Hackers built 4,300 fake travel sites in 2025 to steal hotel guests’ card data using real brand logos.




The ImunifyAV malware scanner for Linux servers, used by tens of millions of websites, is vulnerable to a remote code execution vulnerability that could be exploited to compromise the hosting environment.
The issue affects versions of the AI-bolit malware scanning component prior to 32.7.4.0. The component is present in the Imunify360 suite, the paid ImunifyAV+, and in ImunifyAV, the free version of the malware scanner.
According to security firm Patchstack, the vulnerability has been known since late October, when ImunifyAV’s vendor, CloudLinux, released fixes. Currently, the flaw has not been assigned an identifier.

The Kraken ransomware, which targets Windows, Linux/VMware ESXi systems, is testing machines to check how fast it can encrypt data without overloading them.
According to Cisco Talos researchers, Kraken’s feature is a rare capability that uses temporary files to choose between full and partial data encryption.
The Kraken ransomware emerged at the begining of the year as a continuation of the HelloKitty operation, and engages in big-game hunting attacks with data theft for double extortion.

US government agencies are warning that the Akira ransomware operation has been spotted encrypting Nutanix AHV virtual machines in attacks.
An updated joint advisory from CISA, the FBI, the Department of Defense Cyber Crime Center (DC3), the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and several international partners alerts that Akira ransomware has expanded its encryption capabilities Nutanix AHV VM disk files.
The advisory includes new indicators of compromise and tactics observed through FBI investigations and third-party reporting as recent as November 2025.

A self-spreading package published on npm spams the registry by spawning new packages every every seven seconds, creating large volumes of junk.
The worm, dubbed ‘IndonesianFoods,’ due to its distinctive package naming scheme that picks random Indonesian names and food terms, has published over 100,000 packages according to Sonatype, and the number is growing exponentially.
Although the packages do not have a malicious component for developers (e.g., stealing data, backdooring hosts), this could change with an update that introduces a dangerous payload.


Researchers discovered that a longevity gene from centenarians can reverse heart damage linked to progeria, suggesting a new approach to treating rapid and age-related heart aging.
A major advancement has been made in understanding a rare genetic disorder that causes children to age prematurely. Scientists from the University of Bristol and IRCCS MultiMedica identified “longevity genes” found in people who live beyond 100 years, which appear to protect the heart and blood vessels during aging. Their study suggests these genes could potentially reverse the damage caused by this fatal condition.
Understanding progeria and its effects.
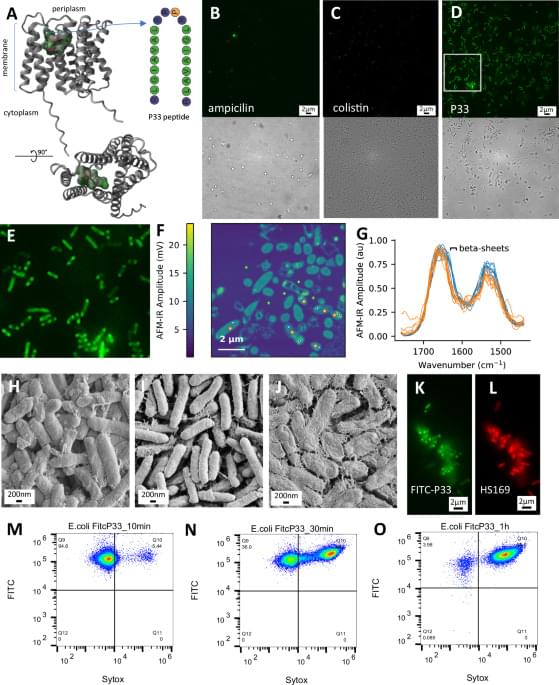
Protein biosynthesis is a major target of existing antibiotics that inhibit the efficiency or fidelity of the bacterial ribosome. Here, the authors show that a synthetic peptide displays bactericidal activity through a different mechanism, inducing co-translational aggregation of nascent peptidic chains.

Scientists at Stanford have created a non-invasive ultrasound method of brain cleansing that boosted the survival rate of mice after stroke by activating natural detoxification mechanisms. The technology, accidentally discovered during experiments with the blood-brain barrier, stimulates microglial immune cells to dispose of toxic waste and improves the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. The method opens the way to treating the consequences of strokes and injuries without drugs.
A non-invasive, drug-free ultrasound method helps cleanse the brain and reduce inflammation, potentially offering a radically simple new approach to treating neurological diseases.