Detour Dog used DNS TXT records and botnets to distribute Strela Stealer via StarFish backdoor.




Signal announced the introduction of Sparse Post-Quantum Ratchet (SPQR), a new cryptographic component designed to withstand quantum computing threats.
SPQR will serve as an advanced mechanism that continuously updates the encryption keys used in conversations and discarding the old ones.
Signal is a cross-platform, end-to-end encrypted messaging and calling app managed by the non-profit Signal Foundation, with an estimated monthly active user base of up to 100 million.
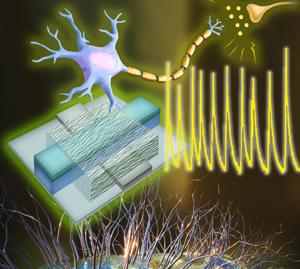
A team of engineers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has announced the creation of an artificial neuron with electrical functions that closely mirror those of biological ones. Building on their previous groundbreaking work using protein nanowires synthesized from electricity-generating bacteria, the team’s discovery means that we could see immensely efficient computers built on biological principles which could interface directly with living cells.
“Our brain processes an enormous amount of data,” says Shuai Fu, a graduate student in electrical and computer engineering at UMass Amherst and lead author of the study published in Nature Communications. “But its power usage is very, very low, especially compared to the amount of electricity it takes to run a Large Language Model, like ChatGPT.”
The human body is over 100 times more electrically efficient than a computer’s electrical circuit. The human brain is composed of billions of neurons, specialized cells that send and receive electrical impulses all over the body. While it takes only about 20 watts for your brain to, say, write a story, a LLM might consume well over a megawatt of electricity to do the same task.

On brain preservation, tests for consciousness, emulation vs. simulation, integrating with AI, personal identity, and more


A team of engineers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has announced the creation of an artificial neuron with electrical functions that closely mirror those of biological ones. Building on their previous groundbreaking work using protein nanowires synthesized from electricity-generating bacteria, the team’s discovery means that we could see immensely efficient computers built on biological principles which could interface directly with living cells.
“Our brain processes an enormous amount of data,” says Shuai Fu, a graduate student in electrical and computer engineering at UMass Amherst and lead author of the study published in Nature Communications. “But its power usage is very, very low, especially compared to the amount of electricity it takes to run a Large Language Model, like ChatGPT.”
The human body is over 100 times more electrically efficient than a computer’s electrical circuit. The human brain is composed of billions of neurons, specialized cells that send and receive electrical impulses all over the body. While it takes only about 20 watts for your brain to, say, write a story, a LLM might consume well over a megawatt of electricity to do the same task.

For over a hundred years, physics has rested on two foundational theories. Einstein’s general relativity describes gravity as the curvature of space and time, while quantum mechanics governs the behavior of particles and fields.
Each theory is highly successful within its own domain, yet combining them leads to contradictions, particularly in relation to black holes, dark matter, dark energy, and the origins of the universe.
My colleagues and I have been exploring a new way to bridge that divide. The idea is to treat information – not matter, not energy, not even spacetime itself – as the most fundamental ingredient of reality. We call this framework the quantum memory matrix (QMM).