In an astonishing talk and tech demo, neurotechnologist Conor Russomanno shares his work building brain-computer interfaces that could enable us to control the external world with our minds. He discusses the quickly advancing possibilities of this field — including the promise of a \.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Johns Hopkins Scientists Identify Key Brain Protein That May Slow Alzheimer’s
Researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine report that findings from a new study funded by the National Institutes of Health are helping to identify a promising new biological target for Alzheimer’s disease. The focus is a protein that produces a crucial gas within the brain.
Studies in genetically engineered mice show that the protein Cystathionine γ-lyase, also known as CSE, plays an essential role in forming memories, says Bindu Paul, M.S., Ph.D., an associate professor of pharmacology, psychiatry and neuroscience at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine who led the research. CSE is best known for generating hydrogen sulfide, the gas responsible for the smell of rotten eggs, but the new findings highlight its importance in brain function.
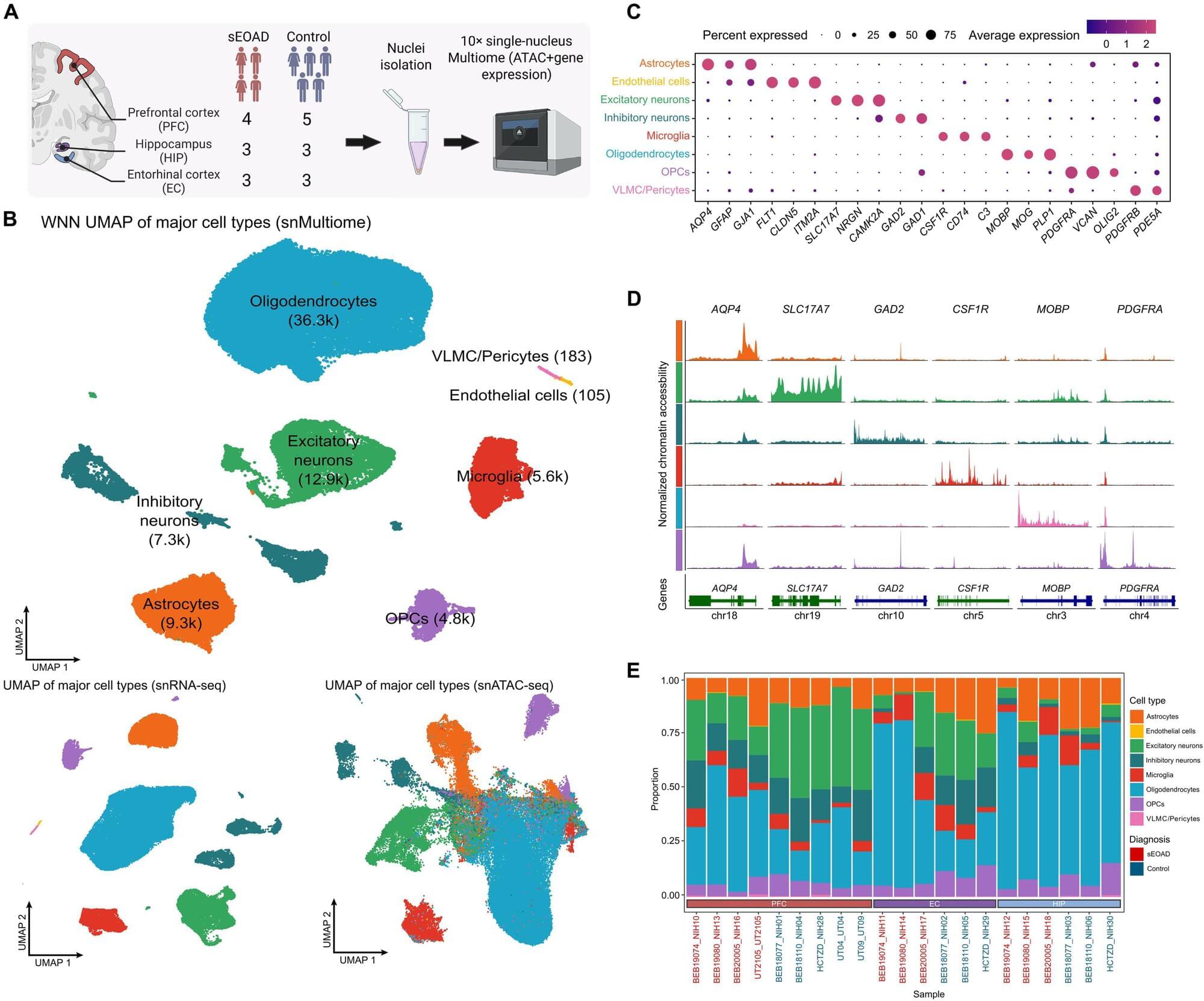
Mapping gene disruptions in sporadic early onset Alzheimer’s disease across key brain regions
A new study led by researchers at UTHealth Houston investigated both gene expression and regulation at single cell levels to reveal disruptions in gene function in three brain regions of patients with sporadic early onset Alzheimer’s disease.
The findings are published in Science Advances.
Only about 5% to 10% of patients with Alzheimer’s disease are younger than 65. Of those patients, 10% have mutations in the APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 genes, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease. The other 90% of these cases are classified as sporadic early onset Alzheimer’s, a rare and aggressive form of the disease that begins before age 65. The genetic tie in early onset Alzheimer’s is largely unidentified, representing a significant but understudied population.
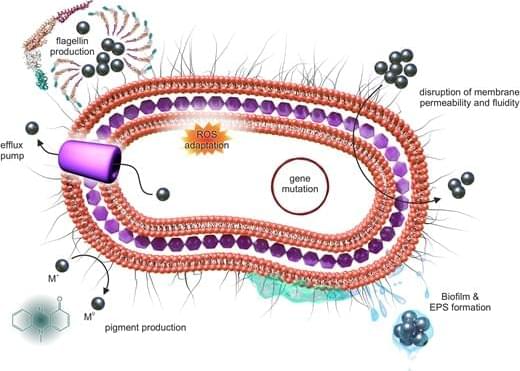
Emerging strategies of bacterial adaptation mechanisms to silver and metal oxide nanomaterials
How do bacteria adapt to antimicrobial nanomaterials? In this review, Suchánková et al. explain microbial adaptation strategies and offer insights for safer and more effective nano-antimicrobials. FEMSMicrobiolRev.
This review explores induced bacterial adaptation to antimicrobial nanomaterials, summarizing known mechanisms across nanomaterial types and bacterial spec.
Blood metabolite signature offers improved prediction of type 2 diabetes risk
Diabetes, a metabolic disease, is on the rise worldwide, and over 90% of cases are type 2 diabetes, where the body does not effectively respond to insulin.
Researchers from Mass General Brigham and Albert Einstein College of Medicine have identified metabolites (small molecules found in blood generated through metabolism) associated with the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future, and have revealed genetic and lifestyle factors that may influence these metabolites. They also developed a metabolomic signature that predicts future risk of type 2 diabetes beyond traditional risk factors.
Their results are published in Nature Medicine.

Combating Antimicrobial Resistance by Resensitising Bacteria to Antibiotics Using CRISPR: A Narrative Review
Background: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) remains a formidable global health threat. Conventional strategy of developing new antibiotics is costly and unsustainable. Thus, innovative approaches for resensitising bacteria using clustered regularly inter-spaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) technology are sought.


Scientists create food powder from waste, increasing shelf life from two weeks to two years
Food waste could actually feed millions of people globally and also have an endless shelf life if we freeze dry it and turn it into powder. This way we can keep large quantities of food for a very long time rather than having to freeze it or pickle it which only last so long due to freezer burn and pickling doesn’t work for long periods of time which can turn to poison essentially if contaminated.
Three students from Lund University in Sweden have set up a business called Fopo (freeze dried food powder) buying expired fruit and vegetables and turning it into food powder to resell back into the F&B market.