Apple fixed 2 exploited flaws in iOS 18.4.1, one flagged by Google TAG, urging urgent updates.
Four Windows Task Scheduler flaws allow attackers to bypass UAC, gain SYSTEM access, and erase logs.
Google on Wednesday revealed that it suspended over 39.2 million advertiser accounts in 2024, with a majority of them identified and blocked by its systems before it could serve harmful ads to users.
In all, the tech giant said it stopped 5.1 billion bad ads, restricted 9.1 billion ads, and blocked or restricted ads on 1.3 billion pages last year. It also suspended over 5 million accounts for scam-related violations.
In comparison, Google suspended over 12.7 million advertiser accounts, stopped 5.5 billion bad ads, restricted 6.9 billion ads, and blocked or restricted ads on 2.1 billion pages in 2023.
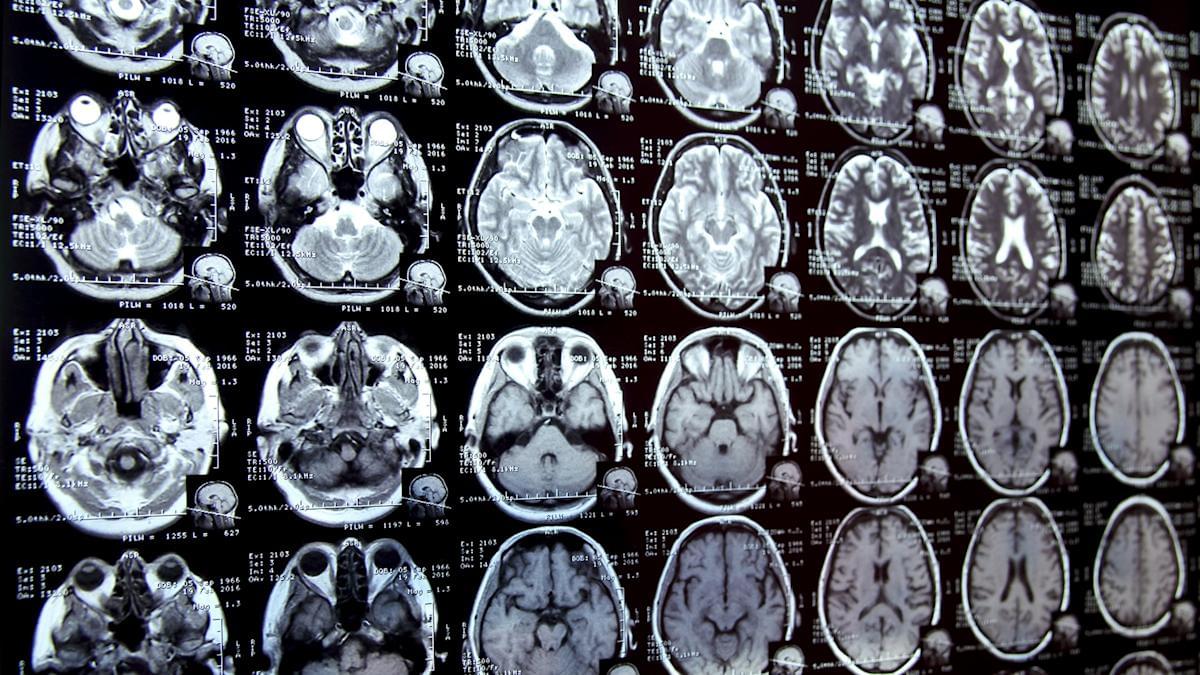
Scientists sound alarm after making disturbing discovery while studying human brains: ‘This stuff is increasing in our world exponentially’
Posted in neuroscience | 1 Comment on Scientists sound alarm after making disturbing discovery while studying human brains: ‘This stuff is increasing in our world exponentially’
“Now studying tissue from cross-sections of a single brain to find out whether certain regions have higher… concentrations.”
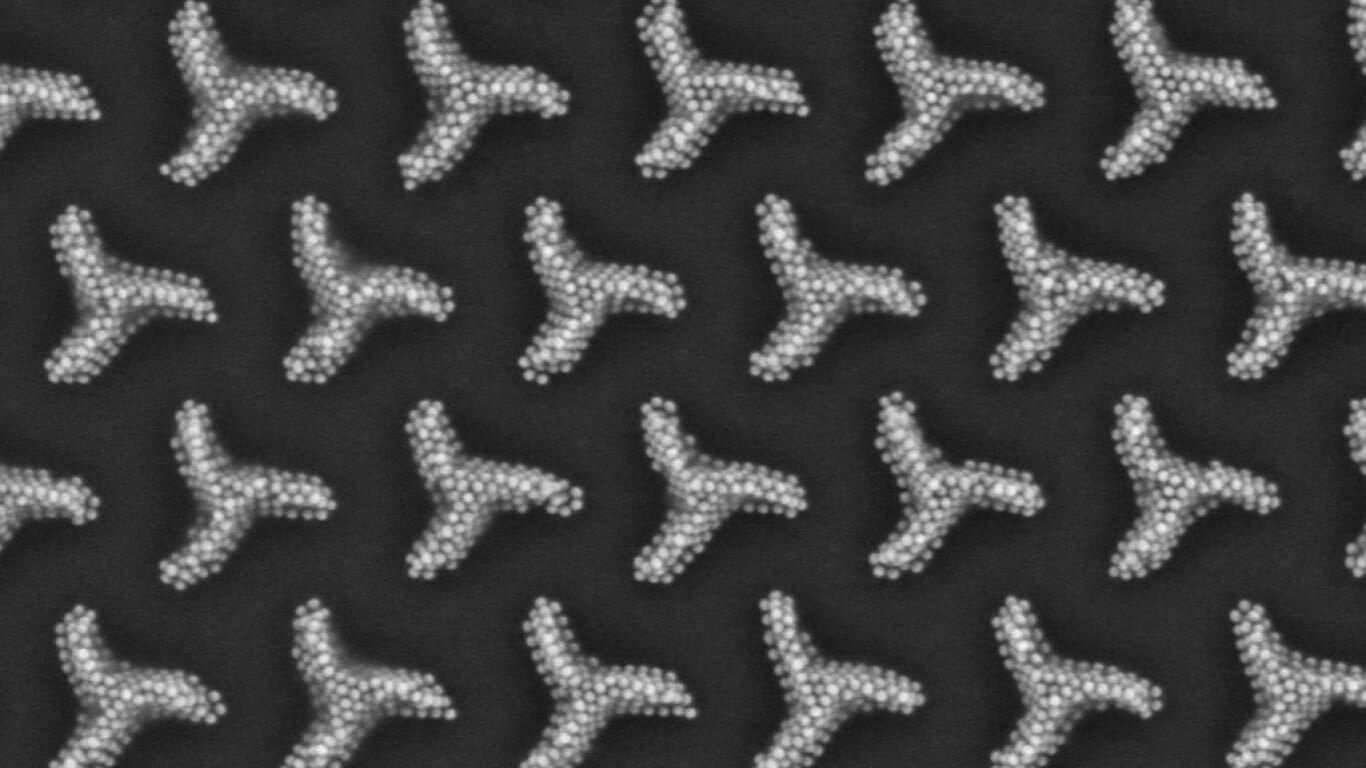
Researchers from ICMAB are revolutionizing how we manipulate light at the nanoscale using chiral plasmonic structures—nanomaterials designed to interact with polarized light in extraordinary ways.
ICMAB researchers from the NANOPTO group at ICMAB have recently published two studies demonstrating how cost-effective fabrication techniques can produce highly efficient chiral nanostructures with potential applications in sensors, imaging, and even quantum technologies.
The first study, published in Nature Communications, showcases self-assembled chiral plasmonic architectures (triskelion patterns) made from gold and silver nanoparticles. These structures demonstrate exceptional optical responses, selectively interacting with circularly polarized light, opening up exciting possibilities for advanced optoelectronic devices.
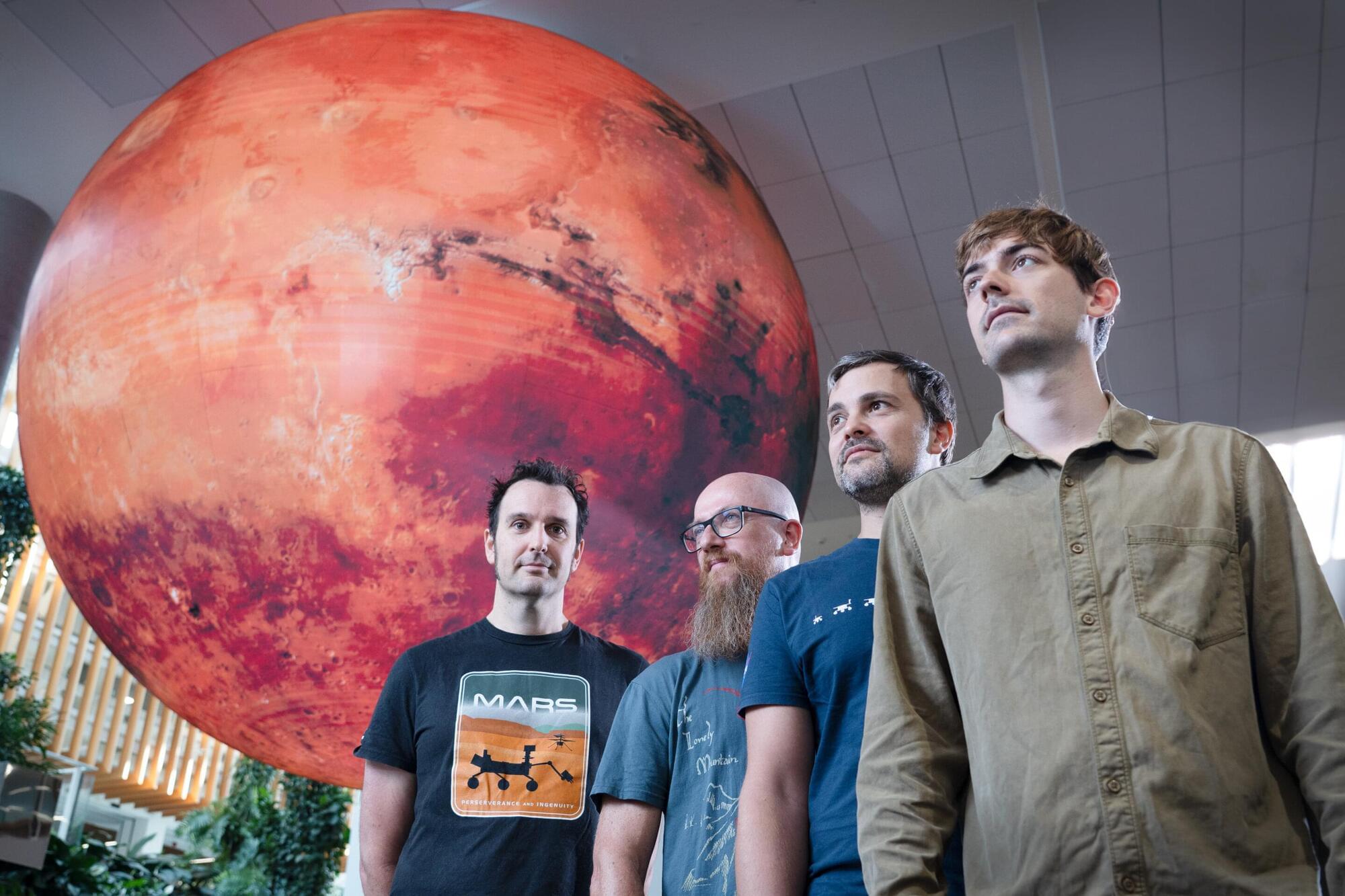
A QUT-led study analyzing data from NASA’s Perseverance rover has uncovered compelling evidence of multiple mineral-forming events just beneath the Martian surface—findings that bring scientists one step closer to answering the profound question: did life ever exist on Mars?
The QUT research team led by Dr. Michael Jones, from the Central Analytical Research Facility and the School of Chemistry and Physics, includes Associate Professor David Flannery, Associate Professor Christoph Schrank, Brendan Orenstein and Peter Nemere, together with researchers from North America and Europe.
The paper, “In-situ crystallographic mapping constrains sulfate precipitation and timing in Jezero crater, Mars” is published in Science Advances.
Researchers at the National University of Singapore (NUS) have shown that a single, standard silicon transistor, the core component of microchips found in computers, smartphones, and nearly all modern electronics, can mimic the functions of both a biological neuron and synapse.
A synapse is a specialized junction between nerve cells that allows for the transfer of electrical or chemical signals, through the release of neurotransmitters by the presynaptic neuron and the binding of receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. It plays a key role in communication between neurons and in various physiological processes including perception, movement, and memory.
Further studies are needed to determine whether K2-18b, which orbits a star 120 light-years away, is inhabited, or even habitable.
Dr. Aubrey de Grey reveals why reversing aging may be easier than slowing it down in this mind-expanding conversation that challenges conventional wisdom about human longevity. The renowned biomedical gerontologist outlines his damage repair approach that’s gaining mainstream scientific acceptance after initial skepticism.
The financial landscape of longevity research has dramatically transformed, with billions flowing into the space. Dr. de Grey provides an insider’s assessment of major players including HEvolution (Saudi-backed), Altos Labs (Bezos-funded), Calico (Google-funded) and Retro Biosciences (Sam Altman’s venture), offering candid insights about which approaches show the most promise and why Google’s Calico has struggled despite substantial resources.
Regulatory innovation emerges as a crucial accelerator for progress. Montana’s groundbreaking expansion of Right to Try legislation now allows anyone to access treatments that have passed FDA safety trials, while special economic zones like Prospera in Honduras are creating regulatory environments specifically designed for biomedical innovation. These developments could create the competitive pressure needed to modernize traditional regulatory structures worldwide.
At the LEV Foundation, Dr. de Grey is conducting a thousand-mouse study combining four different damage repair interventions in middle-aged mice, aiming for a full year of life extension—far beyond the four months typically achieved. Unlike conventional approaches that rely on dietary modifications, this ambitious project incorporates advanced cell and gene therapies that target multiple forms of age-related damage simultaneously.
Looking forward, Dr. de Grey offers his characteristic probabilistic prediction: a 50–50 chance of reaching \.
DNA sequences from the insulin-linked polymorphic region can form non-canonical structures. Here, the authors present a structural investigation into the relationship between native sequence variants and the different structures they form.