Thanks to a recent breakthrough by researchers from Newcastle University and Northumbria University in the UK, that dream may not be so far-fetched.
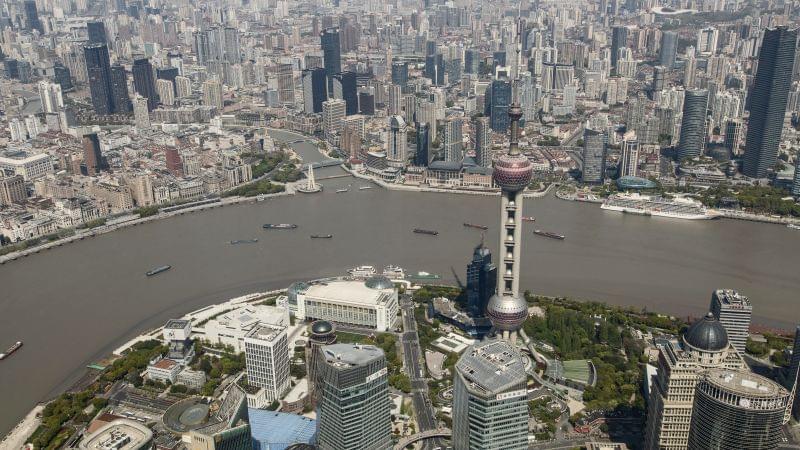


China’s state security authorities raided multiple offices of international advisory firm Capvision, state media reported Monday, part of a broader crackdown on the consulting industry as Beijing tightens control over what it considers sensitive information related to national security.
Officers raided Capvision’s office in the eastern city of Suzhou, questioned its employees and searched office devices, a Jiangsu provincial television station reported Monday. The company was a so-called expert network, which connected its clients with people who provided specialist knowledge, largely in mainland China.
The report did not give an exact date of the raid, but said it was part of a coordinated, nationwide operation carried out simultaneously targeting the company’s branches in cities including Beijing, Shenzhen as well as Shanghai, where Capvision was founded in 2006.
Invertebrates like jellyfish are inspiring flexible ‘soft’ robot designs. They could be used in tight and delicate settings, such as in surgical tools.
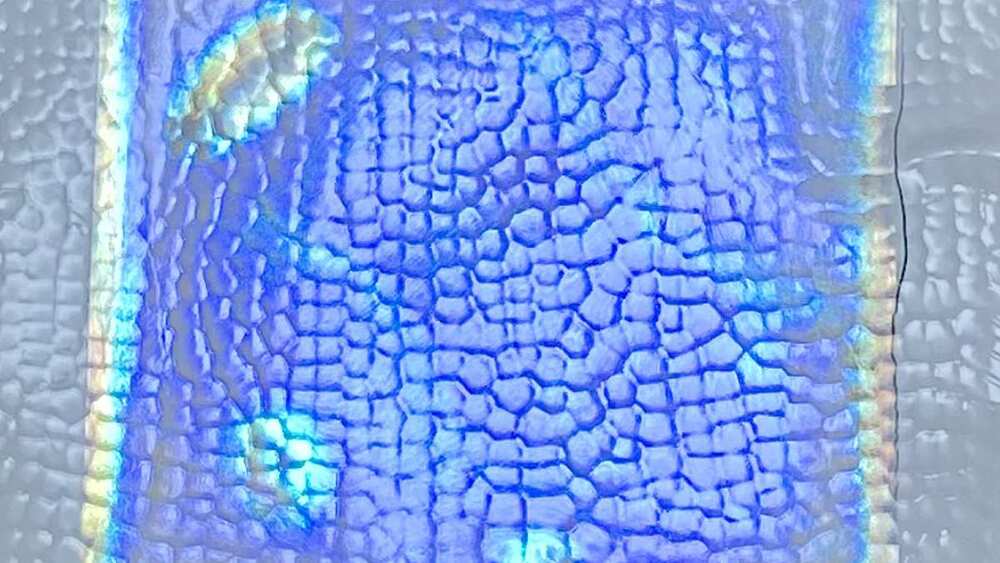
Chemists have made an iridescent, plant-based film that gets cooler in sunlight.
The material, which comes in a range of shining colours, could one day coat buildings and cars, lowering the need for air conditioning.
The film exhibits a smart property: called passive daytime radiative cooling, or PDRC, it doesn’t absorb much light, and it radiates heat out at a wavelength that escapes the atmosphere and zooms straight into space.

Space Renaissance International has recently launched a world-wide campaign for adding an 18th SDG to the United Nations 2030 Agenda for sustainable development. Our initiative suddenly resulted to be in tune with similar initiatives, undertaken by other space advocacy organizations, e.g. the National Space Society of USA, and many others. All of these promoter organizations are now working to a joined campaign. Two initial milestones will be the presentation, by the NSS, of the #Space18SDG to the COPUOS (the United Nations Committee for the Peaceful Use of Outer Space) the first week of June, and a panel organized by SRI at the UN General Assembly in New York, for the 18 of September.
Space for All, on Earth and Beyond, a civilian-led space development, with human communities living and working in outer space to expand and multiply benefits to all the peoples of Earth.
The above is the main concept supporting our proposal, trying to make it evident, in few words, that, though we praise and consider very important the huge contribution so far given by space technologies to the achievement of the Earthly 17 SDGs, we think that they will not be enough to overcome the global crisis of human development on our mother planet, should humanity remain closed and confined inside its limits.


It’s no secret that electricity bills are on the rise. With the P3 P4400 you can cut your energy costs and find out what appliances are actually worth keeping plugged in by finding power-wasting appliances. Simply connect any appliance to the Kill A Watt EZ, it will then assess how efficient each appliance really is.

Elon Musk has been pretty open about the idea of using social media platforms like Twitter to communicate directly with customers. Tesla highlighted this in its 2022 Impact Report, with the company noting that its social media accounts have helped it reach 1 billion views on Twitter last year.
With Twitter now being owned by Elon Musk, it is no surprise that his companies like Tesla are now more active on the platform. And in a recent post, the official Tesla account asked Twitter users what it could improve. The EV community, from fans to longtime owners, responded, to a great degree. As of writing, Tesla’s post has attracted over 22k comments.
A look at the comments on Tesla’s post would show that there are numerous calls for better service. Service has been Tesla’s Achilles heel for some time now, and with the company adopting a “best service is no service” stance, some owners have reported experiencing difficulties contacting Tesla for issues with their vehicles. Comments on Tesla’s post suggest that customer service is still a key point of improvement for the company.

Engineers at the University of Pittsburgh are bringing concrete into the 21st century by reimagining its design. Concrete, which has its roots dating back to the Roman Empire, remains the most widely utilized material in the construction industry.
A new study presents a concept for the development of smart civil infrastructure systems with the introduction of metamaterial concrete. The research presents a concept for lightweight and mechanically-tunable concrete systems with integrated energy harvesting and sensing capabilities.
“Modern society has been using concrete in construction for hundreds of years, following its original creation by the ancient Romans,” said Amir Alavi, assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering at Pitt, who is the corresponding author on the study. “Massive use of concrete in our infrastructure projects implies the need for developing a new generation of concrete materials that are more economical and environmentally sustainable, yet offer advanced functionalities. We believe that we can achieve all of these goals by introducing a metamaterial paradigm into the development of construction materials.”

The 2022 physics Nobel prize was awarded for experimental work demonstrating fundamental breaks in our understanding of the quantum world, leading to discussions around “local realism” and how it could be refuted. Many theorists believe these experiments challenge either “locality” (the notion that distant objects require a physical mediator to interact) or “realism” (the idea that there’s an objective state of reality). However, a growing number of experts suggest an alternative approach, “retrocausality,” which posits that present actions can affect past events, thus preserving both locality and realism.
The 2022 Nobel Prize in physics highlighted the challenges quantum experiments pose to “local realism.” However, a growing body of experts propose “retrocausality” as a solution, suggesting that present actions can influence past events, thus preserving both locality and realism. This concept offers a novel approach to understanding causation and correlations in quantum mechanics, and despite some critics and confusion with “superdeterminism,” it is increasingly seen as a viable explanation for recent groundbreaking experiments, potentially safeguarding the core principles of special relativity.
In 2022, the physics Nobel prize was awarded for experimental work showing that the quantum world must break some of our fundamental intuitions about how the universe works.