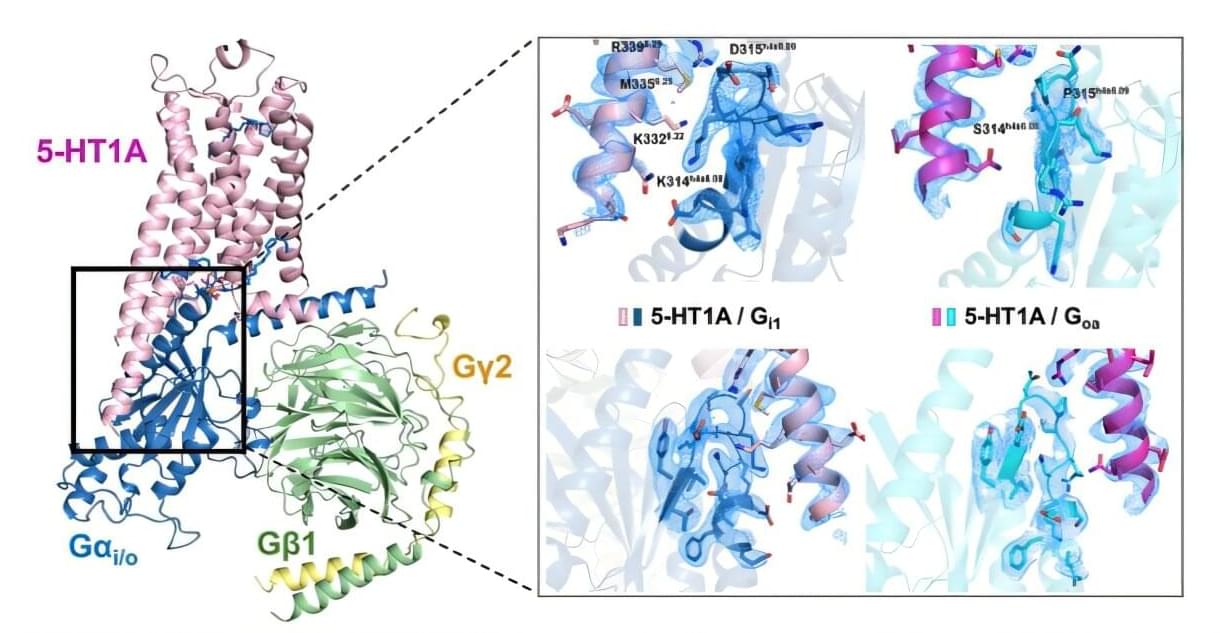
In a discovery that could guide the development of next-generation antidepressants and antipsychotic medications, researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have developed new insights into how a critical brain receptor works at the molecular level and why that matters for mental health treatments.
The study, published in the online issue of Science Advances, focuses on the 5-HT1A serotonin receptor, a major player in regulating mood and a common target of both traditional antidepressants and newer therapies such as psychedelics. The paper is titled “Structural determinants of G protein subtype selectivity at the serotonin receptor 5-HT1A.”
Despite its clinical importance, this receptor has remained poorly understood, with many of its molecular and pharmacological properties largely understudied—until now.