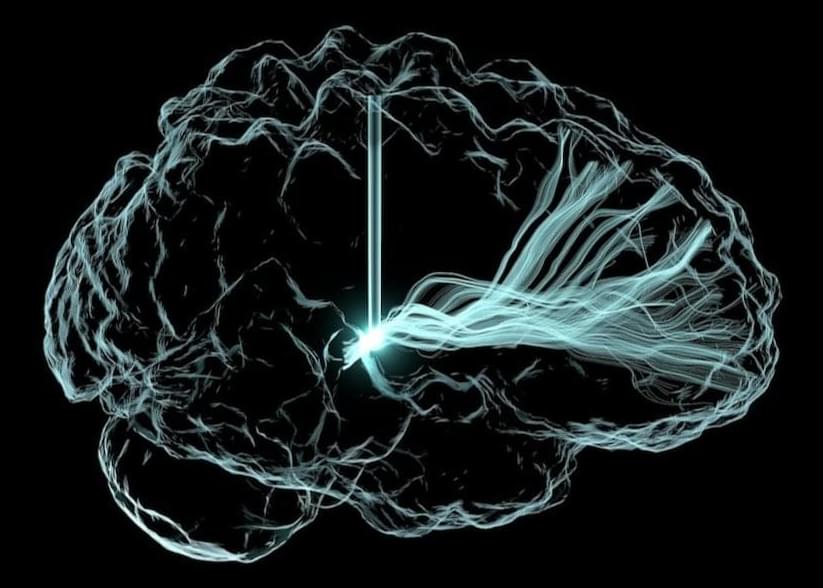
The study is “really pretty remarkable,” said Christopher Whyte at the University of Sydney, who was not involved in the work, to Nature. One of the first to simultaneously record activity in both deep and surface brain regions in humans, it reveals how signals travel across the brain to support consciousness.
Consciousness has teased the minds of philosophers and scientists for centuries. Thanks to modern brain mapping technologies, researchers are beginning to hunt down its neural underpinnings.
At least half a dozen theories now exist, two of which are going head-to-head in a global research effort using standardized tests to probe how awareness emerges in the human brain. The results, alongside other work, could potentially build a unified theory of consciousness.