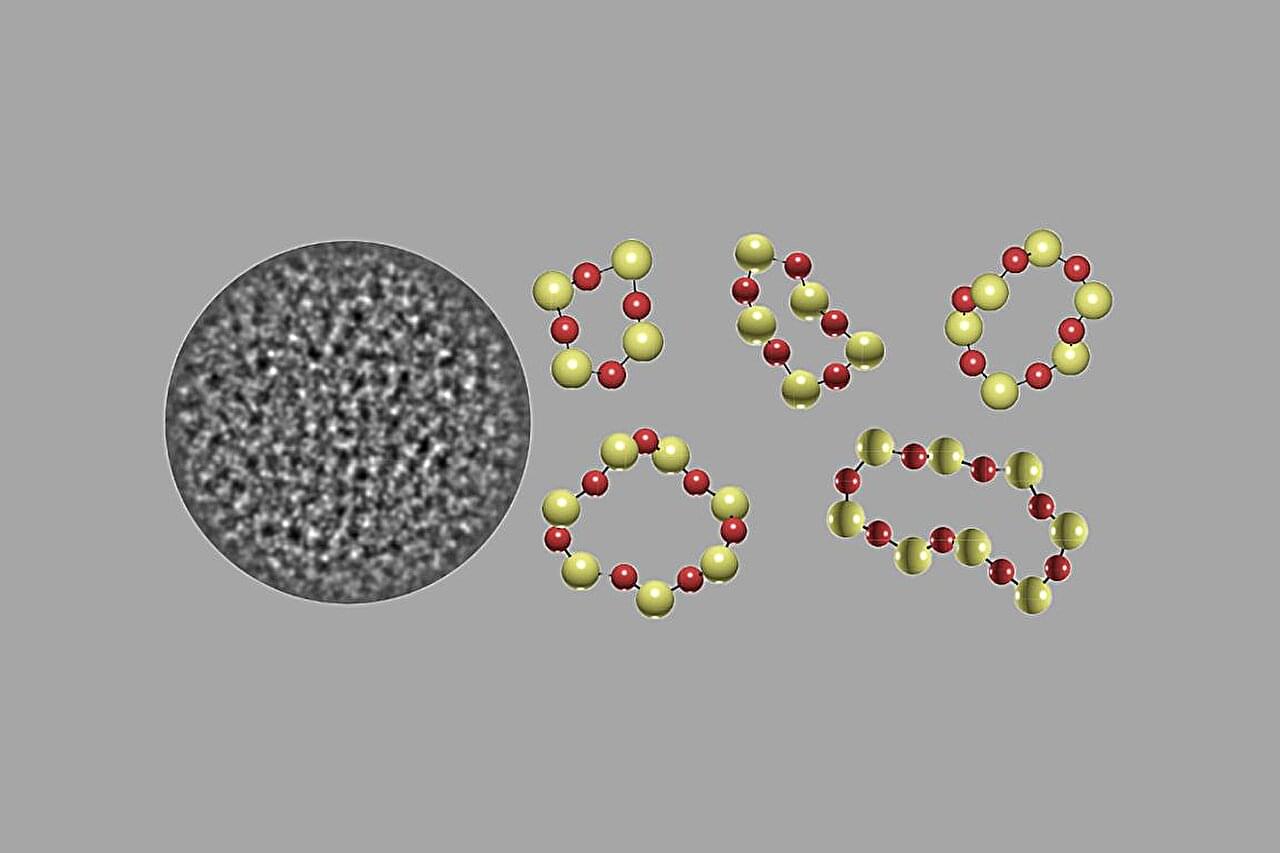
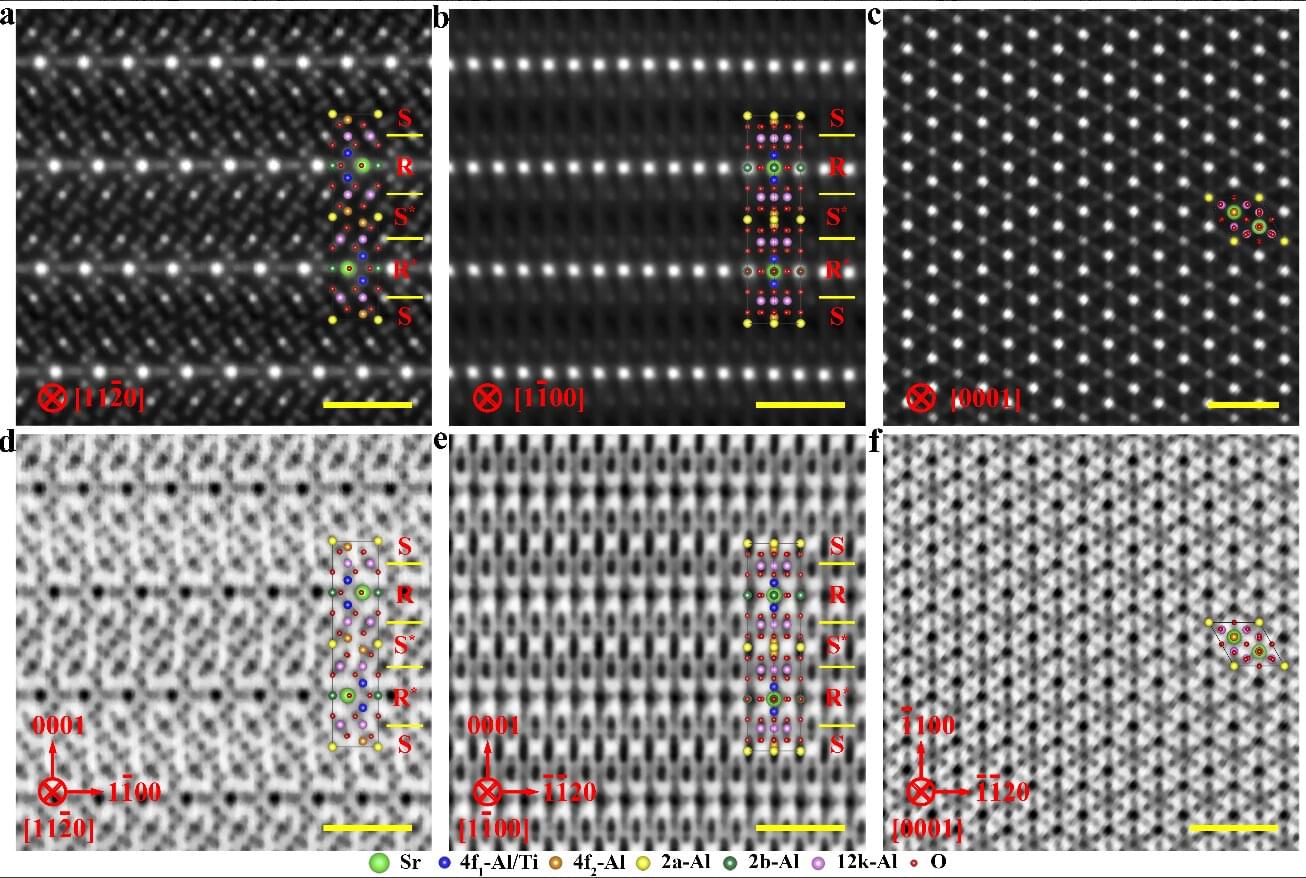
Researchers at the California NanoSystems Institute at UCLA published a step-by-step framework for determining the three-dimensional positions and elemental identities of atoms in amorphous materials. These solids, such as glass, lack the repeating atomic patterns seen in a crystal. The team analyzed realistically simulated electron-microscope data and tested how each step affected accuracy.
The team used algorithms to analyze rigorously simulated imaging data of nanoparticles—so small they’re measured in billionths of a meter. For amorphous silica, the primary component of glass, they demonstrated 100% accuracy in mapping the three-dimensional positions of the constituent silicon and oxygen atoms, with precision about seven trillionths of a meter under favorable imaging conditions.
While 3D atomic structure determination has a history of more than a century, its application has been limited to crystal structures. Such techniques depend on averaging a pattern that is repeated trillions of times.

In its first moments, the infant universe was a trillion-degree-hot soup of quarks and gluons. These elementary particles zinged around at light speed, creating a “quark-gluon plasma” that lasted for only a few millionths of a second. The primordial goo then quickly cooled, and its individual quarks and gluons fused to form the protons, neutrons, and other fundamental particles that exist today.
Physicists at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider in Switzerland are recreating quark-gluon plasma (QGP) to better understand the universe’s starting ingredients. By smashing together heavy ions at close to light speeds, scientists can briefly dislodge quarks and gluons to create and study the same material that existed during the first microseconds of the early universe.
Now, a team at CERN led by MIT physicists has observed clear signs that quarks create wakes as they speed through the plasma, similar to a duck trailing ripples through water. The findings are the first direct evidence that quark-gluon plasma reacts to speeding particles as a single fluid, sloshing and splashing in response, rather than scattering randomly like individual particles.
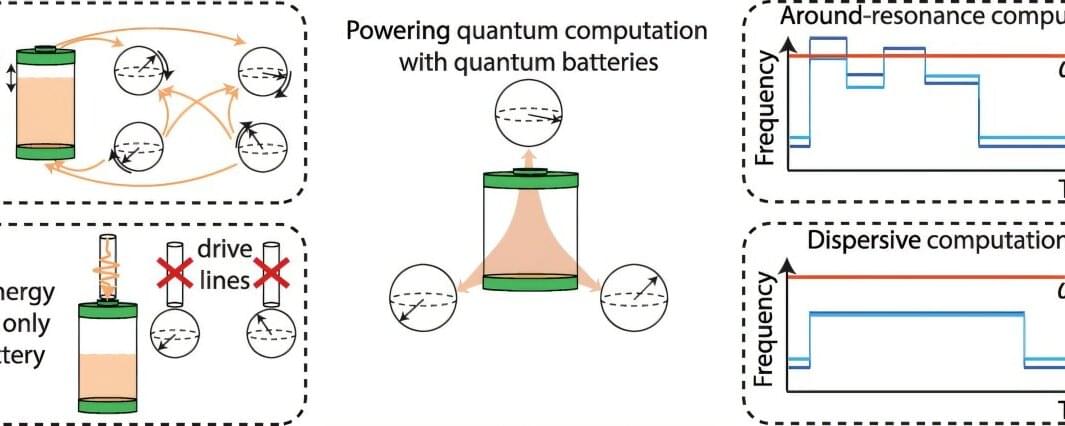
Scientists have unveiled a new approach to powering quantum computers using quantum batteries—a breakthrough that could make future computers faster, more reliable, and more energy efficient.
Quantum computers rely on the rules of quantum physics to solve problems that could transform computing, medicine, energy, finance, communications, and many other fields in the years ahead.
But sustaining their delicate quantum states typically requires room-sized, energy-intensive cryogenic cooling systems, as well as a system of room-temperature electronics.