A team of scientists has used a quantum processor to create an exotic new state of matter, capturing the strange motion of quantum particles in real time.


Full episode with Michael Levin: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c8iFtaltX-s.
As a listener of TOE you can get a special 20% off discount to The Economist and all it has to offer! Visit https://www.economist.com/toe.
Join My New Substack (Personal Writings): https://curtjaimungal.substack.com.
Listen on Spotify: https://tinyurl.com/SpotifyTOE
Become a YouTube Member (Early Access Videos):
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCdWIQh9DGG6uhJk8eyIFl1w/join.
Support TOE on Patreon: https://patreon.com/curtjaimungal.
An exploration of the idea of miniaturizing technology and how aliens might make themselves invisible through this process.
My Patreon Page:
/ johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:
/ eventhorizonshow.
Links:

Simulating consumer decision-making is vital for designing and evaluating marketing strategies before costly real-world deployment. However, post-event analyses and rule-based agent-based models (ABMs) struggle to capture the complexity of human behavior and social interaction. We introduce an LLM-powered multi-agent simulation framework that models consumer decisions and social dynamics. Building on recent advances in large language model simulation in a sandbox environment, our framework enables generative agents to interact, express internal reasoning, form habits, and make purchasing decisions without predefined rules. In a price-discount marketing scenario, the system delivers actionable strategy-testing outcomes and reveals emergent social patterns beyond the reach of conventional methods.
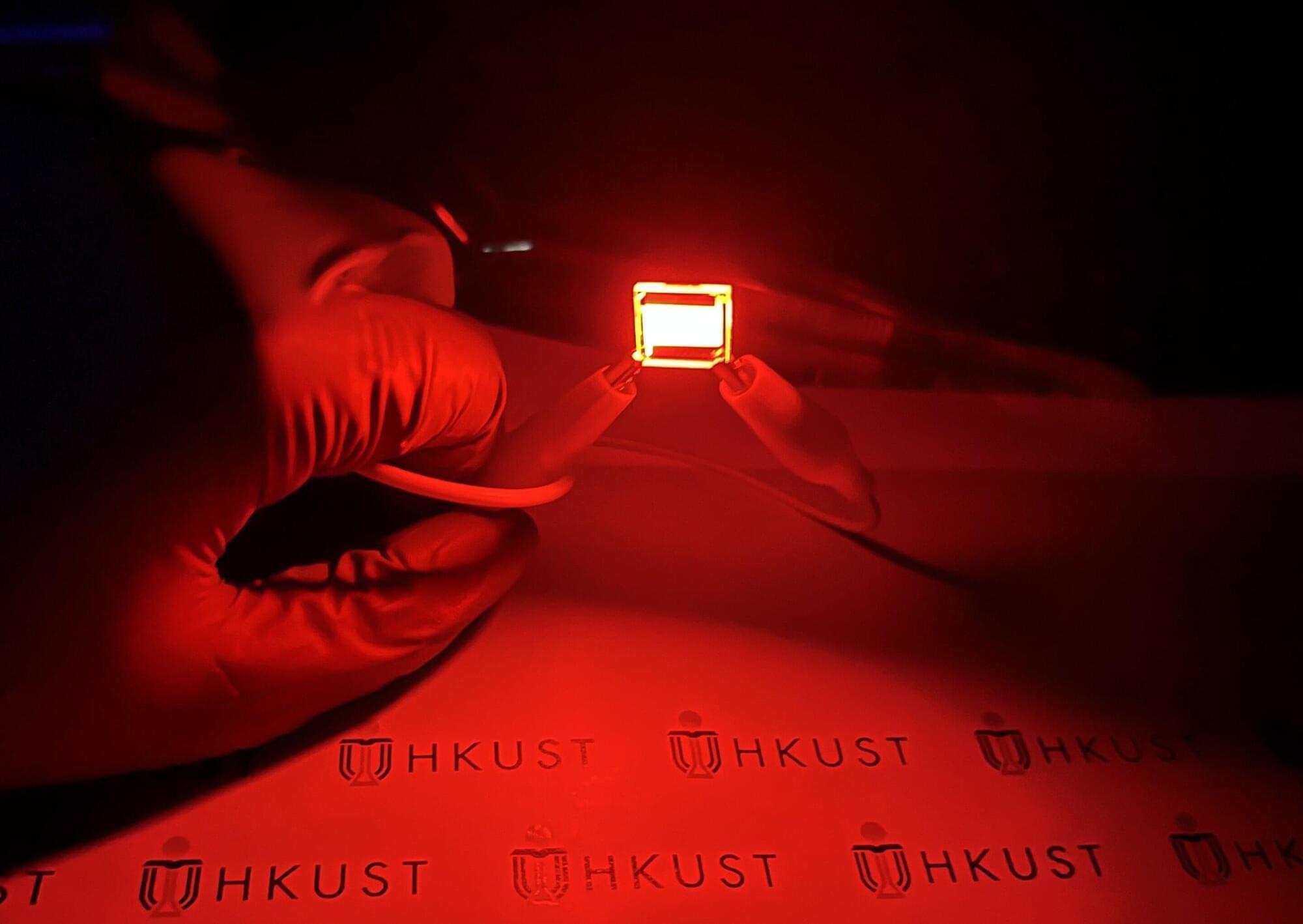
A research team led by the School of Engineering of The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has made significant advances in quantum rod light-emitting diodes (QR-LEDs), setting record-high efficiency level for red QR-LEDs. This innovation is poised to revolutionize next-generation display and lighting technologies, offering smartphone and television users a vibrant and enhanced visual experience. The research is published in the journal Advanced Materials.
LEDs have been widely used in electronic products for decades. Recent developments in quantum materials have given rise to quantum dot LEDs (QD-LEDs) and QR-LEDs. QD-LEDs offer superior color purity (color vividness) and higher brightness compared to current mainstream LEDs. However, outcoupling efficiency has now become the primary obstacle, as it sets a fundamental ceiling for external quantum efficiency (EQE), thereby hindering any further performance improvements.
Quantum rods, on which QR-LEDs are based, are a type of elongated anisotropic nanocrystals with unique optical properties that can be engineered to optimize the light emission direction and ultimately improve outcoupling efficiency. However, QR-LEDs encounter two significant technical challenges: first, the ratio of emitted to absorbed photons (photoluminescence quantum yield) is relatively low after the material absorbs photons; second, there is a substantial leakage current due to poor thin-film quality.
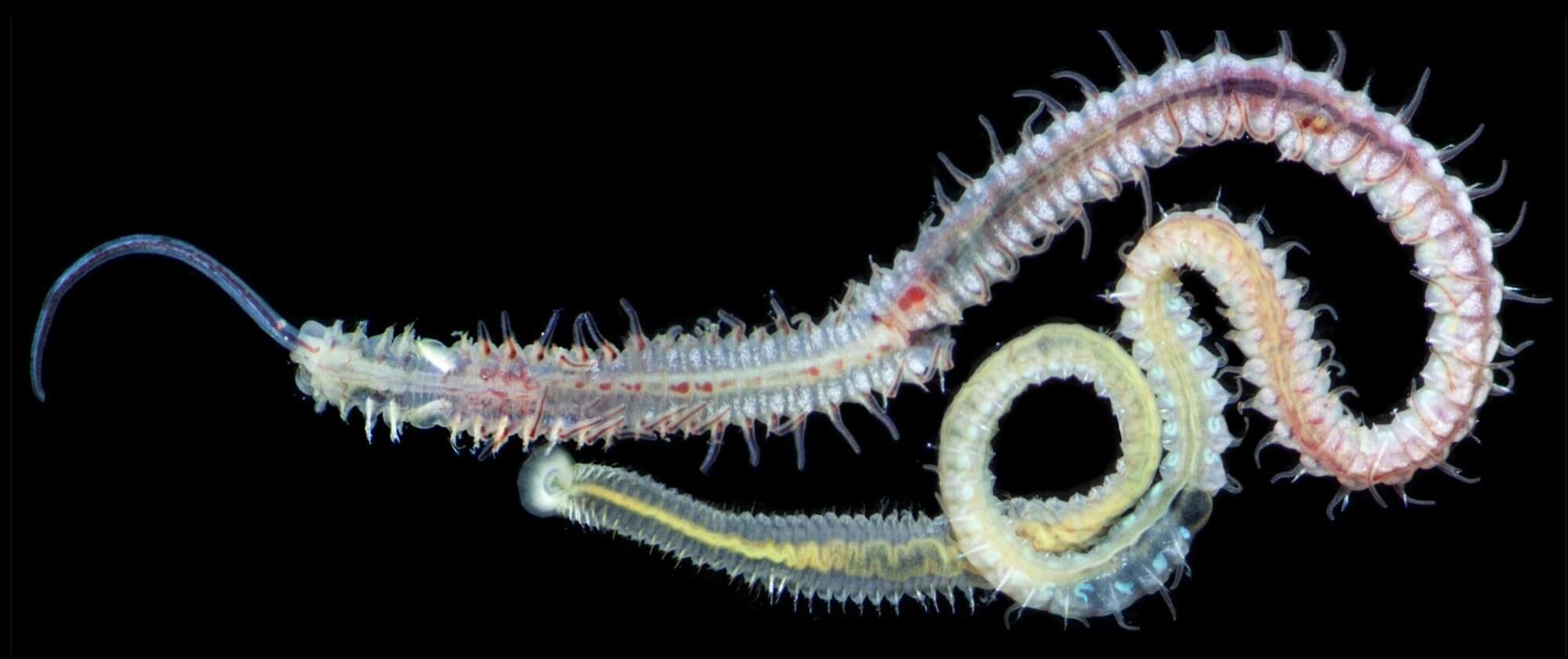

A new study has unexpectedly discovered that a common parasite of modern oysters actually started infecting bivalves hundreds of millions of years before the dinosaurs went extinct.
The research, published in iScience, used high-resolution 3D scans to look inside 480-million-year-old shells from a Moroccan site known for its exceptionally well-preserved sea life. The scans revealed a series of distinctive patterns etched both on the surface of the fossils and hidden inside them.
“The marks weren’t random scratches,” said Karma Nanglu, a UC Riverside paleobiologist who led the research. “We saw seven or eight of these perfect question mark shapes on each shell fossil. That’s a pattern.”
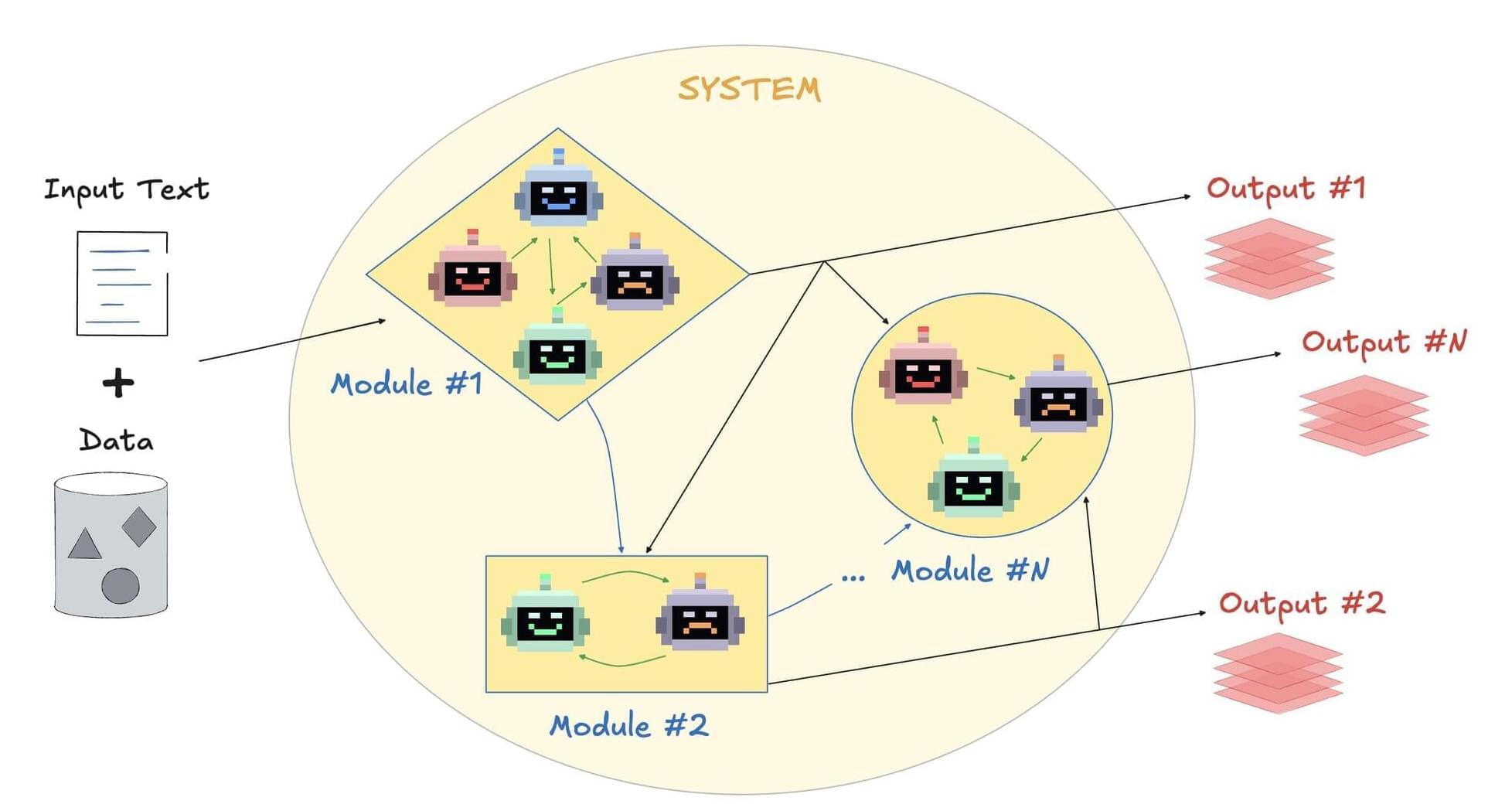
Researchers have developed an AI-powered ‘scientific assistant’ designed to accelerate the scientific process by helping them identify new research questions, analyze and interpret data, and produce scientific documents.
The tool, called Denario, uses large language models to help scientists with tasks from developing new hypotheses to compiling manuscripts. The team hopes Denario will make research faster, more dynamic and more interdisciplinary.
AI can already help with parts of the scientific process: tools like ChatGPT can visualize data or write abstracts, for example. But these tools are typically limited to one step at a time.
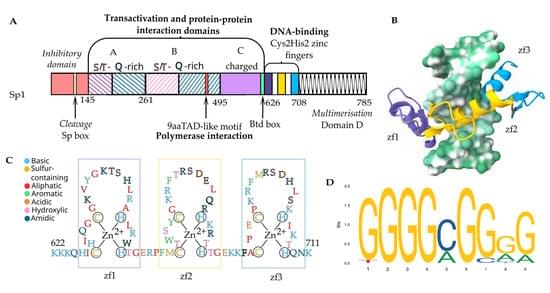
Specificity protein 1 (Sp1) is a highly ubiquitous transcription factor and one employed by numerous viruses to complete their life cycles. In this review, we start by summarizing the relationships between Sp1 function, DNA binding, and structural motifs. We then describe the role Sp1 plays in transcriptional activation of seven viral families, composed of human retro- and DNA viruses, with a focus on key promoter regions. Additionally, we discuss pathways in common across multiple viruses, highlighting the importance of the cell regulatory role of Sp1. We also describe Sp1-related epigenetic and protein post-translational modifications during viral infection and how they relate to Sp1 binding. Finally, with these insights in mind, we comment on the potential for Sp1-targeting therapies, such as repurposing drugs currently in use in the anti-cancer realm, and what limitations such agents would have as antivirals.
The alphabaculovirus Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus (AcMNPV) is the most commonly used virus in the Baculovirus Expression Vector System (BEVS) and has been utilized for the production of many human and veterinary biologics. AcMNPV has a large dsDNA genome that remains understudied, and relatively unmodified from the wild-type, especially considering how extensively utilized it is as an expression vector. Previously, our group utilized CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering that revealed phenotypic changes when baculovirus genes are targeted using either co-expressed sgRNA or transfected sgRNA into a stable insect cell line that produced the Cas9 protein.
What happens when the pursuit of perfection forgets compassion?
SCP-191, known as The Cyborg Child, is one of the most haunting examples of speculative bioengineering ever documented. This essay examines the anatomy, psychology, and philosophy of a child transformed into a machine — a being caught between humanity and technology.
In this episode, we explore:
How cybernetic modification redefines the human body.
The science behind hybrid consciousness and neural integration.
The moral cost of evolution without empathy.
What SCP-191 reveals about the posthuman future.