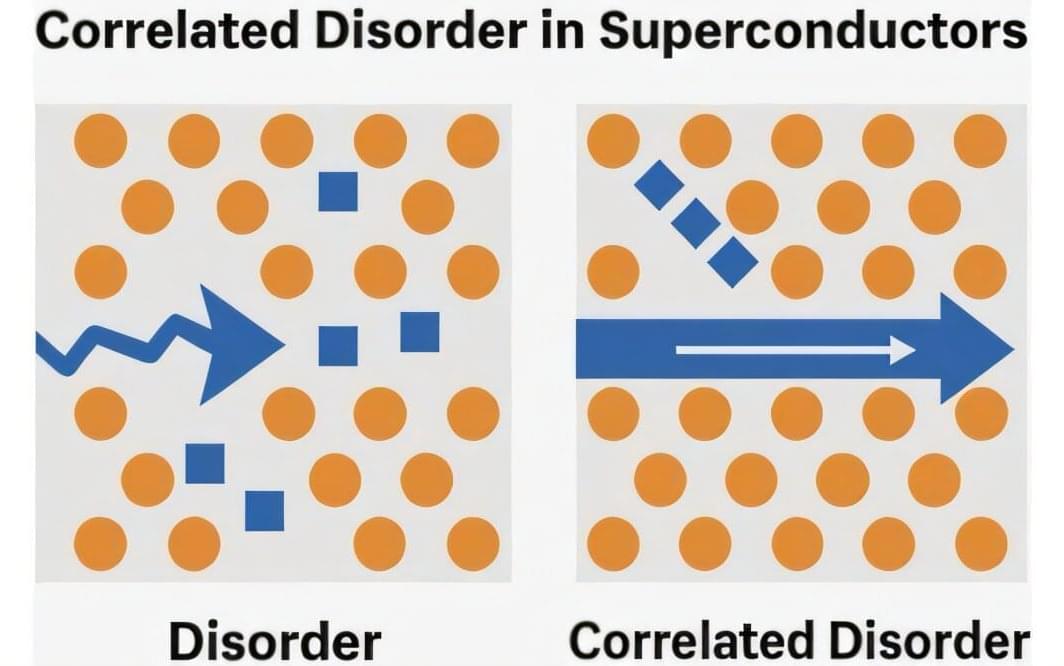
An international team of scientists, including physicists from HSE MIEM, has demonstrated that when defects within a material are arranged in a specific pattern rather than randomly, superconductivity can occur at a higher temperature and extend throughout the entire material. This discovery could help develop superconductors that operate without the need for extreme cooling.
The study has been published in Physical Review B.
Superconductivity is a state in which electric current flows through a material without any energy loss. In conventional conductors, part of the energy is converted into heat, but in superconductors, this does not occur—current flows freely and does not weaken. Today, superconductors are used in applications such as MRI machines, where superconducting coils generate strong magnetic fields.